Identifying Canada's key conservation hot spots highlights problem
First of its kind mapping of most important places for freshwater, recreation and carbon storage provides tool for conservation decisions
2021-01-05
(Press-News.org) To stop biodiversity loss, Canada recently committed to protecting 30% of its land and sea by 2030. But making conservation decisions about where to locate new protected areas is complicated. It depends on data both about biodiversity and about a range of benefits (e.g. freshwater, climate regulation, recreation) that people get from nature. Surprisingly, despite the size of the country, new mapping suggests that less than 1% of Canada's land (0.6% of total area or approximately 56,000 km2) is a hot spot, providing all these benefits in one place. Moreover, the study published today in Environmental Research Letters suggests that some of the most critical areas where people receive these key benefits from nature do not occur within currently protected areas and may be threatened by current or future natural resource extraction.
"This research is especially timely as it should help all levels of government design conservation plans that ensure that both people and nature thrive," says Elena Bennett, from McGill University's Bieler School of the Environment and one of the authors in a multi-institutional team that included researchers from Universities of British Columbia, McGill and Carleton and from the Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative (Y2Y).
Identifying key areas of Canada that provide ecosystem services
The paper highlights multiple places across Canada as important for one or more ecosystem services that include providing freshwater (such as for irrigation, drinking or hydroelectricity), climate regulation (as in the case of forests and wetlands that act as carbon sinks), or for nature-based human recreation. These include the forests of British Columbia and the Hudson Bay lowlands for above- and below-ground carbon; north-central Quebec, the eastern mountains of British Columbia, the eastern slopes of the Rockies in Alberta, and the north shore of Lake Superior for freshwater; and the Rocky Mountains, eastern Ontario, and southern Quebec for nature-based recreation.
"Canada is grappling with where and how to protect nature. Just one example of how this research could be used is in western Alberta. Our research shows that the Eastern Slopes of the Rockies is one of the most important places across the whole country for its combination of freshwater, carbon storage, and recreation -- not to mention important wildlife habitat -- and yet the same area is at risk from open-pit coal mining and other threats," says Dr. Aerin Jacob, co-author and conservation scientist, at the Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative.
A question of both supply and demand
Crucially and unusually, the mapping methods included both nature's capacity to supply these benefits as well as the human access and demand for them.
"Most research that studies the benefits people get from nature only evaluates where nature has the potential to supply these benefits. For example, where rain falls. Because our work also models and maps human access and demand, we could identify where people actually receive these benefits from nature. For example, the key locations producing water that people use for drinking, farming, or hydroelectricity," says Dr. Matthew Mitchell, lead author and Research Associate, Institute for Resources, Environment, and Sustainability, University of British Columbia. "Governments need to know both of these things in order to take action that protects human well-being. Research like this can help society do that."
INFORMATION:
Media:
To explore maps showing the results:
https://forbasin.forestry.ubc.ca/ES_CAN/
High resolution photos are available for download.
To read: "Identifying key ecosystem service providing areas to inform national-scale conservation planning" by Matthew G.E. Mitchell et al in Environmental Research Letters
DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/abc121.
About McGill University
Founded in Montreal, Quebec, in 1821, McGill University is Canada's top ranked medical doctoral university. McGill is consistently ranked as one of the top universities, both nationally and internationally. It is a world-renowned institution of higher learning with research activities spanning two campuses, 11 faculties, 13 professional schools, 300 programs of study and over 40,000 students, including more than 10,200 graduate students. McGill attracts students from over 150 countries around the world, its 12,800 international students making up 31% of the student body. Over half of McGill students claim a first language other than English, including approximately 19% of our students who say French is their mother tongue.
Contacts:
Katherine Gombay
McGill Media Relations Office
1-514-717-2289
katherine.gombay@mcgill.ca
http://www.mcgill.ca/newsroom/
http://twitter.com/McGillU
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-05
Leipzig. The transition from the Medieval Warm Period to the Little Ice Age was apparently accompanied by severe droughts between 1302 and 1307 in Europe; this preceded the wet and cold phase of the 1310s and the resulting great famine of 1315-21. In the journal Climate of the Past, researchers from the Leibniz Institutes for the History and Culture of Eastern Europe (GWZO) and Tropospheric Research (TROPOS) write that the 1302-07 weather patterns display similarities to the 2018 weather anomaly, in which continental Europe experienced exceptional heat and drought. Both the medieval and recent weather patterns resemble the stable weather patterns that have occurred more frequently since the 1980s due to the increased warming of the Arctic. ...
