(Press-News.org) Toronto, CANADA - Male teens who experiment with cannabis before age 16, and have a high genetic risk for schizophrenia, show a different brain development trajectory than low risk peers who use cannabis.
The discovery, made from a combined analysis of over 1,500 youth, contributes to a growing body of evidence implicating cannabis use in adolescence and schizophrenia later in life.
The study was led by Baycrest Health Sciences' Rotman Research Institute in Toronto and is reported in JAMA Psychiatry (online) today, ahead of print publication.
Adolescence is a period of vulnerability with regard to the emergence of psychotic disorders, especially in boys. Environmental influences on the continuing maturation of neural circuits during adolescence are of great interest to neuroscientists and medical professionals.
"Given the solid epidemiologic evidence supporting a link between cannabis exposure during adolescence and schizophrenia, we investigated whether the use of cannabis during early adolescence (by 16 years of age) is associated with variations in brain maturation as a function of genetic risk for schizophrenia," said senior author Tomas Paus, MD, PhD, the Anne and Max Tanenbaum Professor and Chair in Population Neuroscience at Baycrest, University of Toronto, and the Dr. John and Consuela Phelan Scholar at Child Mind Institute, New York.
"Our findings suggest that cannabis use might interfere with the maturation of the cerebral cortex in male adolescents at high risk for schizophrenia by virtue of their polygenic risk score. Their brains showed lower cortical thickness compared with low-risk male participants and low-or-high risk female participants who used the drug."
Dr. Paus, a prominent researcher and pioneer in the field of population neuroscience, strongly cautioned that more research is needed to determine whether lower cortical thickness actually increases the probability of schizophrenia in at-risk males later in life.
The research team used observations from three large samples of typically developing youth in Canada and Europe. Researchers examined data from a total of 1,577 participants (aged 12 - 21 years, 57% male / 43% female), that included information on cannabis use, brain imaging results, and polygenic risk score for schizophrenia. The data came from the Saguenay Youth Study in Quebec (Canada), the Avon Longitudinal Study of parents and Children in the U.K., and the IMAGEN Study in the U.K., Germany, France and Ireland.
According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness: "It is too early to classify schizophrenia as either a neurodevelopmental (impairment of the growth and development of the brain) or a neurodegenerative (progressive loss of structure or function of neurons) disorder, as both seem to occur over the course of the illness. Research strongly suggests the emergence of schizophrenia is a result of both genetic and environmental factors."
"Brain aging is about brain development," said Dr. Paus. "Our study shows the importance of understanding environmental influences on the developing brain in early life as this can have important implications for brain health through the lifespan."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the National Institutes of Health (U.S.), European Union and the Anne and Max Tanenbaum Professor and Chair in Population Neuroscience.
The paper's first author is Leon French, PhD, post-doctoral fellow at Baycrest's Rotman Research Institute.
About Baycrest Health Sciences
Baycrest Health Sciences is a global leader in geriatric residential living, healthcare, research, innovation and education, with a special focus on brain health and aging. As an academic health sciences centre fully affiliated with the University of Toronto, Baycrest provides an exemplary care experience for aging clients combined with an extensive clinical training program for students and the Rotman Research Institute, one of the world's leaders in cognitive neuroscience. Through its commercial and consulting arms, Baycrest is marketing its sought-after expertise and innovation to other healthcare organizations and long-term care homes, both in Canada and internationally.
Putnam Valley, NY. (Aug. 26, 2015) - Liver transplantation is currently the only established treatment for patients with end stage liver failure. However, this treatment is limited by the shortage of donors and the conditional integrity and suitability of the available organs. Transplanting donor hepatocytes (liver cells) into the liver as an alternative to liver transplantation also has drawbacks as the rate of survival of primary hepatocytes is limited and often severe complications can result from the transplantation procedure.
In an effort to find potential therapeutic ...
Washington, DC--New research from a team led by Carnegie's Robert Hazen predicts that Earth has more than 1,500 undiscovered minerals and that the exact mineral diversity of our planet is unique and could not be duplicated anywhere in the cosmos.
