Ancient DNA analysis reveals Asian migration and plague
2021-01-07
(Press-News.org) Northeastern Asia has a complex history of migrations and plague outbursts. That is the essence of an international archaeogenetic study published in Science Advances and lead from the Department of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Stockholm University. Genomic data from archaeological remains from 40 individuals excavated in northeastern Asia were explored in the study.
"It is striking that we find everything here, continuity as well as recurrent migrations and also disease-related bacteria", says Anders Götherström, professor at the Center for Palaeogenetics at Stockholm University and one of the Principal investigators of the study.
The scientists discovered that there were demographic events in the past common for the whole Lake Baikal region. For example, around 8300 years ago there was a migratory event discernible both east and west of Lake Baikal. But there were also events specific for each of the two areas. While the areas west of Lake Baikal provides evidence for recurrent migrations and intense mobility, the areas east of Lake Baikal preserved a long-term continuity for thousands of years, apparently with limited mobility from other areas.
"It is intriguing that our data reveals complex and contrasting patterns of demographic change in one of the least populated regions on earth; including notable gene flow and at the same time a genetic continuity without major demographic changes in the two areas around Lake Baikal", says lead-author Gulsah Merve Kilinc, former postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Stockholm University and currently Lecturer at Department of Bioinformatics at Hacettepe University in Ankara.
The study also provides some new clues to the history of the Paleo-Inuit groups, the people who inhabited northern Greenland and Canada. While it has been suspected that the so called Belkachi-complex, a cultural group in the Baikal area, played a part in the early history of Paleo-Inuits, it has not been possible to evaluate this in detail. The analyses of remains of an individual associated with the Belkachi cultural-complex, dated to more than 6000 years before present now show that there is an association to a previously published Paleo Inuit (Saqqaq) individual (dated c.4000 yrs BP) on Greenland.
"This is the first genetic evidence of a link between a Neolithic period human group in Yakutia and the later Palaeo-Inuit groups, and this will inspire to new of research on the demographic development", says Jan Storå, Professor at Osteoarchaeological Research Laboratory at the Department of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Stockholm University.
Finally, the study provides new data on the most eastern occurrences of the bacteria Yersinia pestis, the plague. One individual from the Lena basin, dated to c. 3800 years ago, and buried with individuals that proved to be close kin genetically, carried DNA from Yersinia pestis. Also, an individual dated to c. 4400 years ago from the area west of Lake Baikal hosted Yersinia pestis. Interestingly, the population west of Lake Baikal seems to have decreased in size around 4400 years ago, judging from the genomic data.
"Despite a need for more data, our discovery of the decrease in effective population size that coincided with the appearance of Yersinia pestis points to a possible presence of a prehistoric plague - possibly a pandemic. However, this is just as an educated guess which needs to wait for confirmation", says Emrah K?rdök, former postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Stockholm University and currently Lecturer at Mersin University in Turkey.
INFORMATION:
The article "Human population dynamics and Yersinia pestis in ancient northeast Asia" is published in the scientific journal Science Advances.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-07
Sleep is ubiquitous in animals and humans and vital for healthy functioning. Thus, sleep after training improves performance on various tasks in comparison to equal periods of active wakefulness. However, it has been unclear so far whether this is due to an active refinement of neural connections or merely due to the absence of novel input during sleep. Now researchers at the Medical Center - University of Freiburg have succeeded in showing that sleep is more than rest for improving performance. The findings, which were published in the journal SLEEP on January 6, 2021, provide important information for planning periods of intensive ...
2021-01-07
January 7, 2021 (BRAMPTON - HAMILTON) -- When dealing with a life-limiting illness, palliative care can improve the quality of life for patients and families. However, for many people, the fear of "end of life" care prevents them from exploring it. A recent study from William Osler Health System (Osler) and McMaster University examined awareness of palliative care in the South Asian community and found that culture plays a critical role in the perception of palliative care. This perception, in turn, affects whether or not patients will be open to receiving it.
Funded by a McMaster University, Department ...
2021-01-07
TORONTO, January 7, 2021- What feels like up may actually be some other direction depending on how our brains process our orientation, according to psychology researchers at York University's Faculty of Health.
In a new study published in PLoS One, researchers at York University's Centre for Vision Research found that an individual's interpretation of the direction of gravity can be altered by how their brain responds to visual information. Laurence Harris, a professor in the Department of Psychology in the Faculty of Health and Meaghan McManus, a graduate student in his lab, found, using virtual reality, that people differ ...
