Smart phone not a smart choice when facing depression
Depressed people who turn to their smart phones for relief may only be making things worse
2015-08-25
(Press-News.org) Depressed people who turn to their smart phones for relief may only be making things worse.
A team of researchers, that included the dean of Michigan State University's College of Communication Arts and Sciences, found that people who substitute electronic interaction for the real-life human kind find little if any satisfaction.
In a paper published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior, the researchers argue that relying on a mobile phone to ease one's woes just doesn't work.
Using a mobile phone for temporary relief from negative emotions could worsen psychological conditions and spiral into unregulated and problematic use of mobile phones, or PUMP, said MSU's Prabu David.
"The research bears out that despite all the advances we've made, there is still a place for meaningful, face-to-face interaction," he said. "The mobile phone can do a range of things that simulate human interaction. It seduces us into believing it's real, but the fact remains it's still synthetic."
Lead author Jung-Hyun Kim, with Sogang University, Seoul, South Korea, said the study shows that face-to-face interaction can buffer the negative effects of heavy mobile phone use.
"Engaging in more face-to-face interaction can work as an antidote to the development of problematic mobile phone use," Kim said.
The researchers examined two pathways for habitual use of a smart phone: To either pass the time or entertain, or to alleviate feelings of sadness or depression by seeking out others.
It's the second reason, David said, that can cause trouble.
"This suggests that problematic use of mobile phone is fueled in part by the purposeful or deliberate use of the mobile phone to relieve or alleviate negative feelings," he said, "whereas habitual or ritualistic use to pass time is not strongly associated with it."
David and the researchers agree that using a mobile phone in moderation - to stay in touch with family or friends, for example - is not a bad thing. But don't let it replace real human interaction.
"If you have a chance to see someone face-to-face, take it," David said. "Life is short."
Mihye Seo, with Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, also contributed to this study.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-25
MADISON -- Colorful and expressive, the eyes are central to the way people interact with each other, as well as take in their surroundings.
That makes amblyopia -- more commonly known as "lazy eye" -- all the more obvious, but the physical manifestation of the most common cause of vision problems among children the world over is actually a brain disorder.
"Most often in amblyopia patients, one eye is better at focusing," says Bas Rokers, a University of Wisconsin-Madison psychology professor. "The brain prefers the information from that eye, and pushes down the signal ...
2015-08-25
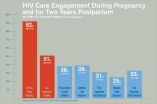
Pregnancy could be a turning point for HIV-infected women, when they have the opportunity to manage their infection, prevent transmission to their new baby and enter a long-term pattern of maintenance of HIV care after giving birth--but most HIV-infected women aren't getting that chance. That is the major message from a pair of new studies in Philadelphia, one published early online this month in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases, and the other published in July in PLOS ONE.
The studies, led by a team of researchers from Drexel University and the Philadelphia Department ...
2015-08-25
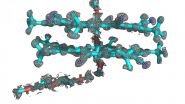
A team from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Indiana University combined two techniques to determine the structure of cyanostar, a new abiological molecule that captures unwanted negative ions in solutions.
When Semin Lee, a chemist and Beckman Institute postdoctoral fellow at Illinois, first created cyanostar at Indiana University, he knew the chemical properties, but couldn't determine the precise atomical structure. Lee synthesized cyanostar for its unique ability to bind with large, negatively charged ions, which could have applications such as ...
2015-08-25
Many political leaders, scientists, educators and parents believe that failure is the best teacher.
Scientists have long understood that the brain has two ways of learning. One is avoidance learning, which is a punishing, negative experience that trains the brain to avoid repeating mistakes. The other is reward-based learning, a positive, reinforcing experience in which the brain feels rewarded for reaching the right answer.
A new MRI study by USC and a group of international researchers has found that having the opportunity to learn from failure can turn it into ...
2015-08-25
Since the early days of fertility treatment, women undergoing IVF treatment have had to place a hormonal gel in their vagina on a daily basis for at least 14 days after embryo transfer. The hormone is necessary to increase the chances of pregnancy, but it may also cause some side effects in the form of irritation and leaky discharge.
However, the results of a new scientific study suggest that women will be able to avoid this kind of discomfort in the future.
"Fertility treatment is a physical and mental challenge for childless couples. The daily treatment with hormonal ...
2015-08-25
Researchers at The Australian National University (ANU) and The University of Sydney have developed a world-first radio-tracking drone to locate radio-tagged wildlife.
Lead researcher Dr Debbie Saunders from the ANU Fenner School of Environment and Society said the drones have successfully detected tiny radio transmitters weighing as little as one gram. The system has been tested by tracking bettongs at the Mulligan's Flat woodland sanctuary in Canberra.
"The small aerial robot will allow researchers to more rapidly and accurately find tagged wildlife, gain insights into ...
2015-08-25
A research team at Linköping University, together with colleagues in Europe and the United States, has shown that at extremely high pressure even the innermost electrons in the atomic nuclei of the metal osmium begin to interact with each other, a phenomenon never witnessed before. The findings have been published in Nature.
"If we know more about how a matter works, we will be in a better position to develop materials that withstand extreme conditions. In research we're constantly making advances, but in this case we've taken a giant leap", says Igor Abrikosov, ...
2015-08-25
A new £6.65 million grant for research aimed at accelerating the discovery and application of new advanced materials for the energy sector was announced today by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
The grant, awarded to a team led by Professor Matthew Rosseinsky of the University of Liverpool, will support a programme, Integration of Computation and Experiment for Accelerated Materials Discovery.
Professor Rosseinsky will head up an expert team at Liverpool and University College London that will work to tackle the challenge of designing ...
2015-08-25
Noroviruses are the predominant cause of gastroenteritis outbreaks in community settings such as hospitals, cruise ships, and schools. The virus is extremely contagious and is mostly transmitted via "fecal-oral-route", i.e., through contaminated hands or contaminated food. Symptoms include violent and sudden onset of diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea.
"It is therefore important to provide a safe and harmless disinfectant against human norovirus," explains Grant Hansman, head of CHS junior research group at the German Cancer Research Center noroviruses and the University ...
2015-08-25
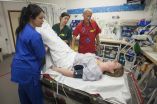
A simple, safe and cost-free modification to a physical technique used to treat patients in the emergency department with an abnormally fast heart rhythm could improve its effectiveness by more than a quarter, according to a study published in The Lancet today (25 August 2015).
An abnormally fast heart rhythm, also called supraventricular tachycardia, can be distressing for patients and many come to emergency departments for treatment. Symptoms can include chest pain, light-headedness, dizziness and breathlessness. Episodes can last from a few seconds or, in extreme cases, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Smart phone not a smart choice when facing depression
Depressed people who turn to their smart phones for relief may only be making things worse