Understanding disease-induced microbial shifts may reveal new crop management strategies
2021-01-05
(Press-News.org) While humanity is facing the COVID-19 pandemic, the citrus industry is trying to manage its own devastating disease, Huanglongbing (HLB), also known as citrus greening disease. HLB is the most destructive citrus disease in the world. In the past decade, the disease has annihilated the Florida citrus industry, reducing orange production for juice and other products by 72%. Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) is the microbe associated with the disease. It resides in the phloem of the tree and, like many plant pathogens, is transmitted by insects during feeding events. Disease progression can be slow but catastrophic. Symptoms begin with blotchy leaves, yellow shoots, and stunting, and progress into yield decline, poor quality fruit, and eventually death.
Currently, the only thing citrus growers can do to protect their crops from HLB is control the insect vector. Dozens of researchers are trying to find ways to manage the disease, using strategies ranging from pesticides to antibiotics to CLas-sniffing dogs. Understanding the plant microbiome, an exciting new frontier in plant disease management, is another strategy.
Dr. Caroline Roper and first author Dr. Nichole Ginnan at the University of California, Riverside led a large research collaboration that sought to explore the microbiome's role in HLB disease progression. Their recent article in Phytobiomes Journal, "Disease-Induced Microbial Shifts in Citrus Indicate Microbiome-Derived Responses to Huanglongbing," moves beyond the single-snapshot view of the microbial landscape typical of microbiome research. Their holistic approach to studying plant-microbe interactions captured several snapshots across three years and three distinct tissue types (roots, stems, and leaves). What is so interesting about this research is the use of amplicon (16S and ITS) sequencing to capture the highly intricate and dynamic role of the microbiome (both bacterial and fungal) as it changes over the course of HLB disease progression.
Ginnan et al. surmised that HLB created a diseased-induced shift of the tree's microbiome. Specifically, the researchers showed that as the disease progresses, the microbial diversity increases. They further investigated this trend to find that the increase in diversity was associated with an increase in putative pathogenic (disease-causing) and saprophytic (dead tissue-feeding) microbes. They observed a significant drop in beneficial microbes in the early phases of the disease. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) were one such beneficial group that the authors highlighted as showing a drastic d????ecline in relative abundance.
The depletion of key microbial species during disease mi??ght be opening the door for other microbes to invade. Certain resources may become more or less available, allowing different microbes to prosper. Dr. Roper and Dr. Ginnan hypothesize that when HLB begins, this depletion event triggers a surge of beneficial microbes to come to the aid of the citrus tree. They suspect that the microbes are initiating an immune response to protect the host.
As the disease proliferates, the citrus tree and its microbiome continue to change. Dr. Ginnan, the lead author on this study, found that there was an enrichment of parasitic and saprophytic microorganisms in severely diseased roots. The enrichment of these microbes may contribute to disease progression and root decline, one side effect of HLB.
Survivor trees, or trees that did not progress into severe disease, had a unique microbial profile as well. These trees were enriched with putative symbiotic microbes like Lactobacillus sp. and Aureobasidium sp. This discovery led the researchers to identify certain microbes that were associated with slower disease progression.
Dr. Ginnan says their "aha" moment during the research was in the data analysis. "Originally we were looking for taxa that increased and decreased in relative abundance as disease rating increased," she said. "Our differential abundance analysis ended up revealing clear enrichment patterns replicated in multiple taxa." This is the moment they began to develop the individual patterns they were seeing into a broader disease model.
This research is the foundation for future projects and collaborations that the authors are excited to continue to develop. They are motivated by the potential function of the microbiome to manage crop diseases. In the near future, they hope that these discoveries and an understanding of beneficial microbes can help establish a microbiome-mediated treatment plan to protect crops from diseases like HLB. In addition, the model they've developed can be applied to understanding diseases of other tree crop systems.
INFORMATION:
This research article was a part of Dr. Nichole Ginnan's Ph.D. thesis under the mentorship of Dr. Caroline Roper (the lead researcher). Dr. Ginnan is now a Postdoctoral Researcher in Dr. Maggie Wagner's Lab at the University of Kansas. She hopes to continue in academia with a research faculty position. Dr. Caroline Roper is a tenured professor at the University of California Riverside. She mentors several Ph.D. students, undergrads, and postdoctoral scholars on cutting edge research in plant-microbe interactions.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-05
BOSTON -- Getting control of COVID-19 will take more than widespread vaccination; it will also require better understanding of why the disease causes no apparent symptoms in some people but leads to rapid multi-organ failure and death in others, as well as better insight into what treatments work best and for which patients.
To meet this unprecedented challenge, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), in collaboration with investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital and the University of Cyprus, have created a mathematical model based on biology that incorporates information ...
2021-01-05
Diabetes continues to be the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults in the United States. But the current shortage of eye-care providers would make it impossible to keep up with demand to provide the requisite annual screenings for this population. A new study looks at the effectiveness of seven artificial intelligence-based screening algorithms to diagnose diabetic retinopathy, the most common diabetic eye disease leading to vision loss.
