(Press-News.org) This news release is available in Japanese.
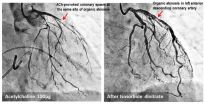
Researchers at Kumamoto University in Japan have found that patients with coronary spasm have a higher risk of experiencing future heart attack particularly when a spasm occurs at the site of atherosclerotic coronary artery narrowing, i.e., coronary atherosclerotic stenosis.
Angina is caused by the narrowing of the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart, and vasospastic angina patients account for about 40% of all angina patients. The incidence and progression of the disease can be reduced through appropriate drug treatment with relatively good prognosis. However, where stenosis of the coronary arteries has developed alongside vasospastic angina, cases of heart attack increase.
A detailed study on the positioning of coronary spasm relative to coronary artery stenosis had not been performed, until now.
Dr. Koichi Kaikita's team examined in detail the positional relationship between coronary spasm and arteriosclerosis, and compared the case data of patients with spasm occurring at sites of coronary atherosclerotic stenosis to those whose spasm occurred at another site.
Data was gathered from 1,760 cardiology patients of Kumamoto University Hospital between 1991 to 2010 who experienced chest pain and underwent cardiac catheterization at rest.
Case data was divided into three groups, one in which the coronary spasm occurred at a site of stenosis of the coronary artery, one where the spasm occurred at another site, and another group that had spasms but no stenosis.
Out of the 1,760 cases, coronary spasm occurred 873 times and constriction of a coronary artery was observed 358 times.
Both coronary spasm and coronary atherosclerotic stenosis occurred in a total of 233 cases and there was a tendency for these patients to have a lower rate of diabetes than in stenosis only cases. Furthermore, patients who had coronary spasm without stenosis were found to be older than patients who had neither stenosis nor coronary spasm.
The group with coronary spasm occurring at the site of stenosis was found to have the highest risk of experiencing heart attack within five years when compared to the group with a coronary spasm without coronary atherosclerotic stenosis, and the group with a coronary spasm at a site different from the coronary atherosclerotic stenosis.
"Our research shows that coronary spasm occurring at the site of coronary atherosclerotic stenosis is a predictor for acute coronary syndrome," said Dr. Koichi Kaikita. "In other words, these people have a high risk for heart attack in the relatively near future."
Checking for the occurrence of a coronary artery spasm at sites of coronary artery stenosis helps predict a person's risk for a future heart attack and may be useful for beginning sufficient preventative therapy.
This study was published online in "The Journal of the American College of Cardiology" on August 31, 2015.
INFORMATION:
ALLENDALE, Mich. -- An international team of scientists, including a Grand Valley State University professor and alumni, recently discovered a species of monkey fossil the team has dated to be more than one million years old.
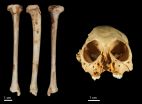
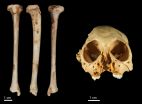
The discovery was made after the team recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The species was roughly the size of a small cat, dwelled in trees, and lived largely on a diet of fruits and leaves.
"We know that there ...
As climate change accelerates ice melt in the Arctic, polar bears may find caribou and snow geese replacing seals as an important food source, shows a recent study published in the journal PLOS ONE. The research, by Linda Gormezano and Robert Rockwell at the American Museum of Natural History, is based on new computations incorporating caloric energy from terrestrial food sources and indicates that the bears' extended stays on land may not be as grim as previously suggested.
"Polar bears are opportunists and have been documented consuming various types and combinations ...
Natural wonders like tumbling waterfalls, jutting rock faces and banks of wildflowers have long drawn visitors to America's national parks and inspired efforts to protect their beauty.
According to a study published Sept. 4 in Park Science, visitors also value and seek to protect a different kind of threatened natural resource in the parks: dark nighttime skies.
Almost 90 percent of visitors to Maine's Acadia National Park interviewed for the study agreed or strongly agreed with the statements, "Viewing the night sky is important to me" and "The National Park Service ...
(Boston)--Patients with spinal stenosis (SS) experienced good short term benefit, lasting from weeks to months, after receiving epidural steroid injections (ESI).
These findings, which appear in a letter in the journal Pain Medicine, contradict a previously published New England Journal Medicine (NEJM) study that found epidural steroid injections were not helpful in spinal stenosis cases.
It has been one year since the publication of "A Randomized Trial of Epidural Glucocorticoid Steroid Injections for Spinal Stenosis." This was a large scale clinical trial evaluating ...
An international team of scientists have dated a species of fossil monkey found across the Caribbean to just over 1 million years old.
The discovery was made after the researchers recovered a fossil tibia (shin bone) belonging to the species of extinct monkey Antillothrix bernensis from an underwater cave in Altagracia Province, Dominican Republic. The fossil was embedded in a limestone rock that was dated using the Uranium-series technique.
In a paper published this week in the well renowned international journal, the Journal of Human Evolution, the team use three-dimensional ...
Tropical Storm Kevin's center was several hundred miles south-southwest of Baja California when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and saw some associated high clouds streaming over the peninsula.
The MODIS and the AIRS instruments aboard Aqua captured visible and infrared images of Kevin on September 3 at 20:50 UTC (4:50 p.m. EDT). The visible image from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided look at Kevin's clouds. MODIS showed a somewhat elongated tropical storm with a fragmented band of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level ...
Scientists studying how a heat-loving microbe transfers its DNA from one generation to the next say it could further our understanding of an extraordinary superbug.
Sulfolobus is part of the Archaea kingdom - a single-cell organism similar to bacteria - which was isolated in hot springs on the island of Hokkaido, Japan.
Some Archaea live ordinary lives in mundane environments such as lakes, seas and insect and mammal intestinal tracts, while others live extraordinary lives pushed to extremes in incredibly harsh habitats such as deep sea hydrothermal vents, volcanic ...
"Objects of granular media, such as a sandcastle, consist of millions or billions of grains. The computation time needed to produce photorealistic images amounts to hundreds to thousands of processor hours," Professor Carsten Dachsbacher of the Institute for Visualization and Data Analysis of KIT explains. Materials, such as sand, salt or sugar, consist of randomly oriented grains that are visible at a closer look only. Image synthesis, the so-called rendering, is very difficult, as the paths of millions of light rays through the grains have to be simulated. "In addition, ...
Nowadays, internet auctions play an important role in online trading. No matter whether you want to buy a hedge trimmer or an antique pocket watch - unlike purchases by a click at a fixed price, online auctions provide the atmosphere of a competition for the auction object. Whoever perceives the competition of real contenders, e.g. by avatars or photos on the screen, wishes to stay in the race - and increases his bid. This is a result of a KIT study with more than 450 test persons.
Online auctions combine shopping with entertainment, fun, and excitement. This is the ...
Action to prevent tooth decay in children, such as supervised tooth brushing and fluoride varnish schemes, are not just beneficial to children's oral health but could also result in cost savings to the NHS of hundreds of pounds per child, so says a leading dental health researcher.
Professor Elizabeth Kay, Foundation Dean of the Peninsula Dental School from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, has carried out the first economic evaluation of public health measures to reduce tooth decay in children at high risk, in association with the National ...