(Press-News.org) Marijuana use among American high school students is significantly lower today than it was 15 years ago, despite the legalization in many states of marijuana for medical purposes, a move toward decriminalization of the drug and the approval of its recreational use in a handful of places, new research suggests.
The Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health researchers say, however, that marijuana use is significantly greater than the use of other illegal drugs, with 40 percent of teens in 2013 saying they had ever smoked marijuana. That number was down from 47 percent in 1999 but up from 37 percent in 2009. By contrast, just three percent had ever tried methamphetamines in 2013 as compared to nine percent in 1999.
The findings, published online this month in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence, also suggest that a gender gap in marijuana use -- where boys outnumbered girls as users of the drug -- is shrinking, with males and females now using marijuana at similar rates. And while white and black teens once used marijuana at similar rates, now blacks report using the drug more often.
Marijuana policy has undergone significant changes over the past 20 years. Since 1996, 34 states have passed legislation removing criminal sanctions for medical use of marijuana. Eleven states have passed laws decriminalizing possession of small amounts of marijuana, adding to nine that passed such laws in the late 1970s. Four states have passed laws allowing for the recreational use of marijuana for people over 21.
"People have been very quick to say that marijuana use is going up and up and up in this country, particularly now that marijuana has become more normalized," says study leader Renee M. Johnson, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor in the Department of Mental Health at the Bloomberg School. "What we are seeing is that since 1999 -- three years after medical marijuana was first approved -- the rates of marijuana use have actually fallen. But we will be watching those states where recreational marijuana use has been legalized to see if that leads to increased use among teens."
Johnson says she isn't sure why rates of marijuana use have fallen since 1999. The 1980s and the early 1990s were a time when it was very difficult to obtain marijuana due to a federal crackdown on illicit drugs and strong anti-drug education programs, such as the "just say no" campaign. But use shot back up in the late 1990s. While rates of use have been falling since 1999, they started to rise again in 2009. Time will tell, she says, whether the recent uptick in marijuana use is just a statistical blip or a sign that greater availability of the drug is leading to a reversal of the decade-long downward trend.
Colorado, Oregon, Alaska, Washington and the District of Columbia have laws that legalize some recreational use of marijuana, which have only been passed in recent years. The longer those laws are in place, Johnson says, the more likely there could be an effect on marijuana use among teens -- even though it is technically illegal to use pot under age 21. Johnson and her colleagues are studying the laws in Colorado and Washington state, whose laws went into effect November 2012 and over 2013, respectively.
Johnson and her colleagues examined data from the National Youth Risk Behavior Survey, a biennial school-based survey of students in grades nine through 12, which gathered information from more than 115,000 adolescents throughout the U.S. They analyzed information from 1999 to 2013. The survey has been conducted by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention since 1990.
Use of other illegal drugs including hallucinogens and cocaine has also fallen throughout the time period, as has use of alcohol and cigarettes among teens. In 2013, 41.1 percent of the teens surveyed said they had smoked cigarettes in their lifetime, while 40.7 percent said they had used marijuana in their lifetime. The rates of cigarette smoking are down from 70.4 percent in 1999. Those who said they had ever tried alcohol fell from 81 percent in 1999 to 66.2 percent in 2013.
The survey found that in 1999, 51 percent of boys and 43 percent of girls had ever used marijuana, and by 2013, 42 percent of boys and 39 of girls say they had used it in their lifetimes. In 1999, 29 percent of both white and black teens reported having used marijuana; whereas in 2013, 29 percent of black teens and 20 percent of white teens had used the drug.
Even though marijuana use is lower today than it was 15 years ago, Johnson says it may be time to promote programs that educate high school students about the specific harms of marijuana use -- something that mostly hasn't been done. The focus has been more on preventing teens from using tobacco and alcohol.
"We've done a really good job in public health of alcohol and tobacco use prevention," she says. "We haven't done the same with marijuana. We would do well to follow the lessons learned from those programs, which have been pretty successful."
INFORMATION:
"Past 15-Year Trends in Adolescent Marijuana Use: Differences by Race/Ethnicity & Sex" was written by Renee M. Johnson; Brian Fairman; Tamika Gilreath; Ziming Xuan; Emily Rothman; Taylor Parnham and Debra Furr-Holden.
The research was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health's National Institute on Drug Abuse (K01DA031738 and T32DA007292) and National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (K01AA017630 and R01AA023376).