Minerals form from novel combinations of elements. These combinations can be facilitated by both geological activity, including volcanoes, plate tectonics, and water-rock interactions, and biological activity, such as chemical reactions with oxygen and organic material.
Nearly a decade ago, Hazen developed the idea that the ...
PHILADELPHIA - In the midst of a growing trend for Medicare patients to receive observation care in the hospital to determine if they should be formally admitted, a new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania shows that for more than a quarter of beneficiaries with multiple observation stays, the cumulative out-of-pocket costs of these visits exceeds the deductible they would have owed for an inpatient hospital admission. According to the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, there were 1.8 million observation patients ...
BATON ROUGE - Ten years after Hurricanes Katrina and Rita devastated the Gulf Coast, LSU researchers have analyzed and documented the recovery effort for the state. Initial reports have been released this week.
Due to the unprecedented destruction of the 2005 storm season, recovery efforts traditionally supported by insurance and FEMA were supplemented by a unique set of programs funded through $13.4 billion of Community Development Block Grant-Disaster Recovery, or CDBG-DR funds.
The researchers from the LSU AgCenter and E. J. Ourso College of Business focused on ...
New Haven, Conn. -- Nearly one in four patients with chronic hepatitis C (HCV) are denied initial approval for a drug therapy that treats the most common strain of the infection, according to a Yale School of Medicine study.
The finding, published Aug. 27 in PLOS ONE, identifies a new barrier to caring for patients with this severe condition.
Prior to the FDA approval of novel antiviral therapies for HCV in 2014, treatment options for patients were limited, requiring weekly injections of interferon-based therapy that caused severe side effects. The new regimens revolutionized ...
For astronauts living in space with objects zooming around them at 22,000 miles per hour like rogue super-bullets, it's good to have a backup plan. Although shields and fancy maneuvers could help protect space structures, scientists have to prepare for the possibility that debris could pierce a vessel. In the journal ACS Macro Letters, one team reports on a new material that heals itself within seconds and could prevent structural penetration from being catastrophic.
It's hard to imagine a place more inhospitable to life than space. Yet humans have managed to travel ...
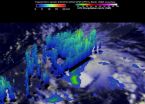
The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM mission core satellite measured rainfall as Tropical Depression Twelve was upgraded to Tropical Storm Ignacio.
Tropical Depression 12E strengthened into Tropical Storm Ignacio at 5 p.m. EDT yesterday, August 25. At that time, it became the ninth named tropical storm of the Eastern Pacific hurricane season.
The GPM core observatory satellite saw Ignacio on August 25, 2015 at 2256 UTC. GPM's Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) found rain falling at a rate of over 74 mm (2.9 inches) per hour with storm tops reaching to altitudes ...
Treatments for cystic fibrosis (CF) have added years to the lives of thousands of Americans. But they can be difficult to administer, and most don't fix the underlying cause. Scientists have now found that a small molecule, when tested in yeast, can substitute for a protein and restore a key cellular function related to those missing in people with CF and similar conditions. Their report appears in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
CF is caused by a genetic mutation that affects certain cellular proteins that make up "channels," which act like gates managing ...
Nobody likes flight delays, but they are a common occurrence: In 2011, about 20 percent of U.S. flights were at least 15 minutes behind schedule. Those delays irritate passengers and, in 2010, added an estimated $6.5 billion to U.S. airlines' operating costs.
Delays tend to hit some airlines harder than others, due to the approach the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) uses to resolve them. This approach places an emphasis on minimizing aggregate system delays, nationwide -- a policy that affects some airlines much more than others at a given time.
But now a study ...
While exploring the remote coral reefs of Raja Ampat in Indonesia, Dr. James Thomas from the Halmos College of Natural Sciences and Oceanography, Florida, and his colleagues from Naturalis Natural History museum in the Netherlands, stumbled across a small but extraordinary crustacean living inside another reef invertebrate in a commensal association (without causing any harm, nor benefit to its host).
In his amazement to the amphipod's unusual form, Dr. Tomas called it L. eltoni after musician and actor Sir Elton John. The research is available in the open access journal ...