INFORMATION:
The greater a country's gender equality in employment, the higher its homicide rate
2015-08-25
(Press-News.org) The greater a country's gender equality when it comes to employment, the higher the overall homicide rate, according to a Baylor University study of 146 countries.
"The finding does not mean that gender equality in employment increases homicide rates, but there is a correspondence," said sociologist Katie Corcoran, Ph.D. "What remains uncertain is the 'why' behind this relationship, although prior research suggests it may be due to threatening male status.
"The research findings are significant because they show that gender inequality does not only affect women," she said.
Corcoran's study was to be presented Tuesday afternoon (Aug. 25) at the American Sociological Association's annual meeting in Chicago.
The study also showed that a cultural measure of equality -- determined by whether women are treated with respect -- is tied to homicide rates. Countries in which women are respected have lower overall homicide rates, said Corcoran, a fellow in Baylor's Institute for Studies of Religion and associate professor of sociology and anthropology at West Virginia University.
Latin American countries' "extraordinarily high rates of homicide" -- second only to Sub-Saharan Africa globally -- are partly explained by Latin Americans' cultural perception that women are not respected in their countries, Corcoran said.
Until now, little research has been done to investigate a link between gender inequality and cross-national homicide, Corcoran said.
"In the past, studies of gender inequality and violence typically focused on male-on-female violence, including rape and homicide," she said. "Yet gender inequality can contribute to broad cultures of violence that may explain male-on-male, female-on-male and female-on-female violence as well."
In her study, Corcoran used social and economic data from the 2009-2011 waves of the Gallup World Polls for 146 countries. The poll is a representative survey of adult residents in more than 150 countries, which make up more than 98 percent of the world's adult population. The survey is given to approximately 1,000 people in each country.
For homicide rates, she used 2005 to 2011 data from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime.
In the area of socioeconomics, gender equality was measured by the adult female share of the labor force and the ratio of females to males employed in such positions as professional workers, managers and executives. In the cultural measure, based on asking respondents whether women in their country are treated with respect and dignity, female and male responses tended to be consistent in most countries, Corcoran said.
Corcoran noted that homicide rate breakdowns by the gender of the victim and perpetrator are available only in a handful of countries, primarily Western ones, which tend to have more gender equality.
"Since gender inequality can have broader effects on violence, I am able to look at overall homicide rates, which greatly increases the number and diversity of the countries included in the study," she said.
Corcoran noted that some scholars argue that the "machismo" culture of Latin America -- characterized by bravery, male dominance and aggressive sexual prowess coupled with rejection of gay men -- may account for Latin America's overall high levels of homicide, although this never has been tested. Corcoran finds that one element of machismo -- cultural gender inequality -- does contribute to explaining Latin America's higher homicide rates.
There are two common hypotheses related solely to violence against women. One predicts that when gender inequality is high, male violence against women also will be high because men have more control over societal institutions, including the criminal justice system, and are thus less accountable for their victimization of women. The other predicts that as gender equality increases, males may feel threatened by women's gains in status, with higher levels of violence against women becoming a consequence.
In the case of greater cultural gender equality corresponding to lower homicide rates overall, "women being treated with more respect and dignity may be a reflection of fewer patriarchal beliefs condoning violence," Corcoran said. "Meanwhile, greater socioeconomic gender equality corresponding to higher homicide rates overall may be due to women's gains in the labor market threatening men's status.
"Gender systems may condone male violence not only against women but other men as well," she said. "As such, gender inequality may contribute to explaining men's violence against both women and men as well as women's typically reactionary violence against men."
Future cross-national violent crime research must consider not only income inequality -- a traditional measure related to homicide rates -- but gender inequality as well, she said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic study finds association between reduced vitamin D and multiple sclerosis risk
2015-08-25
Genetic findings support observational evidence that lower vitamin D levels are associated with increased risk of multiple sclerosis, according to a new research article by Brent Richards, from McGill University, Canada, and colleagues published this week in PLOS Medicine.
Multiple sclerosis is a debilitating autoimmune disease that affects the nerves in the brain and spinal cord. There is no known cure for multiple sclerosis and it usually presents between the ages of 20 and 40 years. While some observational evidence suggests there may be a link between lower vitamin ...
One dose or 2? Cholera vaccination strategies
2015-08-25
A new modeling study appearing this week in PLOS Medicine supports consideration of vaccination campaigns using a single dose of cholera vaccine versus campaigns using the recommended two doses given two weeks apart.. Justin Lessler and colleagues, of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Health, Baltimore, Epicentre, Paris and Médecins Sans Frontières, Geneva focus their modelling analyses on comparing the number of lives that could be saved by adopting a single vaccine dose, which could be more rapidly administered to more people than the internationally licensed ...