2021-01-05
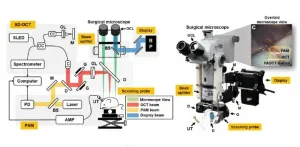
A clear view of anatomical structures is vital for the success of surgery--especially in microsurgery where narrow anatomical cavities or proximity to vulnerable organs and tissues can pose significant risks to patient health. The surgical microscope has evolved to become a powerful tool for improving surgical visualization.
A END ...
2021-01-05
TROY, N.Y. -- A loss of enzymatic processes within the body can increase a person's risk of bone fracture. This new insight was recently published in eLife by an international team of scientists and engineers led by Deepak Vashishth, the director of the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
Enzymatic processes are essential to any number of chemical reactions that occur within the body, including the production of the extracellular matrix within bone that is critical for mechanical support. Phosphorylation -- one of those key enzymatic processes -- is the attachment of a phosphoryl to a protein, and is critical for ...
2021-01-05
Worldwide, marine megafauna are at risk of extinction due to climate change, habitat loss, pollution, overhunting, population fragmentation, and hybridization with related species in areas disturbed by humans. Genetic studies can help determine the conservation status of marine animals, identifying threats to species conservation and informing interventions and policies, such as the protection of diversity hotspots or corridors for gene flow.
In a new study in Frontiers in Marine Science, researchers for the first time measured genetic diversity in manatees ...
2021-01-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A small portion of scientific papers are retracted for research that is in error or fraudulent. But those papers can continue to be cited by other scientists in their work, potentially passing along the misinformation from the retracted articles.
Jodi Schneider, a professor of information sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign who studies scholarly publications and how information gets used, is considering how scientific journals can better communicate about retracted articles. In a new study published in the ...
2021-01-05
Most of the mangrove forests on the coasts of Oman disappeared about 6,000 years ago. Until now, the reason for this was not entirely clear. A current study of the University of Bonn (Germany) now sheds light on this: It indicates that the collapse of coastal ecosystems was caused by climatic changes. In contrast, falling sea level or overuse by humans are not likely to be the reasons. The speed of the mangrove extinction was dramatic: Many of the stocks were irreversibly lost within a few decades. The results are published in the journal Quaternary Research.
Mangroves are trees that occupy a very special ecological niche: They grow in the so-called tidal range, meaning coastal areas that are ...
2021-01-05
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- If everything moved 40,000 times faster, you could eat a fresh tomato three minutes after planting a seed. You could fly from New York to L.A. in half a second. And you'd have waited in line at airport security for that flight for 30 milliseconds.
Thanks to machine learning, designing materials for new, advanced technologies could accelerate that much.
A research team at Sandia National Laboratories has successfully used machine learning -- computer algorithms that improve themselves by learning patterns in data -- to complete cumbersome materials science calculations more than 40,000 times faster than normal.
Their results, published Jan. 4 in END ...
2021-01-05
Australian research has identified a new mechanism in which prostate cancer cells can 'switch' character and become resistant to therapy.
These findings, just published in Cell Reports, are an important development in unravelling how an aggressive subtype of prostate cancer, neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC), develops after hormonal therapies.
It is well established that some tumours show increased cellular 'plasticity' in response to new or stressful conditions, such as cancer therapy, says lead researcher Associate Professor Luke Selth, from the Flinders ...
2021-01-05
What The Study Did: Data from public health surveillance of reported COVID-19 cases and seroprevalence surveys were used in this observational study that reports an estimated 46.9 million SARS-CoV-2 infections, 28.1 million symptomatic infections, 956,174 hospitalizations and 304,915 deaths occurred in the U.S. through November 15, 2020.
Authors: Frederick J. Angulo, D.V.M., Ph.D., of Medical Development and Scientific/Clinical Affairs of Pfizer Vaccines, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33706)
Editor's ...
2021-01-05
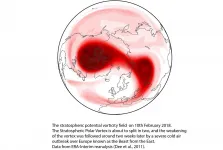
A new study led by researchers at the Universities of Bristol, Exeter, and Bath helps to shed light on the winter weather we may soon have in store following a dramatic meteorological event currently unfolding high above the North Pole.
Weather forecasting models are predicting with increasing confidence that a sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event will take place today, 5 January 2021.
The stratosphere is the layer of the atmosphere from around 10-50km above the earth's surface. SSW events are some of the most extreme of atmospheric phenomena and can see polar stratospheric temperature increase by up to 50°C over the course of a few days. Such events ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Identifying Canada's key conservation hot spots highlights problem
First of its kind mapping of most important places for freshwater, recreation and carbon storage provides tool for conservation decisions