Experts agree on new global definition of 'fermented foods'
New publication clarifies the concept of fermented foods and specifies how they differ from probiotics
2021-01-05
(Press-News.org) Humans have consumed different types of fermented foods - from kimchi to yogurt - for thousands of years. Yet only recently, with the availability of new scientific techniques for analyzing their nutritional properties and microbiological composition, have scientists begun to understand exactly how the unique flavors and textures are created and how these foods benefit human health.
Now, 13 interdisciplinary scientists from the fields of microbiology, food science and technology, family medicine, ecology, immunology, and microbial genetics have come together to create the first international consensus definition of fermented foods. Their paper, published in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, defines fermented foods as: "foods made through desired microbial growth and enzymatic conversions of food components".
The authors take care to note the difference between probiotics and the live microbes associated with fermented foods. The word 'probiotic', they say, only applies in special cases where the fermented food retains live microorganisms at the time of consumption, and only when the microorganisms are defined and shown to provide a health benefit, as demonstrated in a scientific study.
"Many people think fermented foods are good for health--and that may be true, but the scientific studies required to prove it are limited and have mainly focused on certain fermented food types," says first author Maria Marco, Professor in the Department of Food Science and Technology at the University of California, Davis.
Co-author Bob Hutkins, Professor in the Department of Food Science and Technology at University of Nebraska, Lincoln--who has authored a well-known academic textbook on fermented foods--says, "We created this definition to cover the thousands of different types of fermented foods from all over the world, as a starting point for further investigations into how these foods and their associated microbes affect human health."
The consensus panel discussion was organized in 2019 by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP), a non-profit organization responsible for the published scientific consensus definitions of both probiotics (in 2014) and prebiotics (in 2017).
Mary Ellen Sanders, Executive Science Officer of ISAPP, says, "To date, different people have had different ideas of what constitutes a fermented food. The new definition provides a clear concept that can be understood by the general public, industry members and regulators."
Currently, evidence for the positive health effects of fermented foods has relied more on epidemiological and population-based studies and less on randomized controlled trials. The authors expect that, in the years ahead, scientists will undertake more hypothesis-driven research on how different fermented foods from around the globe--derived from dairy products, fruit, vegetables, grains, and even meats--affect human physiology and enhance human health.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-05
Hotel managers have something in common beyond their reputations for charming dispositions and excellent listening skills - they're predominantly men, despite women making up the majority of the accommodations workforce. New research led by the University of Houston Conrad N. Hilton College of Hotel and Restaurant Management suggests hotel companies that promote a woman over an equally qualified man are perceived as fairer and less discriminatory, creating a stronger organizational culture and higher financial performance.
Published in the International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, the study is the first to address gender inequity in promotional opportunities for hotel employees. The researchers surveyed 87 hotel ...
2021-01-05
DENVER/January 5, 2020 - Some English bulldogs diagnosed with a common cancer may instead have a newly described, non-cancerous syndrome called polyclonal B‐cell lymphocytosis. The discovery was made by Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers at Colorado State University during a study to better understand B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (BCLL). The team published their findings in the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
"This could save some dogs from being misdiagnosed, treated for cancer or even euthanized when they shouldn't be," said Dr. Anne Avery, Professor, Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Pathology at Colorado State University. "The dogs may look to their veterinarians like they ...
2021-01-05
BOSTON - (January 4, 2021) - As they age, people with diabetes are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders than are people without diabetes. Scientists at Joslin Diabetes Center now have shown that routine eye imaging can identify changes in the retina that may be associated with cognitive disorders in older people with type 1 diabetes.
These results may open up a relatively easy method for early detection of cognitive decline in this population, providing better ways to understand, diagnose and ultimately treat the decline, said George L. King, MD, Joslin's Chief Scientific Officer and senior author on a paper about the study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Previous research had demonstrated an association ...
2021-01-05
To stop biodiversity loss, Canada recently committed to protecting 30% of its land and sea by 2030. But making conservation decisions about where to locate new protected areas is complicated. It depends on data both about biodiversity and about a range of benefits (e.g. freshwater, climate regulation, recreation) that people get from nature. Surprisingly, despite the size of the country, new mapping suggests that less than 1% of Canada's land (0.6% of total area or approximately 56,000 km2) is a hot spot, providing all these benefits in one place. Moreover, the study published today in Environmental Research Letters suggests that some of the most critical areas where people receive these key benefits from ...
2021-01-05
Leipzig. The transition from the Medieval Warm Period to the Little Ice Age was apparently accompanied by severe droughts between 1302 and 1307 in Europe; this preceded the wet and cold phase of the 1310s and the resulting great famine of 1315-21. In the journal Climate of the Past, researchers from the Leibniz Institutes for the History and Culture of Eastern Europe (GWZO) and Tropospheric Research (TROPOS) write that the 1302-07 weather patterns display similarities to the 2018 weather anomaly, in which continental Europe experienced exceptional heat and drought. Both the medieval and recent weather patterns resemble the stable weather patterns that have occurred more frequently since the 1980s due to the increased warming of the Arctic. ...
2021-01-05
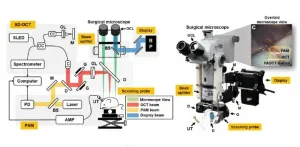
A clear view of anatomical structures is vital for the success of surgery--especially in microsurgery where narrow anatomical cavities or proximity to vulnerable organs and tissues can pose significant risks to patient health. The surgical microscope has evolved to become a powerful tool for improving surgical visualization.
A END ...
2021-01-05
TROY, N.Y. -- A loss of enzymatic processes within the body can increase a person's risk of bone fracture. This new insight was recently published in eLife by an international team of scientists and engineers led by Deepak Vashishth, the director of the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
Enzymatic processes are essential to any number of chemical reactions that occur within the body, including the production of the extracellular matrix within bone that is critical for mechanical support. Phosphorylation -- one of those key enzymatic processes -- is the attachment of a phosphoryl to a protein, and is critical for ...
2021-01-05
Worldwide, marine megafauna are at risk of extinction due to climate change, habitat loss, pollution, overhunting, population fragmentation, and hybridization with related species in areas disturbed by humans. Genetic studies can help determine the conservation status of marine animals, identifying threats to species conservation and informing interventions and policies, such as the protection of diversity hotspots or corridors for gene flow.
In a new study in Frontiers in Marine Science, researchers for the first time measured genetic diversity in manatees ...
2021-01-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A small portion of scientific papers are retracted for research that is in error or fraudulent. But those papers can continue to be cited by other scientists in their work, potentially passing along the misinformation from the retracted articles.
Jodi Schneider, a professor of information sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign who studies scholarly publications and how information gets used, is considering how scientific journals can better communicate about retracted articles. In a new study published in the ...
2021-01-05
Most of the mangrove forests on the coasts of Oman disappeared about 6,000 years ago. Until now, the reason for this was not entirely clear. A current study of the University of Bonn (Germany) now sheds light on this: It indicates that the collapse of coastal ecosystems was caused by climatic changes. In contrast, falling sea level or overuse by humans are not likely to be the reasons. The speed of the mangrove extinction was dramatic: Many of the stocks were irreversibly lost within a few decades. The results are published in the journal Quaternary Research.
Mangroves are trees that occupy a very special ecological niche: They grow in the so-called tidal range, meaning coastal areas that are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Experts agree on new global definition of 'fermented foods'
New publication clarifies the concept of fermented foods and specifies how they differ from probiotics