(Press-News.org) The genomes of egg-laying monotreme mammals, platypus and echidna, have been published in the prestigious journal Nature, providing a valuable public resource for research in mammalian biology and evolution, with applications for their conservation and health.
Monotremes display a unique mix of mammalian and reptilian features and form the most distantly related, and least understood, group of living mammals. Their genetic blueprint provides fundamental insights into their unique biology and into the evolution of all mammals.
"The platypus and echidna are the only egg-laying mammals, and so provide the key to understanding the change in reproductive strategy from egg-laying to the production of live young in all other mammals," Professor Marilyn Renfree from the University of Melbourne's School of BioSciences said.
"During their short in egg incubation, they have kept one of the three major egg proteins that is used to make the yolk in chickens, but after hatching both platypus and echidna have a complex milk like other mammals to support their young during their long lactation."
The research was the result of an international collaboration involving Australian scientists from the Universities of Melbourne, Adelaide, Sydney, LaTrobe University, as well as researchers from China, Japan, USA and Denmark.
The 40 researchers brought together expertise in bioinformatics, cytogenetics, developmental and molecular biology to produce and analyse the first ever echidna genome and a greatly improved, high quality platypus genome sequence.
University of Adelaide Professor Frank Grutzner, who co-led the study, said the findings were significant.
"More than 15 years ago we discovered that monotremes have different sex chromosomes to all other mammals," Professor Grutzner said.
"This finding revolutionised our understanding of mammalian sex chromosome evolution but also raised fundamental new questions. With the new genomes we can now tackle important questions about how sex chromosomes control monotreme sexual development and reproduction, and how they evolved."
Co-first author of the study, University of Adelaide Dr Linda Shearwin-Whyatt, said the system for safe removal of the oxygen carrier, haemoglobin from blood was thought to be common to all mammals.
"We were surprised when we discovered the system was missing from monotremes, implying that it arose quite recently in the ancestor of all other mammals," she said.
In contrast, University of Melbourne Dr Fenelon points out that monotremes have lost several key tooth genes and their adult teeth.
LaTrobe University's Professor Jenny Graves said the egg-laying monotremes, unique to Australia, help to answer some of our deepest questions of mammal evolution.
"We last shared a common ancestor with the platypus and echidna about 180 million years ago, so comparing the monotreme and human genomes can tell us about our common ancestor," Professor Graves said.
Knowledge of monotreme reproduction is also relevant for conservation and captive breeding programs. Researchers are excited that the new genome sequences also provide a roadmap for genetic management of threatened echidna populations and exciting new leads for drug development via the discovery of novel peptides in platypus venom.
Professor Renfree said the new understanding would help conserve these iconic and unique Australian mammals.
INFORMATION:
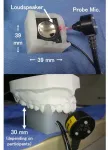
The perception of our own voice depends on sound transmission through air (air-conducted) as well as through the skull bone (bone-conducted or BC). The transmission properties of BC speech are, however, not well understood. Now, scientists from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology report their latest findings on BC transmission under the influence of oral cavity sound pressure, which can boost BC-based technology and basic research on hearing loss and speech impairment.
Ever wondered why your voice sounds different in a recording compared to how you perceive it as you speak? You are not alone. The ...
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. The treatment of bacterial and fungal infections relies particularly on antimicrobial drugs, while the focus in treating viral infections is the alleviation of symptoms.
Initial therapy for infection is often empiric and guided by clinical presentation. Its efficacy on the pathogen is, however, only seldom understood at therapy initiation. Although methods for assessing treatment responses exist, the effectiveness is mainly determined through monitoring symptoms and signs of infections.
Advances in sequencing technology have made characterization of genomes and gene expression products increasingly practical. The technology has also made it possible ...
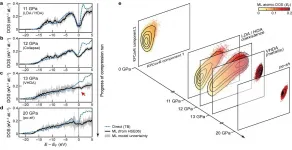
Combining electronic structure calculations and machine learning (ML) techniques has become a common approach in the atomistic modelling of matter. Using the two techniques together has allowed researchers, for instance, to create models that use atomic coordinates as the only inputs to inexpensively predict any property that can be computed by the first-principles calculations that had been used to train them.
