Risk factors associated with all-cause 30-day mortality in nursing home residents with COVID-19
2021-01-04
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: In this observational study of 5,256 U.S. nursing home residents with COVID-19, increased age, male sex and impaired cognitive and physical function were independent risk factors for all-cause 30-day mortality.
Authors: Orestis A. Panagiotou, M.D., Ph.D., of the Brown University School of Public Health in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7968)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and commentary are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7968?guestAccessKey=debfbb69-0f1c-45b8-8213-4fbec3178bda&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=010421
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: The findings of a survey study using data from California suggests the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with increases in self-reported worry about violence for oneself and others, increased firearm acquisition and changes in firearm storage practices.
Authors: Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, Ph.D., M.P.H., University of California Firearm Violence Research Center and Violence Prevention Research Program, Department of Emergency Medicine, University of California Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding ...
2021-01-04
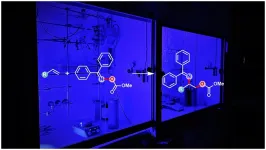
Whether in beta-blockers to treat high blood pressure or in natural products: So-called vicinal aminoalcohols are high-quality organic compounds that are found in many everyday products. However, their production is difficult. For a long time, chemists are trying to develop efficient methods of synthesizing them. In their recent study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, scientists led by Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius of Münster University have found a solution for the production of a special variant of aminoalcohols. "The new method helps to study the properties of the substance and to find applications for these ...
2021-01-04
Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, Princeton researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount data wireless systems can transmit.
The programmable surface, called a metasurface, allows engineers to control and focus transmissions in the terahertz band of the electromagnetic spectrum. Terahertz, a frequency range located between microwaves and infrared light, can transit much more data than current, radio-based wireless systems. With fifth generation (5G) communications systems offering speeds 10 to 100 times faster than the previous generation, demand for bandwidth is ever increasing. Facing the emergence of technologies such as self-driving cars and augmented reality ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: Changes were assessed in abortions performed and at what gestational age following a Texas order postponing nonmedically necessary surgeries due to the COVID-19 pandemic compared with abortions performed during the same months in 2019.
Authors: Kari White, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24096)
Editor's Note: The articles includes conflict of interest and funding/support ...
2021-01-04
What The Viewpoint Says: The rapid spread of scientific misinformation on social media platforms throughout the COVID-19 pandemic is discussed in this Viewpoint, which also proposes strategies to counteract its adverse effects including surveillance of digital data and partnering with trusted messengers to engage the public and advance scientifically sound public health measures.
Authors: Raina M. Merchant, M.D., M.S.H.P., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24514)
Editor's Note: The ...
2021-01-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - From an observatory high above Chile's Atacama Desert, astronomers have taken a new look at the oldest light in the universe.
Their observations, plus a bit of cosmic geometry, suggest that the universe is 13.77 billion years old - give or take 40 million years. A Cornell University researcher co-authored one of two papers about the findings, which add a fresh twist to an ongoing debate in the astrophysics community.
The new estimate, using data gathered at the National Science Foundation's Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), matches the one provided by the standard ...
2021-01-04
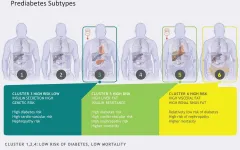
All prediabetes is not the same: in people in the preliminary stages of type 2 diabetes, there are six clearly distinguishable subtypes, which differ in the development of the disease, diabetes risk, and the development of secondary diseases. This is shown in a study by the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, Tübingen University Hospital and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The results have now been published in Nature Medicine. The new classification can help in the future to prevent the manifestation of diabetes ...
2021-01-04
A sugar-binding protein could fuel terrible inflammation and worsen sepsis, a disease that kills more than 270,000 people every year in the US alone, reports a team of researchers led by UConn Health in the 4 January issue of Nature Immunology.
Sepsis is caused mostly by bacterial infections. The immune system runs out of controls and triggers a cytokine storm, a condition in which inflammation-causing proteins flood the blood. Organs may break down, and death often follows.
Other diseases can also cause cytokine storms; medical historians believe cytokine storms were behind the lethality of the ...
2021-01-04
If you type into a search engine - "why do men have to wait before having sex again?" - you will very quickly come across Prolactin. This little hormone is thought to be involved in hundreds of physiological processes in the body. Among them is the male post-ejaculatory refractory period. This period begins when a male ejaculates and ends when he recovers his sexual capacity.
If you search a bit more, you'll see that this theory has even led to the development of so called "treatments". These promise to shorten the length of a person's refractory period by reducing their body's prolactin levels.
Well, here is some bad news for anyone who has bought any such merchandise. A new study in mice by scientists at the Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown ...
2021-01-04
A research study at the University of Chicago has found that in pregnancy, while the T cell response to a fetus becomes tolerant to allow for successful pregnancy, the part of the immune system that produces antibodies (known as the humoral response) becomes sensitized, creating memory B cells that can later contribute to the rejection of a transplanted organ.
The results help to clarify why it is that the immune system can tolerate a fetus during pregnancy, but later may be more likely to become sensitized to and reject an organ transplant. The study was published on January 4, 2021 in the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Risk factors associated with all-cause 30-day mortality in nursing home residents with COVID-19