EPSRC funding boost to aid discovery of new advanced materials
2015-08-25
(Press-News.org) A new £6.65 million grant for research aimed at accelerating the discovery and application of new advanced materials for the energy sector was announced today by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
The grant, awarded to a team led by Professor Matthew Rosseinsky of the University of Liverpool, will support a programme, Integration of Computation and Experiment for Accelerated Materials Discovery.
Professor Rosseinsky will head up an expert team at Liverpool and University College London that will work to tackle the challenge of designing and testing new materials at the atomic level and aims to keep the UK ahead in the global materials competition.
Professor Rosseinsky said: "The controlled arrangement of atoms and molecules to create function is a grand scientific challenge. With the approaches we will develop, we aim to address problems such as how to create materials for sustainable energy production and storage such as safer new battery technologies or the efficient capture and utilisation of solar energy.
"Our team will include specialists in prediction of the structures and properties of materials, in measurement and materials synthesis. We will combine computation and experiment to discover new materials, developing methods that combine calculation with chemical understanding."
The programme will exploit its discoveries and share its approach with its commercial partners via the Knowledge Centre for Materials Chemistry and the new Materials Innovation Factory, a state-of-the-art materials research facility for both academic and industrial users.
Minister for Universities and Science Jo Johnson said: "Advanced materials will be crucial for future energy storage technologies like smaller, longer-lasting batteries and more efficient solar panels. With this £6.65 million investment from government, researchers will be able to develop a smarter design process from the single atom all the way up to new materials that will speed up discovery and strengthen commercial capabilities in this increasingly important field."
Professor Philip Nelson, EPSRC's Chief Executive, said: "The development of new advanced materials is vital to extending our capabilities across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The work planned as part of this programme grant promises to find new materials that will have many applications in the energy sector. This grant will be supporting some of the UK's talented scientists and help achieve EPSRC's vision to make the UK the best place in the world to research, discover and innovate."
INFORMATION:
For further information please contact the EPSRC Press Office on 01793 444 404 or email pressoffice@epsrc.ac.uk
Notes for Editors:
The Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
As the main funding agency for engineering and physical sciences research, our vision is for the UK to be the best place in the world to Research, Discover and Innovate.
By investing £800 million a year in research and postgraduate training, we are building the knowledge and skills base needed to address the scientific and technological challenges facing the nation. Our portfolio covers a vast range of fields from healthcare technologies to structural engineering, manufacturing to mathematics, advanced materials to chemistry. The research we fund has impact across all sectors. It provides a platform for future economic development in the UK and improvements for everyone's health, lifestyle and culture.
We work collectively with our partners and other Research Councils on issues of common concern via Research Councils UK. http://www.epsrc.ac.uk
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-25
Noroviruses are the predominant cause of gastroenteritis outbreaks in community settings such as hospitals, cruise ships, and schools. The virus is extremely contagious and is mostly transmitted via "fecal-oral-route", i.e., through contaminated hands or contaminated food. Symptoms include violent and sudden onset of diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea.
"It is therefore important to provide a safe and harmless disinfectant against human norovirus," explains Grant Hansman, head of CHS junior research group at the German Cancer Research Center noroviruses and the University ...
2015-08-25
A simple, safe and cost-free modification to a physical technique used to treat patients in the emergency department with an abnormally fast heart rhythm could improve its effectiveness by more than a quarter, according to a study published in The Lancet today (25 August 2015).
An abnormally fast heart rhythm, also called supraventricular tachycardia, can be distressing for patients and many come to emergency departments for treatment. Symptoms can include chest pain, light-headedness, dizziness and breathlessness. Episodes can last from a few seconds or, in extreme cases, ...
2015-08-25
This news release is available in German. Trillions of bacteria populate the human gut - which makes them more common than any other cells in our body. The composition of this bacterial population is very variable and influenced by our diet. Diseases, but also antibiotic treatments can induce significant shifts in this equilibrium. If entire bacterial groups suddenly multiply heavily, critical situations occur. They damage the intestinal tissue and cause inflammations. How such shifts are triggered largely remained a mystery. Physiologists from the University of Zurich ...
2015-08-25
This news release is available in German.
Root bacteria are known to form symbiotic relationships with plants by improving the plants' supply of nutrients. Yet as scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, found recently, the bacteria actually play a much more profound role. During field experiments in Utah, in the western USA, researchers discovered that the right mixture of soil microbiota directly influences the survival of Nicotiana attenuata, a species of wild tobacco. Plants that had been unable to establish a protective ...
2015-08-25
University of Manchester scientists have bridged a gap between two separate pieces of small intestine kept alive outside the body, in an advance which could have implications for surgery in human adults and babies.
It is not currently possible to study the intestine in embryos when inside the body, which holds back advances in treatment for conditions causing damage in infants. However, new techniques used by the researchers in this study have allowed organs to be kept alive and grown on supports which allow the absorption of nutrients.
A video is available here
or ...
2015-08-25
In an era where popular culture is increasingly recognized for its impact on lay understanding of health and medicine, few scholars have looked at television's powerful role in the creation of patient expectations, especially regarding pregnancy and birth.
As part of a larger research project funded by a National Science Foundation Dissertation Improvement Grant, Danielle Bessett, University of Cincinnati assistant professor of sociology in the McMicken College of Arts and Sciences examined how women understand their television viewing practices regarding pregnancy and ...
2015-08-25
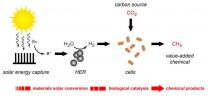
A team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) developing a bioinorganic hybrid approach to artificial photosynthesis have achieved another milestone. Having generated quite a buzz with their hybrid system of semiconducting nanowires and bacteria that used electrons to synthesize carbon dioxide into acetate, the team has now developed a hybrid system that produces renewable molecular hydrogen and uses it to synthesize carbon dioxide into methane, the primary constituent of natural gas.
"This study represents ...
2015-08-25
Waterford, Ireland, August 24, 2015 - Ongoing European Research Council-funded research at Waterford Institute of Technology's (WIT) Macular Pigment Research Group (MPRG) is investigating the potential link between cognitive function and levels of a vital eye pigment linked to diet. The study suggests that measuring macular pigment offers potential as a biomarker of cognitive health. The results of this study are highlighted to a global audience through the prestigious international medical journal, the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
The Waterford clinical trial research, ...
2015-08-25
Tahiti is a popular tourist destination, but one unwanted visitor has decided to make its home there: the brown widow spider (Latrodectus geometricus). A paper published in the Journal of Medical Entomology has reported the discovery of the spider for the first time on Tahiti and also on four of the Cook Islands.
The brown widow is a known invasive species. It has been found in South America, Central America, North America, the Caribbean islands, and a host of Pacific islands. It was first found in French Polynesia in 2006, when it was discovered on the island of Moorea. ...
2015-08-25
WASHINGTON (Aug. 25, 2015)--In the most comprehensive study to date, researchers at the George Washington University have identified a potential link between microbes (viruses, bacteria and fungi) in the throat and schizophrenia. This link may offer a way to identify causes and develop treatments of the disease and lead to new diagnostic tests.
"The oropharynx of schizophrenics seems to harbor different proportions of oral bacteria than healthy individuals," said Eduardo Castro-Nallar, a Ph.D. candidate at GW's Computational Biology Institute (CBI) and lead author of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] EPSRC funding boost to aid discovery of new advanced materials