In a paper published Jan. 5 in Diabetes Care, researchers compared the algorithms against the diagnostic expertise of retina specialists. Five companies produced the tested algorithms - two in the United States (Eyenuk, Retina-AI Health), one in China (Airdoc), one in Portugal (Retmarker), ...
2021-01-05
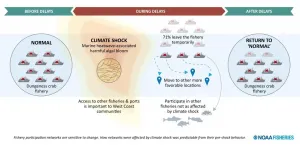
Fishermen contend with regulations, natural disasters, and the ups and downs of the stocks they fish, along with many other changes. As a result, fishing communities are quite resilient. That is, they can withstand, recover from, and adapt to change.
But how much pressure can they stand? The 2014-2016 North Pacific marine heatwave, known as the Blob, led to a harmful algal bloom of unprecedented scale. It necessitated substantial delays in the opening of the 2015-16 U.S. West Coast Dungeness crab fishery. The fishery is vital to West Coast communities. It produces around 26 percent of all annual fishing revenue and supports more than 30 percent of all commercial fishing vessels.
Understanding ...
2021-01-05
Humans have consumed different types of fermented foods - from kimchi to yogurt - for thousands of years. Yet only recently, with the availability of new scientific techniques for analyzing their nutritional properties and microbiological composition, have scientists begun to understand exactly how the unique flavors and textures are created and how these foods benefit human health.
Now, 13 interdisciplinary scientists from the fields of microbiology, food science and technology, family medicine, ecology, immunology, and microbial genetics have come together to create the first international consensus definition of fermented ...
2021-01-05
Hotel managers have something in common beyond their reputations for charming dispositions and excellent listening skills - they're predominantly men, despite women making up the majority of the accommodations workforce. New research led by the University of Houston Conrad N. Hilton College of Hotel and Restaurant Management suggests hotel companies that promote a woman over an equally qualified man are perceived as fairer and less discriminatory, creating a stronger organizational culture and higher financial performance.
Published in the International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, the study is the first to address gender inequity in promotional opportunities for hotel employees. The researchers surveyed 87 hotel ...
2021-01-05
DENVER/January 5, 2020 - Some English bulldogs diagnosed with a common cancer may instead have a newly described, non-cancerous syndrome called polyclonal B‐cell lymphocytosis. The discovery was made by Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers at Colorado State University during a study to better understand B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (BCLL). The team published their findings in the Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
"This could save some dogs from being misdiagnosed, treated for cancer or even euthanized when they shouldn't be," said Dr. Anne Avery, Professor, Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Pathology at Colorado State University. "The dogs may look to their veterinarians like they ...
2021-01-05
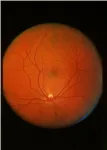
BOSTON - (January 4, 2021) - As they age, people with diabetes are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders than are people without diabetes. Scientists at Joslin Diabetes Center now have shown that routine eye imaging can identify changes in the retina that may be associated with cognitive disorders in older people with type 1 diabetes.
These results may open up a relatively easy method for early detection of cognitive decline in this population, providing better ways to understand, diagnose and ultimately treat the decline, said George L. King, MD, Joslin's Chief Scientific Officer and senior author on a paper about the study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Previous research had demonstrated an association ...
2021-01-05
To stop biodiversity loss, Canada recently committed to protecting 30% of its land and sea by 2030. But making conservation decisions about where to locate new protected areas is complicated. It depends on data both about biodiversity and about a range of benefits (e.g. freshwater, climate regulation, recreation) that people get from nature. Surprisingly, despite the size of the country, new mapping suggests that less than 1% of Canada's land (0.6% of total area or approximately 56,000 km2) is a hot spot, providing all these benefits in one place. Moreover, the study published today in Environmental Research Letters suggests that some of the most critical areas where people receive these key benefits from ...
2021-01-05
Leipzig. The transition from the Medieval Warm Period to the Little Ice Age was apparently accompanied by severe droughts between 1302 and 1307 in Europe; this preceded the wet and cold phase of the 1310s and the resulting great famine of 1315-21. In the journal Climate of the Past, researchers from the Leibniz Institutes for the History and Culture of Eastern Europe (GWZO) and Tropospheric Research (TROPOS) write that the 1302-07 weather patterns display similarities to the 2018 weather anomaly, in which continental Europe experienced exceptional heat and drought. Both the medieval and recent weather patterns resemble the stable weather patterns that have occurred more frequently since the 1980s due to the increased warming of the Arctic. ...
2021-01-05
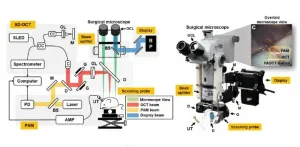
A clear view of anatomical structures is vital for the success of surgery--especially in microsurgery where narrow anatomical cavities or proximity to vulnerable organs and tissues can pose significant risks to patient health. The surgical microscope has evolved to become a powerful tool for improving surgical visualization.
A END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Understanding disease-induced microbial shifts may reveal new crop management strategies