INFORMATION:
Co-author Professor Darren Croft of the University of Exeter added: "In the broader context our findings show that swimming efficiently is something that fish may have to learn and practice. As with learning to swim in humans, this takes time and energy, both of which are very costly for these fish. This can explain why it is only the fish that are exposed to higher levels of harassment from males which develop the refined swimming technique".
The study was funded by the Natural Environment Research Council and the Leverhulme Trust.
Female guppies become better swimmers to escape male sexual harassment
A new study on guppies led by the universities of Glasgow and Exeter has given scientists insight into howmale cooercion can lead to physiological changes, much like those in athletes who train to perform better
2015-08-25
(Press-News.org) In the animal world, sexual reproduction can involve males attempting to entice or force females to mate with them, even if they are not initially interested.
This male behaviour is driven by conflicts of interest over reproduction and exerts selective pressures on both sexes.
A new study on guppies led by the universities of Glasgow and Exeter has given scientists insight into how this behaviour can lead to physiological changes, much like those in athletes who train to perform better.
Dr Shaun Killen, of the University of Glasgow, said: "Sexual coercion of females by males is widespread across sexually reproducing species.
"Typically, male reproductive success is limited by access to females, and males of many species will try to overcome this using a number of behaviours, such as chasing and even attacking females in an attempt to gain a mating.
"These types of behaviours are considered sexually harassing as males are attempting to coerce females into mating with them. Females can spend a lot of energy avoiding males in these situations and can even be injured.
"To reduce these costs, one possibility is that females may be able to change their own behaviour or physiology in ways that reduce the negative energetic consequences of harassment or allows them to more easily escape male coercion."
Dr Killen and his colleagues tested this idea in a laboratory setting by exposing female Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata) for several months to varying levels of male harassment that they would normally encounter in the wild.
Dr Safi Darden of the University of Exeter explained: "In the wild, male guppies spend most of their time courting and coercing females in an attempt to mate with them. Most of this male attention is unwanted and females attempt to avoid males by rapidly swimming away from them during pursuits."
After five months, females exposed to higher levels of harassment were able to swim much more efficiently, using less energy to swim at a given speed compared to those exposed to lower levels of harassment.
Dr Darden said: "It seems that prolonged increases in high-intensity swimming in females, caused by male harassment, leads to changes in the physiology or swimming mechanics of individual fish, which reduces the energy costs of swimming and could allow female guppies to reduce the burden of this coercive behaviour."
Dr Killen added: "An important factor appears to be swimming technique, and female guppies that experienced lower levels of harassment spent more time swimming with their pectoral fins extended, an indicator of an inefficient swimming technique.
"This change is very similar to that seen in human athletes who train to become better at their sports."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Catastrophic landslides post-earthquake
2015-08-25
Boulder, Colo., USA - In the last few months, it has once more become clear that large earthquakes can solicit catastrophic landsliding. In the wake of the Nepal earthquake, the landslide community has been warning of persistent and damaging mass wasting due to monsoon rainfall in the epicentral area. However, very little is actually known about the legacy of earthquakes on steep, unstable hillslopes.
Using a dense time series of satellite images and air photos, Odin Marc and colleague reconstructed the history of landsliding in four mountain areas hit by large, shallow ...
Hepatitis A-like virus identified in seals
2015-08-25
Washington, DC - August 25, 2015 - Scientists in the Center for Infection and Immunity at the Mailman School of Public Health have discovered a new virus in seals that is the closest known relative of the human hepatitis A virus. The finding provides new clues on the emergence of hepatitis A. The research appears in the July/August issue of mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Until now, we didn't know that hepatitis A had any close relatives and we thought that only humans and other primates could be infected by such viruses," ...
New Moffitt study finds black women have higher frequency of BRCA mutations than previously reported
2015-08-25
TAMPA, Fla. - Women who have inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are more likely to develop breast cancer or ovarian cancer, especially at a younger age. Approximately 5 percent of women with breast cancer in the United States have mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 based on estimates in non-Hispanic white women. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers recently conducted the largest U.S. based study of BRCA mutation frequency in young black women diagnosed with breast cancer at or below age 50 and discovered they have a much higher BRCA mutation frequency than that previously ...
