(Press-News.org) Marginalized residents of Vancouver's Downtown Eastside are dying at more than eight times the national average, and treatable conditions are the greatest risk factors for mortality, researchers at the University of British Columbia have found.
In research outlined in the British Medical Journal Open, investigators recruited 371 study participants aged 23 to 72 from single room occupancy hotels and the Downtown Community Court. Over the course of nearly four years, 31 participants died--a mortality rate 8.29 times the average for Canadians of the same age and sex. For participants between the ages of 20 to 59, the mortality rates were even more astounding: more than 10 times the national rate.
When the researchers looked into the associated risk factors for mortality, they did not find any link with HIV or substance addiction. Instead, they found psychosis and hepatitis C-related liver dysfunction to be significantly associated with increased mortality, particularly among participants under the age of 55.
"We were somewhat surprised because most people thinking about the Downtown Eastside think about HIV/AIDS or the possibility of overdosing on opioids like heroin," said Dr. William Honer, professor and head of UBC's Department of Psychiatry and co-author of the study. "Our system is not doing as well in getting treatments out there for psychosis and hepatitis C in this group, and it's interesting that those two illnesses are causing risk for early mortality."
While close to two-thirds of participants living with HIV were receiving antiretroviral treatment, not one of the 57 participants with active hepatitis C infection and related liver dysfunction was receiving treatment. Only one third of the 173 participants diagnosed with psychosis were receiving treatment.
"Psychosis is an extremely prevalent issue among inner city populations and we need to address this," said lead author Andrea Jones, an MD/PhD candidate in mental health and addictions research at UBC. "We need to be ready to detect and treat mental illness in an integrated way that really meets the patients where they're at. We need to improve the detection and treatment of psychosis and hepatitis C in marginalized people across Canada."
BACKGROUND
About the study
About 3,800 people live in subsidized single room occupancy (SRO) housing in the DTES. The Downtown Community Court (DCC) is a partnership of justice, social and health care services, and processes 2,500 cases a year.
Between November 2008 and August 2012, researchers recruited 371 study participants, 81 of them women, from SROs and the DCC. The participants were followed for an average of 3.8 years. Mental and physical illnesses were identified and assessed with psychiatric evaluations, neuropsychological testing and MRI scans, as well as blood tests.
For the 31 participants who died during the study, Coroner's reports were requested, healthcare providers were interviewed, and medical and mental-health related hospital records were obtained for the year prior to death.
INFORMATION:
The study, Mortality from treatable illnesses in marginally housed adults: a prospective cohort study, was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the BC Mental Health and Substance Use Services: http://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/5/8/e008876.full
Scientists believe that about 4 billion years ago, during a period called the Late Heavy Bombardment, the moon took a severe beating, as an army of asteroids pelted its surface, carving out craters and opening deep fissures in its crust. Such sustained impacts increased the moon's porosity, opening up a network of large seams beneath the lunar surface.
Now scientists at MIT and elsewhere have identified regions on the far side of the moon, called the lunar highlands, that may have been so heavily bombarded -- particularly by small asteroids -- that the impacts completely ...
Researchers from Northwestern University and Yale University have developed a user-friendly technology to help scientists understand how proteins work and fix them when they are broken. Such knowledge could pave the way for new drugs for a myriad of diseases, including cancer.
The human body has a nifty way of turning its proteins on and off to alter their function and activity in cells: phosphorylation, the reversible attachment of phosphate groups to proteins. These "decorations" on proteins provide an enormous variety of function and are essential to all forms of life. ...
Alexandria, VA - In a study covered by EARTH Magazine, geoscientists identified fossils that are helping close the 15-million-year period in the fossil record known as Romer's Gap - the time from when fish showed early evidence of arms and legs until we definitively see four-legged land animals.
Scientists have been wondering for decades whether Romer's Gap exists because tetrapod fossils from that time were not preserved, or because their fossils simply have not been discovered yet. These new fossils are starting to close the gap and change the way scientists interpret ...
IVF cycles using embryos that have been frozen and thawed are just as successful as fresh embryos according to a new UNSW report.
The Assisted Reproductive Technology in Australia and New Zealand 2013 report, by UNSW's National Perinatal Epidemiology and Statistics Unit (NPESU), shows in the five years to 2013, fresh embryo IVF cycles that resulted in a baby remained stable at around 23%.
However, there has been a more than 25% increase in the birth rate for frozen embryo transfers in the last five years, rising from 18% to 23%.
The report also found a growing number ...
Patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (sinus infection) and obstructive sleep apnea report a poor quality of life, which is substantially improved following endoscopic sinus surgery, according to a study published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
A growing body of literature has highlighted the important links between quality of life (QOL), sleep, and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), such that disease severity has been correlated with worse QOL and patients with worse QOL have poor sleep. It is possible that CRS propagates sleep dysfunction through many ...
This news release is available in German.
The goal of brain simulations using supercomputers is to understand the processes in our brain. This is a mammoth task: the activity of an estimated 100 billion nerve cells - also known as neurons - must be represented . It is also a task that has historically been impossible because even the most powerful computers in the world can only simulate one percent of the nerve cells due to memory constraints. For this reason, scientists have turned to downscaled models. However, this downscaling is problematic, as shown by a recent ...
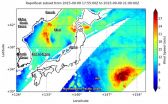
Japan has experienced large rainfall that caused flooding and large evacuations as a result of two weather systems. NASA's GPM Core satellite measured rainfall as NASA's RapidScat saw Etau and Typhoon Kilo on either side of Japan.
Over the past week Japan has experienced extreme rainfall that resulted in flooding, landslides and many injuries. A nearly stationary front that was already moving over Japan caused much of the rain but Tropical Storm Etau also interacted with the front and magnified the scale of the deluge.
Heavy rainfall led to the evacuation of over one ...
NEW YORK, NY (September 10, 2015)--Researchers have discovered why long-term use of L-DOPA (levodopa), the most effective treatment for Parkinson's disease, commonly leads to a movement problem called dyskinesia, a side effect that can be as debilitating as Parkinson's disease itself.
Using a new method for manipulating neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's, a Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) research team found that dyskinesia arises when striatonigral neurons become less responsive to GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter. This suggests that it may be possible ...
Alexandria, VA - The American Geosciences Institute's (AGI) is pleased to announce the release of a community consensus statement on access and inclusion of geoscientists with disabilities. This statement was inspired by the 2014 AGI Leadership Forum, which brought together the Executive Directors and Presidents of AGI's Member Societies to discuss the issue of access and inclusion of persons with disabilities in the geosciences.
The meeting was facilitated by the Executive Director of the International Association for Geoscience Diversity (IAGD) Christopher Atchison, ...
NASA's RapidScat instrument analyzed the sustained surface winds of Tropical Storm Henri on Sept. 8 as the storm was intensifying.
When the International Space Station flew over Tropical Depression 8 in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean on September 8 at 1p.m. EDT, NASA's RapidScat instrument aboard captured data on the storm's surface winds. RapidScat showed that there were tropical-storm-force winds north and east of the center near 27 meters per second (60.4 mph/97.2 kph). However, sustained winds on the west and southwestern quadrants were near 12 meters per second (26.8 ...