(Press-News.org) Marijuana use increases throughout the calendar year, with use up 13 percent on average at the end of each year (2015-2019) compared to the beginning, according to a new study published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
"We found that marijuana use is consistently higher among those surveyed later in the year, peaking during late fall or early winter before dropping at the beginning of the following year. We think this may be due, in part, to a 'Dry January' in which some people stop drinking alcohol or even stop using marijuana as part of a New Year's resolution," said Joseph Palamar, PhD, MPH, an associate professor of population health at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, an affiliated researcher with the Center for Drug Use and HIV/HCV Research (CDUHR) at NYU School of Global Public Health, and the study's lead author. "We're now in the time of year when people are the least likely to use marijuana."
Prior research shows that alcohol and drug use vary by time of year, with drug use often increasing during summer months, possibly due, in part, to social events. These seasonal variations can inform interventions--for instance, studies show that programs to reduce heavy drinking among college students should begin during the summer.
To better understand seasonal trends in marijuana use, Palamar and his colleagues analyzed data from 282,768 adolescents and adults who responded to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health from 2015 to 2019. The survey asked participants about their past-month use of marijuana and other substances, and the researchers estimated their use within each calendar quarter: January through March, April through June, July through September, and October through December.
Each year, as the calendar year progressed, marijuana use grew, increasing in summer and fall months before dropping as each new year began. While 8.9 percent reported using marijuana in January through March, 10.1 percent reported using in October through December, a 13-percent relative increase.
These seasonal trends occurred independently of annual growth in marijuana use and were seen across nearly all groups surveyed, regardless of sex, race/ethnicity, and education level. Teens were one exception; their marijuana use grew in the summer but declined in the fall months back to winter and spring levels.
Recreational use may be driving the growth throughout the year, as similar small increases occurred among those living in states with and without legal medical marijuana, and among those without a prescription for medical marijuana. Seasonal marijuana use also increased among those who reported using other substances, including alcohol, nicotine, and especially LSD.
The researchers note that the consistent dip in marijuana use during winter months could be a result of a variety of factors: a lower supply this time of year from cannabis harvests, colder weather keeping people inside who usually smoke outdoors, or people quitting marijuana as a New Year's resolution.
"Ultimately, we hope that these findings can be utilized by researchers and clinicians alike," said study coauthor Austin Le, DDS, a research associate at NYU Langone Health and orthodontic resident at NYU College of Dentistry. "Researchers studying marijuana use should consider seasonal variation, as surveys administered at the end of the year may yield different results than at the beginning of the year. And for those who wish to reduce marijuana use, it appears the best time for such targeting may be later in the year--when use is highest."
In addition to Palamar and Le, Benjamin Han of the University of California, San Diego's Department of Medicine, Division of Geriatrics co-authored the study. The research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health (grants R01DA044207 and K23DA043651).
About CDUHR
The mission of the Center for Drug Use and HIV/HCV Research (CDUHR) is to end the HIV and HCV epidemics in drug using populations and their communities by conducting transdisciplinary research and disseminating its findings to inform programmatic, policy, and grass roots initiatives at the local, state, national, and global levels. CDUHR is a Core Center of Excellence funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (Grant #P30 DA011041). It is the first center for the socio-behavioral study of substance use and HIV in the United States and is located at the NYU School of Global Public Health. For more information, visit http://www.cduhr.org.
About NYU Langone Health
NYU Langone Health is a world-class, patient-centered, integrated academic medical center, known for its excellence in clinical care, research, and education. Included in the 260+ locations throughout the New York area are six inpatient locations: Tisch Hospital, its flagship acute-care facility in Manhattan; Rusk Rehabilitation, ranked as one of the top 10 rehabilitation programs in the country; NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital, a dedicated inpatient orthopedic hospital in Manhattan with all musculoskeletal specialties ranked top 10 in the country; Hassenfeld Children's Hospital at NYU Langone, a comprehensive pediatric hospital, also in Manhattan, supporting a full array of children's health services; NYU Langone Hospital--Brooklyn, a full-service teaching hospital and level 1 trauma center located in Sunset Park, Brooklyn; and NYU Langone Hospital--Long Island, a full-service teaching hospital and level 1 trauma center located in Nassau County on Long Island. Also part of NYU Langone Health is the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center, a National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer center; NYU Grossman School of Medicine, which since 1841 has trained thousands of physicians and scientists who have helped to shape the course of medical history; and NYU Long Island School of Medicine. For more information, go to nyulangone.org, and interact with us on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Instagram.
About NYU School of Global Public Health
At the NYU School of Global Public Health (NYU GPH), we are preparing the next generation of public health pioneers with the critical thinking skills, acumen, and entrepreneurial approaches necessary to reinvent the public health paradigm. Devoted to employing a nontraditional, interdisciplinary model, NYU GPH aims to improve health worldwide through a unique blend of global public health studies, research, and practice. The School is located in the heart of New York City and extends to NYU's global network on six continents. Innovation is at the core of our ambitious approach, thinking and teaching. For more, visit: http://publichealth.nyu.edu/
# # #
INFORMATION:
The gut plays a central role in the regulation of the body's metabolism and its dysfunction is associated with a variety of diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, colitis and colorectal cancer that affect millions of people worldwide. Targeting endocrine dysfunction at an early stage by stimulating the formation of specific enteroendocrine cells from intestinal stem cells could be a promising regenerative approach for diabetes therapy. For this, however, a detailed understanding of the intestinal stem cell lineage hierarchy and the signals regulating the recruitment of the different intestinal cell types is critical.