Is incense bad for your health?
2015-08-25
The burning of incense might need to come with a health warning. This follows the first study evaluating the health risks associated with its indoor use. The effects of incense and cigarette smoke were also compared, and made for some surprising results. The research was led by Rong Zhou of the South China University of Technology and the China Tobacco Guangdong Industrial Company in China, and is published in Springer's journal Environmental Chemistry Letters.
Incense burning is a traditional and common practice in many families and in most temples in Asia. It is not ...
Smart phone not a smart choice when facing depression
2015-08-25
Depressed people who turn to their smart phones for relief may only be making things worse.
A team of researchers, that included the dean of Michigan State University's College of Communication Arts and Sciences, found that people who substitute electronic interaction for the real-life human kind find little if any satisfaction.
In a paper published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior, the researchers argue that relying on a mobile phone to ease one's woes just doesn't work.
Using a mobile phone for temporary relief from negative emotions could worsen psychological ...
'Lazy eye' may bully the brain into altering its wiring
2015-08-25
MADISON -- Colorful and expressive, the eyes are central to the way people interact with each other, as well as take in their surroundings.
That makes amblyopia -- more commonly known as "lazy eye" -- all the more obvious, but the physical manifestation of the most common cause of vision problems among children the world over is actually a brain disorder.
"Most often in amblyopia patients, one eye is better at focusing," says Bas Rokers, a University of Wisconsin-Madison psychology professor. "The brain prefers the information from that eye, and pushes down the signal ...
Pregnancy is a missed opportunity for HIV-infected women to gain control over condition
2015-08-25
Pregnancy could be a turning point for HIV-infected women, when they have the opportunity to manage their infection, prevent transmission to their new baby and enter a long-term pattern of maintenance of HIV care after giving birth--but most HIV-infected women aren't getting that chance. That is the major message from a pair of new studies in Philadelphia, one published early online this month in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases, and the other published in July in PLOS ONE.
The studies, led by a team of researchers from Drexel University and the Philadelphia Department ...
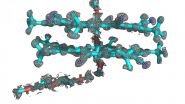
Researchers combine disciplines, computational programs to determine atomic structure
2015-08-25
A team from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Indiana University combined two techniques to determine the structure of cyanostar, a new abiological molecule that captures unwanted negative ions in solutions.
When Semin Lee, a chemist and Beckman Institute postdoctoral fellow at Illinois, first created cyanostar at Indiana University, he knew the chemical properties, but couldn't determine the precise atomical structure. Lee synthesized cyanostar for its unique ability to bind with large, negatively charged ions, which could have applications such as ...
Making a mistake can be rewarding, study finds
2015-08-25
Many political leaders, scientists, educators and parents believe that failure is the best teacher.
Scientists have long understood that the brain has two ways of learning. One is avoidance learning, which is a punishing, negative experience that trains the brain to avoid repeating mistakes. The other is reward-based learning, a positive, reinforcing experience in which the brain feels rewarded for reaching the right answer.
A new MRI study by USC and a group of international researchers has found that having the opportunity to learn from failure can turn it into ...
Women undergoing fertility treatment can succeed with fewer hormones
2015-08-25
Since the early days of fertility treatment, women undergoing IVF treatment have had to place a hormonal gel in their vagina on a daily basis for at least 14 days after embryo transfer. The hormone is necessary to increase the chances of pregnancy, but it may also cause some side effects in the form of irritation and leaky discharge.
However, the results of a new scientific study suggest that women will be able to avoid this kind of discomfort in the future.
"Fertility treatment is a physical and mental challenge for childless couples. The daily treatment with hormonal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Female guppies become better swimmers to escape male sexual harassmentA new study on guppies led by the universities of Glasgow and Exeter has given scientists insight into howmale cooercion can lead to physiological changes, much like those in athletes who train to perform better