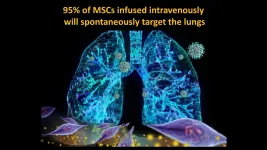
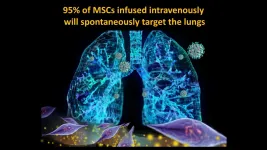
(Press-News.org) Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last April, was initiated by The Cure Alliance, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization of research scientists founded ten years ago by Dr. Ricordi for scientists around the world to share knowledge and accelerate cures of all diseases. At the start of the pandemic, all focus pivoted to ending suffering caused by COVID-19. Dr. Ricordi created a "mini-Manhattan project," the result of which has yielded this important new weapon in the arsenal against COVID-19, especially during this critical time when distribution of the new vaccines is slower than anticipated and the infection rate and death toll are still surging.
The SCTM paper describes findings from 24 patients hospitalized at University of Miami Tower or Jackson Memorial Hospital with COVID-19 who developed severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS), a dangerous and often fatal complication marked by severe inflammation and fluid buildup in the lungs. Each patient received two infusions of either mesenchymal stem cells or a placebo, given days apart.
"It was a double-blind study. Neither doctors nor patients knew who received the treatment, who got the placebo," said Dr. Ricordi, the lead investigator.
At one month,100% of patients ( END
UC-MSC infusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
'Like smart bomb technology to the lung,' randomized trial shows
2021-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UC-MSC transfusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases
2021-01-05
Dr. Camilo Ricordi, director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, and his team of international collaborators are reporting the results of a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the most severe COVID-19 patients. Dr. Ricordi's peer-reviewed paper has just been published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM) January 2021.
The clinical trial, authorized by the FDA last April, was initiated by The Cure Alliance, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization of research scientists founded ten years ago by Dr. Ricordi for scientists ...
A plant's way to its favorite food
2021-01-05
Like any other plant, Arabidopsis thaliana or mouse-ear cress, needs nitrogen to survive and thrive. But, like maize, beans and sugar beet, it prefers nitrogen in the form of nitrate, growing better on nitrate rich soil. Whereas, pine and rice for example preferentially grow on ammonium nutrition, another form of the key macronutrient nitrogen. If the concentration or the availability of the different forms of nitrogen fluctuate, plants have to adapt quickly. "One of the most important questions is, what is the role of plant hormones in adaptation to the nitrogen availability? How do the machineries within a plant cope with their changing environment?" asks Eva Benková, developmental biologist and Professor at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria.
Finding the balance
In ...
University of Miami leads groundbreaking trial for COVID-19 treatment
2021-01-05
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine researchers led a unique and groundbreaking randomized controlled trial showing umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cell infusions safely reduce risk of death and quicken time to recovery for the severest COVID-19 patients, according to results published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine in January 2021.
The study's senior author, Camillo Ricordi, M.D., director of the Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) and Cell Transplant Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, said treating COVID-19 with mesenchymal stem cells makes sense.
Results: treatment group vs. ...
3D-printed smart gel changes shape when exposed to light
2021-01-05
Inspired by the color-changing skin of cuttlefish, octopuses and squids, Rutgers engineers have created a 3D-printed smart gel that changes shape when exposed to light, becomes "artificial muscle" and may lead to new military camouflage, soft robotics and flexible displays.
The engineers also developed a 3D-printed stretchy material that can reveal colors when light changes, according to their study in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Their invention is modeled after the amazing ability of cephalopods such as cuttlefish, octopuses and squids to change the color and texture of their soft skin for camouflage and communication. This is achieved by the ...
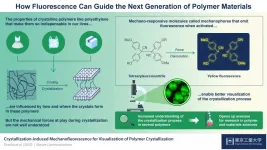
Mechanophores: Making polymer crystallization processes crystal clear
2021-01-05
In modern times, manufacturers produce highly specialized materials for a wide array of uses, called polymers. Polymers have a variety of purposes owing to their versatile properties, ranging from being used in construction due to their high tensile strength and resistance to manufacturing plastic bags that require more lightweight, flexible materials, such as nylon or polyethene.
These differences between the properties of different polymers stems from their internal structure. Polymers are made up of long chains of smaller sub-units, called "monomers." Crystallization occurs when crystalline polymers are melted, then cooled down slowly, which enables the chains to organize themselves into neatly arranged ...
Uncovering how grasslands changed our climate
2021-01-05
Grasslands are managed worldwide to support livestock production, while remaining natural or semi-natural ones provide critical services that contribute to the wellbeing of both people and the planet. Human activities are however causing grasslands to become a source of greenhouse gas emissions rather than a carbon sink. A new study uncovered how grasslands used by humans have changed our climate over the last centuries.
Grasslands are the most extensive terrestrial biome on Earth and are critically important for animal forage, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. They absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO2), and emit methane (CH4) from grazing livestock and nitrous oxide (N2O) from soils, especially when manure or ...
Increase in pleasurable effects of alcohol over time can predict alcohol use disorder
2021-01-05
A new study out of the University of Chicago Medicine following young adult drinkers for 10 years has found that individuals who reported the highest sensitivity to alcohol's pleasurable and rewarding effects at the start of the trial were more likely to develop an alcohol use disorder (AUD) over the course of the study.
Moreover, when retested on their responses 10 years later, those who became alcoholics had the highest levels of alcohol stimulation, liking and wanting - and these were heightened compared to their baseline with no signs of tolerance to these pleasurable effects.
The research, published on Jan. 5 in the American Journal of Psychiatry, followed a ...
Eurasian eagle owl diet reveals new records of threatened giant bush-crickets
2021-01-05
Bird diets provide a real treasure for research into the distribution and conservation of their prey, such as overlooked and rare bush-cricket species, point out scientists after studying the diet of the Eurasian Eagle Owl (Bubo bubo) in southeastern Bulgaria.
In their END ...
The true cost of chemotherapy
2021-01-05
Chemotherapy for breast cancer costs the UK economy more than £248 million annually, including 'out-of-pocket' personal costs of more than £1,000 per patient - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today is the first to investigate the total non-healthcare cost of chemotherapy to the UK.
It includes the cost of lost productivity, work absence, and personal costs such as paying for transport and parking for treatment, the cost of wigs and new bras, and over the counter medications.
The UEA research team say that better targeting of treatment could help avoid placing unnecessary costs upon patients, their caregivers and wider society.
Prof Richard Fordham, from UEA's ...
State laws promoting flu vaccination for hospital workers may help prevent deaths from flu and pneum
2021-01-05
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. State laws promoting flu vaccination for hospital workers may help prevent deaths from flu and pneumonia
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-0413
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
Research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] UC-MSC infusion helps repair COVID-19 damage in severe cases'Like smart bomb technology to the lung,' randomized trial shows