Modeling the helicase to understand hepatitis C
NS3 behaves like a 'caterpillar' and helps the virus to replicate
2015-09-10
(Press-News.org) NS3 is an enzyme specific to the hepatitis C virus. If developed, a drug capable of recognizing and selectively attacking it could fight the disease without side effects for the body. However, to be able to develop one we need to know more about the behavior of this important protein in the virus replication process. Some SISSA scientists have provided a detailed and comprehensive view of the behavior of NS3. The study has been published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research.
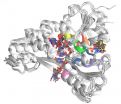
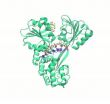
According to the WHO, a good 140 million people are affected by hepatitis C (3/4 million new cases per year). This is still a subtle disease which, in the event of chronic infection, heavily affects the patients' quality of life and whose complications can lead to death. One of the molecules involved in the reproduction mechanism of the virus in the body is a helicase, NS3, an enzyme that interacts with the RNA (the viral genome, which is not like our DNA) by climbing onto it and helping the pathogen's replication process.
"By knowing in detail how this helicase works, in the future we could try to block the viral replication, and thus stop the disease from proliferating in the body" explains Giovanni Bussi, SISSA professor and among the study authors. NS3 facilitates the work of the polymerases, the molecules that build a replica of the RNA strand, by "opening" and preparing the RNA to the action of the second enzyme. "NS3 crawls along the RNA strand contracting and extending like a caterpillar and, as it does so, it releases the part of the virus to which the polymerase then attaches" explains Andrea Pérez-Villa, SISSA student and first author of the paper. "We decided to analyze this protein because, unlike others, it is only present in the hepatitis C virus. This way, any drug capable of targeting its interaction with the RNA would not damage other proteins, for example, those belonging to the body being attacked by the virus. This means that, theoretically, the drug would have no side effects".
"Our work was based on a computer simulation, starting from the available experimental data", explains Pérez-Villa. So far, crystallography studies succeeded in obtaining a limited number of "images" of NS3, too few to be able to reconstruct the whole process. Based on existing data, Pérez-Villa and Bussi (as well as Maria Darvas, SISSA research scientist who took part in the study) created a model of the protein and had it interact with the viral RNA. But not only that.
"During the process, ATP, the "fuel" utilized by proteins, is consumed. Therefore our simulation also reproduced the system's interaction with ATP and subsequently with ADP, a waste product together with phosphate, after ATP had been utilized" concludes Bussi. So for the first time we provided a detailed description of the process, which will serve as a guide for future steps forward, whether theoretical or experimental.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-09-10
While sexual contact is not the most efficient means of hepatitis C (HCV) transmission, there have been several reports of outbreaks of sexually transmitted HCV in HIV-positive men who have sex with men (MSM). HCV infections are more likely to become persistent and to lead to progressive liver disease in people who are HIV-infected, even if they are receiving HIV treatment. Factors underlying these infections in HIV-positive MSM are only partially understood.
Researchers at NYU's Center for Drug Use and HIV Research (CDUHR) at the College of Nursing (NYUCN) have conducted ...
2015-09-10
Future computers will require a magnetic material which can be manipulated ultra-rapidly by breaking the strong magnetic coupling. A study has been published in Nature Communications today in which Swedish and German scientists demonstrate that even the strongest magnetic coupling may be broken within picoseconds (10-12 s). This will open up an exciting new area of research.
The element gadolinium is named after the Uppsala chemist Johan Gadolin who discovered the first rare-earth metal yttrium in the late 1700s. Gadolinium is in the same class of elements and it has ...
2015-09-10
Dublin, Thursday September 10th, 2015 - Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have discovered that one gene mutation in a single species can trigger dramatic changes in whole biological communities; changes can be as great as those caused by the extinction of a top predator.
By using bacteria to replicate ecological systems in the lab, they found that mutations of a single gene that alter how one bacterial species interacts with others had huge structural impacts across their multi-species microbial communities. These 'social mutants' varied in their ability to produce ...
2015-09-10
Mathematicians investigating one of science's great questions -- how to unite the physics of the very big with that of the very small -- have discovered that when the understanding of complex networks such as the brain or the Internet is applied to geometry the results match up with quantum behavior.
The findings, published today (Thursday) in Scientific Reports, by researchers from Queen Mary University of London and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, could explain one of the great problems in modern physics.
Currently ideas of gravity, developed by Einstein and Newton, ...
2015-09-10
This news release is available in Japanese.
The Earth's atmosphere contains oxygen because plants continuously produce it through photosynthesis. This abundant supply of oxygen allows life forms like animals to flourish. Therefore, oxygen had been thought to be an essential biomarker for life on extrasolar planets. But now, a research assistant professor Norio Narita of the Astrobiology Center of National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS), which was founded in April 2015, and an associate professor Shigeyuki Masaoka, of the Institute of Molecular Science of NINS, ...
2015-09-10
DENVER (Sept. 10, 2015) - An international team of scientists, including one from the University of Colorado Denver and another from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora, announced the discovery Thursday of a new species of hominin, a small creature with a tiny brain that opens the door to a new way of thinking about our ancient ancestors.
The discovery of 15 individuals, consisting of 1,550 bones, represents the largest fossil hominin find on the African continent.
"We found adults and children in the cave who are members of genus Homo but ...
2015-09-10
A new study conducted in collaboration with Facebook using anonymised data from the social networking site shows a correlation between people's social and financial status, and the levels of internationalism in their friendship networks - with those from higher social classes around the world having fewer friends outside of their own country.
Despite the fact that, arguably, people from higher social classes should be better positioned to travel and meet people from different countries, researchers found that, when it comes to friendship networks, people from those ...
2015-09-10
ATLANTA -September 10, 2015- A new study finds breast cancer incidence and death rates are increasing in several low and middle income countries, even as death rates have declined in most high income countries, despite increasing or stable incidence rates. The findings come from a new report examining global patterns and trends in breast cancer using the most up-to-date cancer registry-based data available. It appears early online in Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention.
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among all women worldwide overall and ...
2015-09-10
Mothers who quit smoking in pregnancy are more likely to light-up again after their baby is born if they feel stressed - according to a new report from the University of East Anglia.
Researchers studied interviews with more than 1,000 new mothers and found that the stress of caring for a newborn, sleepless nights, social pressure, and the idea that they no longer need to protect the baby - all contribute to relapse.
The study also found that women who felt they were being supported by a partner were less likely to start smoking again.
Lead researcher Dr Caitlin Notley, ...
2015-09-10
Major European study moves a step closer to treatments for severe asthma
Initial findings from a major European study have helped identify key characteristics of severe asthma, which will help with the development of new treatments for patients with the condition.
The new paper, published online today (10 September, 2015) in the European Respiratory Journal, is one of the largest assessments of adults with severe asthma to date, looking at several characteristics including symptoms, patients' quality of life and blood and airway measurements.
Over 30 million adults ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Modeling the helicase to understand hepatitis C
NS3 behaves like a 'caterpillar' and helps the virus to replicate