2021-01-07
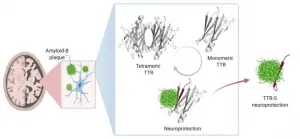
DALLAS - Jan. 7, 2020 - A protein that wreaks havoc in the nerves and heart when it clumps together can prevent the formation of toxic protein clumps associated with Alzheimer's disease, a new study led by a UT Southwestern researcher shows. The findings, published recently in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, could lead to new treatments for this brain-ravaging condition, which currently has no truly effective therapies and no cure.
Researchers have long known that sticky plaques of a protein known as amyloid beta are a hallmark of Alzheimer's and are toxic to brain cells. As early as the mid-1990s, other proteins were discovered in these plaques as well.
One of these, a protein known as transthyretin (TTR), ...
2021-01-07
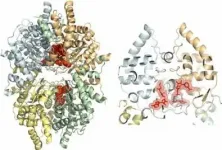
Brazilian researchers have managed to decipher the structure of a protein found in parasites that cause neglected tropical diseases, paving the way to the development of novel medications. Thanks to the discovery it will be possible to seek more potent molecules capable of destroying the pathogens directly, with fewer adverse side-effects for patients.
The study detailed the structural characteristics of the protein deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS), found in Brugia malayi, one of the mosquito-borne parasites that cause elephantiasis, and in Leishmania major, the protozoan that causes cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Elephantiasis, also known as lymphatic filariasis, is an infection of the lymph system that can lead to swelling of the legs, arms, and genitalia. It may also harden and ...
2021-01-07
HOUSTON - (Jan. 7, 2021) - Proteogenomic analysis may offer new insight into matching cancer patients with an effective therapy for their particular cancer. A new study identifies three molecular subtypes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) that could be used to better determine appropriate treatment. The research led by Baylor College of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University and the National Cancer Institute's Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) is published in the journal Cancer Cell.
Researchers profiled proteins, phosphosites and signaling ...
2021-01-07
TROY, N.Y. -- In a money-saving revelation for organizations inclined to invest in specialized information technology to support the process of idea generation, new research suggests that even non-specialized, everyday organizational IT can encourage employees' creativity.
Recently published in the journal Information and Organization, these findings from Dorit Nevo, an associate professor in the Lally School of Management at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, show standard IT can be used for innovation. Furthermore, this is much more likely to happen when the technology is in the hands of employees who are motivated to master technology, understand their role in the organization, ...
2021-01-07
In a study to examine a Mediterranean diet in relation to prostate cancer progression in men on active surveillance, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center found that men with localized prostate cancer who reported a baseline dietary pattern that more closely follows the key principles of a Mediterranean-style diet fared better over the course of their disease.
"Men with prostate cancer are motivated to find a way to impact the advancement of their disease and improve their quality of life," said Justin Gregg, M.D., assistant professor of Urology and lead author of the study, published today in Cancer. ...
2021-01-07
Tsukuba, Japan - Does losing weight while you sleep sound too good to be true? According to a study by the University of Tsukuba, it seems that drinking oolong tea might help you do just that.
While all tea comes from the same plant, Camellia sinensis, the degree of oxidation, a chemical reaction that turns tea leaves black, defines its specific type. For example, green tea is unoxidized and mild in flavor, while the distinctive color of black tea comes from complete oxidation. Oolong tea, being only partially oxidized, lies somewhere in between and displays characteristics ...
2021-01-07
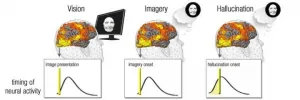
Some people have lost their eyesight, but they continue to "see." This phenomenon, a kind of vivid visual hallucination, is named after the Swiss doctor, Charles Bonnet, who described in 1769 how his completely blind grandfather experienced vivid, detailed visions of people, animals and objects. Charles Bonnet syndrome, which appears in those who have lost their eyesight, was investigated in a study led by scientists at the Weizmann Institute of Science. The findings, published today in Brain, suggest a mechanism by which normal, spontaneous activity in the visual centers of the brain can trigger visual hallucinations in the blind.
Prof. Rafi Malach and his group members of the Institute's Neurobiology Department research the phenomenon of spontaneous "resting-state" ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ancient DNA analysis reveals Asian migration and plague