Less may be more in slowing cholera epidemics
2015-08-25
An oral cholera vaccine that is in short supply could treat more people and save more lives in crisis situations, if one dose were dispensed instead of the recommended two, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health research suggests.
More than 1.5 billion people around the world are at risk for cholera, a severe diarrheal illness caused by bacteria linked to poor water and sanitation. It is a major killer worldwide, causing an estimated two to three million cases and 100,000 deaths each year, primarily in developing nations.
A relatively new vaccine -- internationally ...
Adaptive mutation mechanism may explain some forms of antibiotic resistance
2015-08-25
Evolutionary theory says mutations are blind and occur randomly. But in the phenomenon of adaptive mutation, cells can peek under the blindfold, increasing their mutation rate in response to stress.
Scientists at Winship Cancer Institute, Emory University have observed that an apparent "back channel" for genetic information called retromutagenesis can encourage adaptive mutation to take place in bacteria.
The results are scheduled for publication in PLOS Genetics on Tuesday, August 25.
"This mechanism may explain how bacteria develop resistance to some types of antibiotics ...
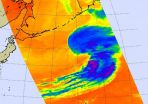
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Atsani bow out
2015-08-25
Tropical Cyclone Atsani appeared to look more like a frontal system in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite.Early on August 26, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued their final bulletin on the system as it was transitioning into an extra-tropical cyclone,
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that also flies aboard Aqua captured infrared data on the storm on August 25 at 14:47 UTC (10:47 a.m. EDT). Cloud top temperatures in thunderstorms northeast of the center were colder than -63F/-52C, indicating high, strong thunderstorms with the potential ...
Study in bats and rodents offers insights on how viruses spread across species
2015-08-25
Bats are natural reservoirs of several important emerging viruses, and because cross-species transmission appears to be quite common among bats, it's important to study bats in a community context rather than concentrating on individual species.
Researchers have now used such an approach to identify characteristics of cross-species virus transmission in bats and rodents, another important viral host. The investigators uncovered evidence to suggest that viruses pass more easily between bat species than between rodent species, and they found that characteristics unique ...
Optimal breastfeeding practices may help save infants' lives
2015-08-25
In a new review of all relevant medical research on breastfeeding practices, infants 0 to 5 months of age who were predominantly, partially, or not breastfed had 1.5-, 4.8-, and 14.4-times higher risks of dying, respectively, compared with exclusively breastfed infants. Also, children aged 6 to 23 months who were not breastfed had about a 2-times higher risk of dying than children who were continued on breastfeeding.
"The findings underscore the importance of optimal breastfeeding practices during infancy and early childhood," said Dr. M. Jeeva Sankar, lead author of ...
Adverse effects of common prostate enlargement and hair growth drugs: A review
2015-08-25
(Boston)--Twenty-five percent of men currently taking Finasteride or Dutasteride, popularly known as Proscar and Avodart, for the treatment of benign prostate enlargement (BPH), appear not to benefit from taking these medications. Those prescribed Propecia or Avodart for male pattern hair loss (known as alopecia) are also at risk for adverse events elicited by these drugs.
These findings are part of an international, collaborative review currently online in the journal Endocrine Reviews and Metabolic Disorders. Led by Abdulmaged Traish, PhD, professor of biochemistry ...
Rare nautilus sighted for the first time in 3 decades
2015-08-25
In early August, biologist Peter Ward returned from the South Pacific with news that he encountered an old friend, one he hadn't seen in over three decades. The University of Washington professor had seen what he considers one of the world's rarest animals, a remote encounter that may become even more infrequent if illegal fishing practices continue.
The creature in question is Allonautilus scrobiculatus, a species of nautilus that Ward and a colleague had previously discovered off of Ndrova Island in Papua New Guinea. Nautiluses are small, distant cousins of squid and ...
Sequencing of barley genome achieves new milestone
2015-08-25
RIVERSIDE, Calif. - Barley, a widely grown cereal grain commonly used to make beer and other alcoholic beverages, possesses a large and highly repetitive genome that is difficult to fully sequence. Now a team led by scientists at the University of California, Riverside has reached a new milestone in its work, begun in 2000, on sequencing the barley genome. The researchers have sequenced large portions of the genome that together contain nearly two-thirds of all barley genes.
The new information, published in The Plant Journal, will not only expand geneticists' knowledge ...