GI side effects of chemotherapy reduced in mice by targeting gut microbes
2015-09-10
(Press-News.org) The blame for some of chemotherapy's awful side effects may lie with our gut microbes, early evidence suggests. As chemotherapy drugs are eliminated from the body, bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract can latch onto them and transform them into toxic species that cause severe diarrhea. In a Chemistry & Biology article published online on September 10, researchers present ways to shut down the ability of GI microbes to convert chemotherapy drugs to a toxic species in mice as a first step to helping cancer patients.
"The GI microbiota are the great crowd-sourcers of chemistry, using a dizzying array of enzymes to process drugs and other chemicals, occasionally with terrible consequences," says senior study author Matthew Redinbo, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. "We show that the bacteria in the GI contain 'druggable targets,' ones that we can modulate with the same types of small molecule approaches that have transformed other aspects of human health."
Bacteria consume a sugar called glucuronic acid through the use of a bacterial enzyme termed Beta-glucuronidase. This enzyme scavenges the sugar from small chemicals that the body sends to the gastrointestinal track for elimination. The chemotherapy drug irinotecan is linked to glucuronic acid to mark it for elimination, and when the GI bacteria remove the sugar, they release a virulently toxic drug back into the intestines. This causes diarrhea in up to 90% of patients who take irinotecan.
Previous research by Redinbo and others revealed that inhibiting Beta-glucuronidase helps reduce the GI toxicity associated with irinotecan, suggesting that bacteria are responsible for the drug's side effects. This may be true for other drugs as well--for example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs also cause GI problems and contain glucuronic acid.
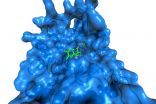
Redinbo and his team now characterize various forms of Beta-glucuronidase produced by different strains of bacteria residing in the gut, and they show that inhibiting GI bacterial Beta-glucuronidases in mice does not affect irinotecan that is circulating in the blood and is needed to combat cancer. Their findings provide a better understanding of bacterial Beta-glucuronidases and a promising new set of targets for controlling drug-induced GI toxicity.
INFORMATION:
The work was supported by the University Cancer Research Fund of North Carolina and the US National Institutes of Health.
Chemistry & Biology, Wallace and Roberts et al.: "Structure and Inhibition of Microbiome Beta-Glucuronidases Essential to the Alleviation of Cancer Drug Toxicity" http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.08.005
Chemistry & Biology, published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes reports of novel investigations in all areas at the interface of chemistry and biology. Each issue contains articles of relevant interest to chemists and biologists, such as studies of the underlying chemistry of biological processes or the application of chemical tools to provide unique insight into biological functions and mechanisms. For more information, please visit http://www.cell.com/chemistry-biology. To receive media alerts for Chemistry & Biology or other Cell Press journals, contact press@cell.com.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-09-10
Have you ever touched someone else and wondered why his or her skin felt so incredibly soft? Well, now researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 10 present evidence that this experience may often be an illusion.
In a series of studies led by Aikaterini Fotopoulou of the University College London, participants consistently rated the skin of another person as being softer than their own, whether or not it really was softer. The researchers suggest that this phenomenon may exist to ensure that humans are motivated to build social bonds ...
2015-09-10
Those of you who spend hours at the gym with the aim of burning as many calories as possible may be disappointed to learn that all the while your nervous system is subconsciously working against you. Researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 10 have found that our nervous systems are remarkably adept in changing the way we move so as to expend the least amount of energy possible. In other words, humans are wired for laziness.
The findings, which were made by studying the energetic costs of walking, likely apply to most of our movements, ...
2015-09-10
For patients and clinicians alike, it's long been a mystery: why do symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS) seem to get better in the winter and worse in the summer? A group led by Francisco Quintana, PhD, at the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) and collaborators have found an explanation that could lead to a deeper understanding of the disease and more targeted treatment options for patients. By first looking broadly at possible environmental factors and then deeply at preclinical models of MS, the research team found that melatonin ...
2015-09-10
The face of a chimpanzee is decidedly different from that of a human, despite the fact that the apes are our nearest relative in the primate tree. Now researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have begun to pinpoint how those structural differences could arise in two species with nearly identical genetic backgrounds.
The key lies in how genes involved in facial development and human facial diversity are regulated -- how much, when and where the genes are expressed-- rather than dissimilarities among the genes themselves. In particular, the researchers ...
2015-09-10
NEW YORK, NY - A timed vision test that involves rapidly reading numbers off of cards can be a valuable sideline tool for detecting whether a concussion occurred while playing sports, according to a meta-analysis and systematic review led by NYU Langone Medical Center concussion specialists.
Researchers at the NYU Langone Concussion Center reviewed studies that involved athletes who sustained a concussion during sporting activities and found the vision test, known as the King-Devick test, was 86 percent sensitive in detecting whether a concussion had occurred, as confirmed ...
2015-09-10
HOUSTON -- (Sept. 10, 2015) - "Help us find others like Tess." Bo Bigelow's plea jumps off the page of his blog, echoing across the continent from his leafy green home city of Portland, Maine.
When he posted his call to action, all he knew was that his young daughter has a mutation in her USP7 gene and that she has global developmental delay, hip dysplasia and visual impairment caused by her brain (not a problem in her eyes themselves) among other health issues. An article in the New Yorker magazine by Seth Mnookin gave him hope that finding other children with the same ...
2015-09-10
Cancer cells commonly rely on glycolysis, the type of metabolism that does not use oxygen to generate their energy however, researchers from Queen Mary University of London's Barts Cancer Institute and the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) in Madrid have now found that not all cancer cells are alike when it comes to metabolism.
PancSCs can make use of a more efficient form of metabolism, called oxidative phosphorylation or OXPHOS, which does use oxygen. OXPHOS uses a part of the cell called mitochondria and it is this which can be targeted with anti-diabetic ...
2015-09-10
Targeting exhausted immune cells may change the prognosis for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) relapse after a stem cell transplant, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers.
There is currently no effective treatment for this stage of leukemia, and patients have only a 5 percent chance of survival over five years.
AML is a fast-moving cancer of the blood and bone marrow. In patients with AML, the bone marrow produces abnormal white or red blood cells or platelets. Powerful rounds of chemotherapy can damage bone marrow, so many patients are given ...
2015-09-10
While it is known that the incidence and outward symptoms of schizophrenia are strongly influenced by ethnic factors--for instance, patients from Asian ethnicities are more likely to experience visual hallucinations, whereas patients from western cultures and Caucasian ethnicities are more likely to suffer from auditory hallucinations--it was unclear if brain deficits would differ amongst suffers from various ethnic backgrounds. Previous research had indicated that there were neuroanatomical signatures for schizophrenia, but a study titled, "A Neuroanatomical Signature ...
2015-09-10
Marginalized residents of Vancouver's Downtown Eastside are dying at more than eight times the national average, and treatable conditions are the greatest risk factors for mortality, researchers at the University of British Columbia have found.
In research outlined in the British Medical Journal Open, investigators recruited 371 study participants aged 23 to 72 from single room occupancy hotels and the Downtown Community Court. Over the course of nearly four years, 31 participants died--a mortality rate 8.29 times the average for Canadians of the same age and sex. For ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] GI side effects of chemotherapy reduced in mice by targeting gut microbes

