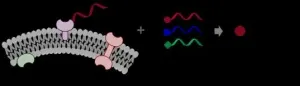
Switching DNA functions on and off by means of light
Biochemists use protein engineering to transfer photocaging groups to DNA
2021-01-02
(Press-News.org) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the basis of life on earth. The function of DNA is to store all the genetic information, which an organism needs to develop, function and reproduce. It is essentially a biological instruction manual found in every cell. Biochemists at the University of Münster have now developed a strategy for controlling the biological functions of DNA with the aid of light. This enables researchers to better understand and control the different processes which take place in the cell - for example epigenetics, the key chemical change and regulatory lever in DNA. The results have been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Background and methodology
The cell's functions depend on special molecules, the enzymes. Enzymes are proteins, which carry out chemical reactions in the cell. They help to synthesize metabolic products, make copies of the DNA molecules, convert energy for the cell's activities, change DNA epigenetically and break down certain molecules. A team of researchers headed by Prof. Andrea Rentmeister from the Institute of Biochemistry at the University of Münster used a so-called enzymatic cascade reaction in order to understand and track these functions better. This sequence of successive reaction steps involving different enzymesmakes it possible to transfer so-called photocaging groups - chemical groups, which can be removed by means of irradiation with light - to DNA. Previously, studies had shown that only small residues (small modifications such as methyl groups) could be transferred very selectively to DNA, RNA (ribonucleic acid) or proteins. "As a result of our work, it is now possible to transfer larger residues or modifications such as the photocaging groups just mentioned," explains Nils Klöcker, one of the lead authors of the study and a PhD student at the Institute of Biochemistry. Working together with structural biologist Prof. Daniel Kümmel, who also works at the Institute of Biochemistry, it was also possible to explain the basis for the changed activity at a molecular level.
Using so-called protein engineering - a method for which a Nobel prize was awarded in 2018 - the Münster researchers engineered one enzyme in the cascade, making it possible to switch DNA functions on and off by means of light. With the aid of protein design, it was possible to expand the substrate spectrum of enzymes - in this case, methionine adenosyltransferases (MATs). In their work, the researchers examined two MATs. The modifications carried out offer a starting point for developing other MATs with an expanded substrate spectrum. "Combining these MATs with other enzymes has potential for future cellular applications. This is an important step for implementing in-situ generated, non-natural substances for other enzymes in epigenetic studies," says Andrea Rentmeister.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-02
A research team led by Dr Xiaoyu LI from the Research Division for Chemistry, Faculty of Science, in collaboration with Professor Yizhou LI from School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chongqing University and Professor Yan CAO from School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University in Shanghai has developed a new drug discovery method targeting membrane proteins on live cells.
Membrane proteins play important roles in biology, and many of them are high-value targets that are being intensively pursued in the pharmaceutical ...
2021-01-02
New research produced jointly by The Swire Institute of Marine Science (SWIMS), Faculty of Science, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), and The Nature Conservancy (TNC), published recently in the scientific journal Restoration Ecology, shows the enormous potential of restoring lost oyster reefs, bringing significant environmental benefits.
Benefits of oyster reefs
Hong Kong was once home to thriving shellfish reefs, but due to a combination of factors including over-exploitation, coastal reclamation and pollution, shellfish populations have declined drastically. Restoring oyster reefs along urbanized ...
2021-01-02
Angiosarcomas are clinically aggressive tumours that are more prevalent in Asian populations
Study led by Singapore clinician-scientists has found a way to classify angiosarcomas into three subtypes, allowing for more targeted treatment, better outcomes for patients and the development of new therapies
Findings were published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation in October this year
Singapore, 29 December 2020 - A new study led by clinician-scientists from the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), with collaborators from research institutions worldwide, has found that angiosarcomas have unique genomic and immune profiles which allow them ...
2021-01-02
A fast, green and one-step method for producing porous carbon spheres, which are a vital component for carbon capture technology and for new ways of storing renewable energy, has been developed by Swansea University researchers.
The method produces spheres that have good capacity for carbon capture, and it works effectively at a large scale.
Carbon spheres range in size from nanometers to micrometers. Over the past decade they have begun to play an important role in areas such as energy storage and conversion, catalysis, gas adsorption and storage, drug and enzyme delivery, and water treatment.
They are also at the heart of carbon capture technology, ...
2021-01-02
Researchers at the University of Turku have discovered what type of neural mechanisms are the basis for emotional responses to music. Altogether 102 research subjects listened to music that evokes emotions while their brain function was scanned with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The study was carried out in the national PET Centre.
The researchers used a machine learning algorithm to map which brain regions are activated when the different music-induced emotions are separated from each other.
- Based on the activation of the auditory and motor cortex, we were able to accurately predict whether the research subject was listening ...
2021-01-02
In a series of commissions awarded by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) to the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), the question is whether for certain surgical procedures, a correlation can be shown between the volume of services provided per hospital and the quality of treatment results. IQWiG's rapid report on heart transplantations is now available.
According to the findings, a positive correlation can be inferred between the volume of services and the quality of treatment results for heart transplantations in adults: In hospitals with larger case volumes, fewer of the transplanted patients die, both in timely association with the intervention ...
2021-01-02
Quantum computer: One of the obstacles for progress in the quest for a working quantum computer has been that the working devices that go into a quantum computer and perform the actual calculations, the qubits, have hitherto been made by universities and in small numbers. But in recent years, a pan-European collaboration, in partnership with French microelectronics leader CEA-Leti, has been exploring everyday transistors--that are present in billions in all our mobile phones--for their use as qubits. The French company Leti makes giant ...
2021-01-02
Imaging techniques enable a detailed look inside an organism. But interpreting the data is time-consuming and requires a great deal of experience. Artificial neural networks open up new possibilities: They require just seconds to interpret whole-body scans of mice and to segment and depict the organs in colors, instead of in various shades of gray. This facilitates the analysis considerably.
How big is the liver? Does it change if medication is taken? Is the kidney inflamed? Is there a tumor in the brain and did metastases already develop? ...
2021-01-02
December 28, 2020 - Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment, which involves injecting a small amount of a patient's own blood to release various growth factors from platelets, continues to increase in popularity. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons has tracked the procedure since 2015 and reports a 25 percent increase in cosmetic PRP use in the last four years.
That increase in popularity could in part trace back to celebrities extolling the procedure's cosmetic benefits. Yet with so much information coming from so many different sources about the treatment's ...
2021-01-02
Cells, the basic unit of life, are surrounded by a limiting membrane called the plasma membrane. Inside cells, there are various membrane-bounded organelles, each of which has various and distinctive functions. How these organelles, which individually boast different functions, have been developed during evolution remains unknown. This phenomenon has fascinated many researchers.
In the study published in Nature Communications, the evolutionary relationship between two different organelles in liverwort cells has been revealed: the cell plate, which divides ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Switching DNA functions on and off by means of light
Biochemists use protein engineering to transfer photocaging groups to DNA