While the earliest and by now most advanced efforts have focused on using predictions of total energies and atomic forces to construct interatomic potentials, more recent efforts have targeted additional properties of crystals and molecules such as ionization energies, NMR chemical shieldings, dielectric response properties and charge density. In the paper "Learning ...
It is during rare merging events that galaxies undergo dramatic changes in their appearance and in their stellar content. These systems are excellent laboratories to trace the formation of star clusters under extreme physical conditions.
The Milky Way typically forms star clusters with masses that are 10 thousand times the mass of our Sun. This doesn't compare to the masses of the star clusters forming in colliding galaxies, which can reach millions of times the mass of our Sun.
These dense stellar systems are also very luminous. Even after the collision, when the resulting galactic system begins to fade into a more quiescent phase, these very massive star clusters will shine throughout their host galaxy, as long-lasting witnesses of past merging events.
By studying the six galaxy ...
Autoimmune diseases are diseases of "mistaken identity", where the immune system - which is supposed to protect us against infectious diseases and neoplasias - mistakenly attacks and destroys components of our own body. The incidence of autoimmune diseases is increasing on a worldwide basis, and these diseases - including type 1 diabetes (T1D), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) - now affect up to 5% of the population in different regions. There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, and while the immune target of T1D, SLE, MS, and RA are distinct, they share several similar elements, including up to 50% common genetic risk, chronic local inflammation and mechanisms ...
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg now suggest a possible cure for children with hard-to-treat forms of neuroblastoma using a new combination of drugs. In a new study in the journal Cancer Research, they describe how a two small molecule-based drug combination likely inhibit the tumor's growth.
Neuroblastoma is the most common form of childhood cancer, derived from the peripheral nervous system, i.e., the part of the nervous system that is not the brain or spinal cord. The disease can occur in the chest, neck, abdomen and adrenal glands and can also spread to the spine. Symptoms include general aches, anemia and skeletal pain.
The ...
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, is a common gastrointestinal malignancy. Peritoneal metastasis occurs in a majority of patients with advanced stomach cancer and is considered as an aggressive disease with poor outcomes.
Patients with peritoneal metastasis are typically not eligible for curative surgery. Therefore, preoperative detection and diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis are critical to inform treatment decision-making and avoid unnecessary surgery.
A new study published in the JAMA Network Open on Jan. 5 shows that deep learning can help predicting the occult peritoneal metastasis in stomach cancer. It provides a novel and noninvasive approach for ...
Olduvai (now Oldupai) Gorge, known as the Cradle of Humankind, is a UNESCO World Heritage site in Tanzania, made famous by Louis and Mary Leakey. New interdisciplinary field work has led to the discovery of the oldest archaeological site in Oldupai Gorge as reported in Nature Communications, which shows that early human used a wide diversity of habitats amidst environmental changes across a 200,000 year-long period.
Located in the heart of eastern Africa, the Rift System is a prime region for human origins research, boasting extraordinary records of extinct human species and environmental records spanning several million years. For more than a century, archaeologists and human palaeontologists have been exploring the East African Rift outcrops and unearthing hominin fossils in surveys ...
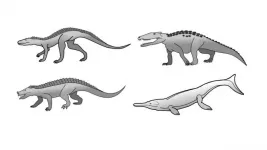
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol explains how a 'stop-start' pattern of evolution, governed by environmental change, could explain why crocodiles have changed so little since the age of the dinosaurs.
Crocodiles today look very similar to ones from the Jurassic period some 200 million years ago. There are also very few species alive today - just 25. Other animals such as lizards and birds have achieved a diversity of many thousands of species in the same amount of time or less.
Prehistory also saw types of crocodile we don't see today, including giants as big as dinosaurs, plant-eaters, fast ...
Scientists at the University of Birmingham, UK, have shown that a novel low molecular weight dextran-sulphate, ILB® could play a key role in treating open angle glaucoma (OAG), a neurodegenerative disease that affects over 70 million people worldwide and causes irreversible blindness.
OAG develops slowly over many years. Excessive matrix deposition (fibrosis) within the eye's main fluid drainage site can lead to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), resulting in damage to the optic nerve.1
The research, reported in npj Regenerative Medicine, has ...