(Press-News.org) To understand how confidence in parenting may predict parenting behaviors in women who were abused as children, psychologists at the University of Rochester have found that mothers who experienced more types of maltreatment as children are more critical of their ability to parent successfully. Intervention programs for moms at-risk, therefore, should focus on bolstering mothers' self-confidence--not just teach parenting skills, the researchers said.
"We know that maltreated children can have really low self-esteem," said Louisa Michl, a doctoral student in the department of psychology at the University of Rochester. "And when they become adults, we've found that some of these moms become highly self-critical about their ability to parent effectively. Research has shown that this type of self-doubt is related to poor parenting--yelling, hitting, and other kinds of negative parenting behaviors."
The study, conducted at the University of Rochester's Mt. Hope Family Center and published online today in Child Maltreatment, found that mothers who experienced more types of abuse as children--sexual abuse, physical or emotional abuse, and physical or emotional neglect--have higher levels of self-criticism, and therefore greater doubt in their ability to be effective parents.
This study included mothers who were clinically depressed, as well as those who were not. "Our research shows that self-criticism leads to lower-confidence in parenting abilities in previously maltreated mothers and this was true in non-depressed moms as well as depressed mothers," said Michl, the lead researcher of the study.
Prior research has found that a mother's confidence is closely linked to her motivation to use positive child-rearing strategies. "When a mom has confidence in her ability to use positive strategies when under stress--like when her child throws a tantrum in a grocery store--then she is more likely to parent effectively," Michl explained.
All of the mothers in the study were from low-income households. "For families living in poverty, daily stresses can quickly add up, and parenting--which can be challenging for anyone--can become overwhelming," she said.
"So many parenting interventions are didactic. They're teaching parenting skills: 'if your baby cries, do this'; 'this is how you feed your baby'; 'this is how you burp your baby,'" said Michl.
"That's all well and good--moms can learn those skills. But what happens when they are in a stressful situation? What do they do? If they don't have the attitude--the belief that they can do this, that they can be a good mom and enact all those things they learned--then they may fall back on how they themselves were treated as children."
There is a positive side. Previous research has shown that beliefs of maternal efficacy are modifiable, Michl said. "If a mom who was maltreated as a child can sustain some strong beliefs in her competency as a mom, then it may help break the cycle of abuse and buffer her children against that kind of experience she had. That is where this research has led us so far."
"My hope is that community services that offer intervention support will focus on moms' mental health--how her critical self-beliefs are getting in the way of believing she can be a good parent," said Michl, who is also a clinical therapist. "Making sure moms have good parenting skills is really important. But we can support these moms in a more holistic way--provide her the facts, but also help her to believe in herself."
INFORMATION:
Elizabeth Handley, Fred Rogosch, Dante Cicchetti, and Sheree L. Toth of the University of Rochester and Mt. Hope Family Center contributed to the study. Cicchetti is also a professor of psychology at the University of Minnesota. The National Institute of Mental Health supported the research.
A simple change in the wording of a traffic sign - from "Share the Road" to "Bicycles May Use Full Lane" - could help clarify the rules of the road for bicyclists and motorists, according to a North Carolina State University study.
"'Share the Road' signs are common but what that means in terms of how drivers and bicycle riders should interact can be ambiguous," says George Hess, natural resources professor and co-author of the study in PLOS One. Some bicyclists complain that motorists consider them to be in the way, while some motorists accuse bicyclists of hogging ...
Consider the pendulum of a grandfather clock. If you forget to wind it, you will eventually find the pendulum at rest, unmoving. However, this simple observation is only valid at the level of classical physics--the laws and principles that appear to explain the physics of relatively large objects at human scale. However, quantum mechanics, the underlying physical rules that govern the fundamental behavior of matter and light at the atomic scale, state that nothing can quite be completely at rest.
For the first time, a team of Caltech researchers and collaborators has ...
Washington DC - August 28, 2015 - Oysters not only transmit human norovirus; they also serve as a major reservoir for these pathogens, according to research published August 28 in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology. "More than 80 percent of human norovirus genotypes were detected in oyster samples or oyster-related outbreaks," said corresponding author Yongjie Wang, PhD.
"The results highlight oysters' important role in the persistence of norovirus in the environment, and its transmission to humans, and they demonstrate ...
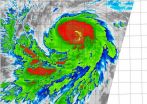
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite flew over Hurricane Jimena in the Eastern Pacific and saw the strongest thunderstorms building up quickly, especially in the northern quadrant of the storm. Jimena intensified rapidly overnight on August 27 and early August 28 and the National Hurricane Center expects it to become a major hurricane.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard the satellite provided infrared data of the storm that showed the coldest cloud top temperatures, which indicate the strongest thunderstorms were in Jimena's northern ...
Generating and storing renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, is a key barrier to a clean-energy economy. When the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (JCAP) was established at Caltech and its partnering institutions in 2010, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub had one main goal: a cost-effective method of producing fuels using only sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, mimicking the natural process of photosynthesis in plants and storing energy in the form of chemical fuels for use on demand. Over the past five years, researchers at ...
If you think that performing CPR on a person whose heart has stopped is a surefire way to save their life, you may be watching too much TV.
The truth is more depressing than fiction, according to a new study by University of Southern California Davis School of Gerontology researchers. While medical dramas Grey's Anatomy and House show cardiopulmonary resuscitation saving a patient's life nearly 70 percent of the time, the real immediate survival rate is nearly half that - around 37 percent.
Researchers also found another discrepancy between reality and TV: Half of ...
TAMPA, Fla. - Pancreatic cancer is the fourth most common cause of cancer-related death in the United States and has a 5-year survival rate of only 6 percent, which is the lowest rate of all types of cancer according to the American Cancer Society. This low survival rate is partially attributed to the difficulty in detecting pancreatic cancer at an early stage. According to a new 'proof of principle' study published in Aug. 27 issue of Cancer Prevention Research, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers hope to improve pancreatic cancer survival rates by identifying markers in ...
Beach sand contains all kinds of microorganisms, including those that can harm human health. Yet current guidelines are focused exclusively on monitoring the levels of microbes in the water.
Now, an international panel of scientists is recommending monitoring the sand at recreational beaches, to minimize health risks for beachgoers. Their advice is based on the general consensus reached during the international conference "Trends in Environmental Microbiology and Public Health," held in Lisbon Portugal in September 2014.
"Beach sands accumulate contaminants and people ...
A collaboration between biologists and engineers at Monash University has led to the development of a new non-invasive image processing technique to visualise embryo formation. Researchers were able to see, for the first time, the movement of all of the cells in living mammalian embryos as they develop under the microscope. This breakthrough has important implications for IVF (in vitro fertilisation) treatments and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). In the future, this approach could help with embryo selection before the embryo is implanted back into the uterus to ...
A German-French team has developed a light-sensitive switch that regulates a protein implicated in the neurobiology of synaptic plasticity. The agent promises to shed new light on the phenomenology of learning, memory and neurodegeneration.
Learning is made possible by the fact that the functional connections between nerve cells in the brain are subject to constant remodeling. As a result of activation-dependent modification of these links ('synaptic plasticity'), circuits that are repeatedly stimulated "learn" to transmit signals ever more efficiently. This process is ...