Heiko Lickert ...
How the larvae of colorful clownfish that live among coral reefs in the Philippines are dispersed varies widely, depending on the year and seasons - a Rutgers-led finding that could help scientists improve conservation of species.
Right after most coral reef fish hatch, they join a swirling sea of plankton as tiny, transparent larvae. Then currents, winds and waves disperse them, frequently to different reefs.
During seven years of surveys of coral reef-dwelling clownfish, scientists measured how the dispersal of larvae varied over the years and seasonally, including during monsoons, according Rutgers-led research in the journal Molecular Ecology. They found that larvae dispersal varied a lot on both timescales.
Their research suggests that when scientists ...
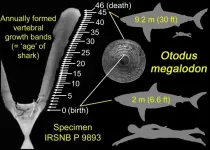
A new study shows that the gigantic Megalodon or megatooth shark, which lived nearly worldwide roughly 15-3.6 million years ago and reached at least 50 feet (15 meters) in length, gave birth to babies larger than most adult humans.
This latest research shedding light on the reproductive biology, growth and life expectancy of Megalodon (formally called Otodus megalodon) appears in the international journal Historical Biology.
Although Otodus megalodon is typically portrayed as a super-sized, monstrous shark in novels and films such as the 2018 sci-fi film "The Meg," scientific data support a more modest but still impressive estimate of about 50 feet (15 meters) for the presently known largest individuals. The ...
Positive "tipping points" could spark cascading changes that accelerate action on climate change, experts say.
A tipping point is a moment when a small change triggers a large, often irreversible, response.
Professor Tim Lenton, Director of the Global Systems Institute (GSI) at the University of Exeter, has previously warned the world is "dangerously close" to several tipping points that could accelerate climate change.
But in a new paper in the journal Climate Policy, Professor Lenton and Simon Sharpe, a Deputy Director in the UK Cabinet Office COP 26 unit, identify tipping points in human societies that could rapidly ...
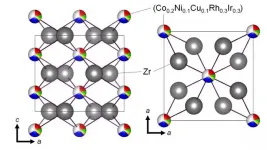
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University mixed and designed a new, high entropy alloy (HEA) superconductor, using extensive data on simple superconducting substances with a specific crystal structure. HEAs are known to preserve superconducting characteristics up to extremely high pressures. The new superconductor, Co0.2Ni0.1Cu0.1Rh0.3Ir0.3Zr2, has a superconducting transition at 8K, a relatively high temperature for an HEA. The team's approach may be applied to discovering new superconducting materials with specific desirable properties.
It's been over a hundred years since the discovery of superconductivity, where certain materials were found to suddenly show minimal resistance to electrical currents below a transition temperature. As we explore ...
A new risk-stratification tool which can accurately predict the likelihood of deterioration in adults hospitalised with COVID-19 has been developed by researchers from the UK Coronavirus Clinical Characterisation Consortium (known as ISARIC4C).
Researchers say the online tool, made freely available to NHS doctors from today (Friday 8 January 2021), could support clinicians' decision making - helping to improve patient outcomes and ultimately save lives.
The tool assesses 11 measurements* routinely collected from patients, including age, gender, and physical measurements (such as oxygen levels) along with some standard laboratory tests and calculates a percentage risk ...
Study of 1,733 patients first diagnosed in Wuhan (China) between January and May followed to June and September.
76% of COVID-19 patients have at least one symptom six months after symptom onset.
Fatigue or muscle weakness is the most common symptom, with sleep difficulties and anxiety or depression also frequently reported.
Lower antibodies against COVID-19 in patients six months after becoming ill compared with during acute infection raises concerns about the possibility of re-infection.
More than three quarters of COVID-19 patients have at least one ongoing symptom six months after initially becoming unwell, according to research published in The Lancet.
The cohort study, looking at long-term effects of COVID-19 infection on people hospitalised ...
COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care in the early months of the pandemic were subject to a significantly higher burden of delirium and coma than is typically found in patients with acute respiratory failure. Choice of sedative medications and curbs on family visitation played a role in increasing acute brain dysfunction for these patients.
That's according to an international study published Jan. 8 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, led by researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in coordination with researchers in Spain.
The study, which is far the largest of its kind to date, tracks the incidence of delirium and coma in 2,088 COVID-19 patients admitted before April 28, 2020, to 69 adult intensive care units across 14 countries.
ICU delirium is ...
Hundreds of cancer patients have benefitted from using computer algorithms to manage their symptoms and improve their wellbeing in a unique UK trial.
The early stage colorectal, breast or gynecological cancer patients took part in the trial of the eRAPID system, developed by the University of Leeds, which allowed them to report online symptoms from home and receive instant advice on whether to self-manage or seek medical attention.
Patients reported better symptom control and physical wellbeing in the early weeks of treatment, with the system preventing symptom deterioration in about 9% of patients after 12 weeks. Patients reported more confidence in managing ...
A year ago, trying to find patients who would agree to see their University of Michigan mental health provider through a video screen felt like pulling teeth.
Only 26 video visits with a few early-adopters had happened in nearly six months, compared with more than 30,000 in-person visits.
But Jennifer Severe, M.D., one of the three psychiatrists who helped launch a test of telehealth initiatives in the U-M's outpatient psychiatry clinic, wasn't about to give up.
She prepared to give a talk at the beginning of April of 2020, hoping to convince more of her colleagues to give telepsychiatry a try, now that a major insurance ...