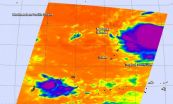
The twentieth tropical depression of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean formed early on September 14 and became a tropical storm the next day, triggering a tropical storm watch. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the low pressure area as it was consolidating and saw powerful thunderstorms circling the center.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathers data in infrared light that provides information about temperatures. The colder the cloud top temperature, the higher the storms are in the troposphere (because the higher ...
TORONTO, Sept. 15, 2015 - A commonly prescribed drug for heart disease may do more good than previously thought. Researchers at York University have found that beta-blockers may prevent further cell death following a heart attack and that could lead to better longer term patient outcomes.
Human hearts are unable to regenerate. When cardiac muscle cells die during and immediately after a heart attack, there is no way to bring the organ back to full health, which contributes to the progression towards eventual heart failure.
Preventing the cells from dying in the first ...
Millions of years ago, our primate ancestors turned from trees and shrubs to search for food on the ground. In human evolution, that has made all the difference.
The shift toward a grass-based diet marked a significant step toward the diverse eating habits that became a key human characteristic, and would have made these early humans more mobile and adaptable to their environment.
New evidence just published by a research team led by a Johns Hopkins University scientist shows that this significant shift took place about 400,000 years earlier than experts previously ...
Washington, DC - September 15, 2015 - For years, researchers have known that the human skin is home to a diverse community of microorganisms, collectively known as the skin microbiome. Now a new study has shown that individuals with a particular skin microbiome can effectively clear bacteria that cause chancroid, a sexually transmitted disease common in the developing world that has been linked to enhanced HIV transmission. The study, published in the September 15th issue of mBio, is the first prospective study to show that the skin microbiome can influence the outcomes ...
Experts should take note of local knowledge and beliefs when making plans about how to help people in vulnerable regions cope with the impacts of climate change. This will ensure that such interventions are money well spent, and are not culturally insensitive, advises Conor Murphy of Ireland's Maynooth University. Together with an interdisciplinary research team from universities in Malawi, Zambia and Ireland he interviewed community members in rural Malawi and Zambia to assess how well they are able to adapt to the way they produce food within the context of shifting belief ...
A novel radiopharmaceutical probe developed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has the potential of providing physicians with information that could save the lives of patients with ischemic stroke or pulmonary embolism - conditions caused when important blood vessels are blocked by a clot that has traveled from another part of the body. In a report that will appear in the October issue of the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology and has been published online, the MGH team describes using this new probe to conduct full-body scans in an animal model. ...
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 15, 2015 - Nearly 1 in 5 recently surveyed high school seniors report having smoked tobacco from a hookah in the past year, and more than a third of them reported smoking hookahs often enough to be considered regular users, an analysis led by the University of Pittsburgh Center for Research on Media, Technology, and Health (CRMTH) revealed.
The findings, published online and scheduled for a coming print issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, add to evidence that hookah use among adolescents is increasing in both prevalence and frequency. ...
In recent years, there has been an increase in emergence and use of a variety of new drugs, so-called "novel psychoactive substances" (NPS) in the US and worldwide. However, there is little published survey data estimating the prevalence of use in the US. Media reports about use of new drugs such as "Spice" ("synthetic marijuana") and "bath salts" such as "Flakka" are now common, yet very few health surveys ask about use of such drugs.
A new study, published in Drug and Alcohol Dependence by researchers affiliated with New York University's Center for Drug Use and HIV ...
Montreal, September 15, 2015 -- With the federal election around the corner, child care has become a major ballot issue. While every party has its own idea of how best to offset the costs of raising children, no one is looking at how we perceive and value those who provide the education and care.
Concordia researcher Sandra Chang-Kredl wants that to change. In a paper recently published in the Journal of Media & Cultural Studies, she writes that "invariably, the focus of the debate is on the children's needs, the parents' needs and society's needs. The educator is rarely ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- Energy companies used nearly 250 billion gallons of water to extract unconventional shale gas and oil from hydraulically fractured wells in the United States between 2005 and 2014, a new Duke University study finds.
During the same period, the fracked wells generated about 210 billion gallons of wastewater.
Large though those numbers seem, the study calculates that the water used in fracking makes up less than 1 percent of total industrial water use nationwide.
While fracking an unconventional shale gas or oil well takes much more water than drilling ...