Closer to a treatment for the 'asthma of the esophagus'
Scientists elucidate the role of a key molecule involved in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and pave the way to a treatment for this enigmatic and hard-to-treat food allergy
2015-08-31
(Press-News.org) Scientists from the D'Or Institute of Research and Education (IDOR), the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and the Yale University School of Medicine have elucidated the chemical process behind a mysterious gastrointestinal disease that is becoming more frequent every day: the eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), also known as the "asthma of the esophagus". The researchers identified a molecule which plays a key role in this condition and that can be a target in a new therapeutic strategy.
The eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the esophagus. In patients with this condition, a type of white blood cell from the immune system, the eosinophil, builds up in the lining of the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, the esophagus. This buildup inflames and injures the esophageal tissue leading to tissue scarring and fibrosis, which causes difficulty for swallow. In severe cases, the patients may need to undergo a procedure to dilate the esophagus to let the food pass.
The disease is relatively new, with the first diagnosis made in the 70's. Scientists don't know yet what can trigger this kind of esophageal inflammation. The most accepted hypothesis is that it may be caused by allergic hypersensitivity to certain foods (like nuts and milk), air pollution or chemical components present in the modern industrialized foods and oral hygienic products.
Trying to better understand the disease, the leader of the study, Heitor De Souza, from IDOR, decided to look for a molecule called MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor), which his group had already seen involved in other allergenic inflammations. MIF is released by our immune cells, including eosinophils, when our body is under attack of pathogens.
Analyzing biopsies from patients diagnosed with EoE, De Souza saw that MIF was highly expressed in their esophageal mucosa compared with healthy people and patients suffering from other esophageal diseases, like gastroesophageal reflux disease. The presence of MIF could explain the accumulation of eosinophils, as this molecule is known to attract immune cells and prevent them from dying. Indeed, in vitro experiments proved that MIF significantly increases the attraction of eosinophils.
The researchers also tested the role of MIF in mice modeled for EoE. Sick mice genetically modified to be MIF deficient have reduced inflammation compared with mice that have not been modified. Furthermore, the early administration of a drug that blocks the effect of MIF prevented the eosinophils accumulation in the esophagus and the development of esophagitis in treated mice.
"Our work is the first to show the role of MIF in EoE", says De Souza. "Together, our results implicate MIF in the pathogenesis of EoE and suggest that targeting MIF might represent a novel therapy for EoE."
There is no cure for EoE. The current treatment for the disease is based on the intake of corticosteroids, which can lead to side effects and cannot be taken uninterruptedly. The study can pave the way to an effective and safer therapy for patients with this condition.
"If we could give the patients a medicine that blocks MIF, it would be more effective and safer than giving them corticosteroids like we do today", points out De Souza. "We are now one step closer to an effective treatment for this condition."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-31
While the French High Council for Public Health (HCSP) made public on Monday, 24 August 2015, a positive opinion regarding the relevance of the 5-colour code for the public, a team of researchers (Inserm/INRA/Paris 13 University) directed by Serge Hercberg, on publication of their article in the journal Nutrients, demonstrated that the 5-colour nutrition label (5-CNL) is the most effective nutritional information system for allowing consumers to recognise and compare the nutritional quality of foods, including "at-risk" populations (older subjects, those with a lower educational ...
2015-08-31
Amsterdam, NL, August 31, 2015 -- Every week in the U.S. an average of 645 people lose their lives to firearm violence and 1,565 more are treated in an emergency department for a firearm-related injury. Most of these events do not make headlines, but they account for about 7% of the premature deaths before age 65 in the U.S. In a special issue of Preventive Medicine, preventive medicine and health policy experts address a wide range of critical topics related to firearm violence, from the interaction of alcohol abuse with gun violence, effects of changes to gun laws in ...
2015-08-31
Alzheimer's disease is associated with the appearance of characteristic neurotoxic protein aggregates in various regions in the brain. Chemical analysis of these insoluble deposits reveals that they are made up of a family of short protein fragments, referred to as beta-amyloid peptides, which are derived from a precursor protein called APP by the sequential action of two enzymes. An international team of researchers led by Christian Haass (Professor of Metabolic Biochemistry at LMU and Speaker for the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Munich) and Dr. Michael ...
2015-08-31
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- About 20 percent of colorectal cancer patients have cancers that have spread (metastasized) beyond the colon at the time of their diagnosis. The liver is the most common site for these metastases. The approach to treating primary tumors within the colon and metastatic tumors in the liver continues to evolve; however, it typically involves chemotherapy plus surgical removal (resection) of both types of tumors. However, experts continue to debate whether surgical resection of primary tumors and metastatic tumors should be performed at the same time (synchronously) ...
2015-08-31
LAWRENCE -- Renewable wind energy is experiencing a boom, with more wind turbines popping up across landscapes in the U.S. and abroad. Indeed, wind energy accounted for 3.3 percent of electricity generation in the United States in 2011, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Globally, that number was 2.9 percent for the same year.
But as wind turbines proliferate, researchers at the University of Kansas are looking at how these forests of turbines affect the wind itself. What happens to the wind when a larger number of wind turbines removes more and ...
2015-08-31
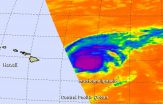
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Ignacio and viewed the storm in infrared light, providing valuable temperature data. Aqua saw a weaker Ignacio moving parallel to the Hawaiian Islands.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathers infrared data that shows temperatures. That AIRS data was made into a false-colored infrared image from August 30 at 22:47 UTC (6:47 p.m. EDT) and showed high, cold, strong thunderstorms surrounded the center of Hurricane Ignacio.
AIRS imagery also showed a thick band of thunderstorms spiraling into the ...
2015-08-31
Researchers link babies' performance on cognitive tasks to later learning progress
Study underscores importance of talking to your baby well before they can talk back
Findings may eventually contribute to reducing "vocabulary gap"
EVANSTON, Ill. --- At 12 months old, your infant's ability to group objects according to the names associated with them -- as opposed to their appearance alone -- offers a glimpse into how his or her vocabulary will develop by the time they are 18 months, Northwestern University researchers have found.
The research, by Brock Ferguson, ...
2015-08-31
This news release is available in Spanish. Marine energy has a great future potential according to the experts, but there is still a long way to go before it can be used on a large scale. Despite the problem of intermittency, wave energy has an advantage over wind energy, for example: it is easier to predict optimum swell than some suitable gusts of wind. That is why knowing how much energy the waves will be bringing within a few hours is as important as having available efficient prototypes to make use of wave power. If this information is known, the energy produced ...
2015-08-31
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 31, 2015 -- People with hostile personality traits who watch more television than their peers may be at a greater risk for injury, potentially because they are more susceptible to the influence of television on violence and risk-taking behaviors, a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health analysis discovered.
The research, published online in the International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion, suggests that a reduction in television viewing and content rating systems geared not just to age, but also personality traits, ...
2015-08-31
Life on an island isn't always easy. To make the most of the little there is to eat on many Greek islands, the digestive system of Balkan green lizards has evolved considerably compared to family members on the mainland. Surprisingly, many of these insect-eating lizards even have special valves that help to digest plants. These are some of the findings¹ from a study led by Konstantinos Sagonas of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens in Greece, published in Springer's journal The Science of Nature².
Reptiles can adjust their digestive system and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Closer to a treatment for the 'asthma of the esophagus'
Scientists elucidate the role of a key molecule involved in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and pave the way to a treatment for this enigmatic and hard-to-treat food allergy