Confined growth of ZIF-8 in organosilica nanoparticles to regulate mRNA translation
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) Delivery of genetic molecules such as mRNA into cells is vital with important applications such as vaccine development. Various agents have been developed for mRNA delivery. However, conventional mRNA nanocarriers mainly focus on their physical interaction with mRNA molecules, or protection / delivery of mRNA, such as adjusting physical properties of nanocarriers to control binding with mRNA or cellular uptake. Moreover, effective mRNA delivery in hard-to-transfect APCs remains a challenge. The hard-to-transfect nature in APCs is partly attributed to the suppressed mRNA translation associated with the intrinsic high intracellular glutathione (GSH) level. Thus, tetrasulfide bond bridged DMONs modified with polyethylenimine (PEI) have been reported to oxidize GSH to GSSG (oxidized GSH) to upregulate mRNA translation in APCs. However, the intrinsic cellular regeneration of GSH from GSSG catalyzed by glutathione reductase (GR) could hinder the regulatory efficiency. Besides, the PEI modification to induce endosomal escape raises unwanted cytotoxicity. Therefore, it is highly desired to develop a new mRNA delivery platform with good biocompatibility and long-term bioregulatory capability towards mRNA translation.
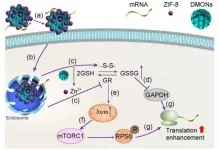
ZIF-8 is a type of metal organic frameworks and an emerging delivery system for a variety of molecules, including amino acids, proteins and plasmids. These biomolecules are generally encapsulated by biomimetic mineralization of ZIF-8, where ZIF-8 are mainly used as delivery vehicles. To date, ZIF-8 has not been applied for mRNA delivery. Recent research indicates each components of ZIF-8 can possess great potential to regulate mRNA translation and enhance mRNA delivery: the acidic pH responsive breakage of zinc-ligand bonds in ZIF-8 is expected to release zinc for GR inhibition and GSSG reduction, and imidazole for endosomal escape.
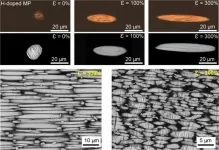
In a new research article published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, the research team led by Professor Chengzhong Yu from the University of Queensland reports the confined growth of ZIF-8 nanocrystals partially in the large mesopores of DMONs (DMONs-ZIF-8) for long-term upregulated mRNA translation. Different from previous works, this delivery system avoids the use of cytotoxic polymer modification. All components in DMONs-ZIF-8 contribute to mRNA delivery: (a) high mRNA loading capacity enabled by large mesopores for cellular uptake; (b) successful endosomal escape contributed by imidazole group in ZIF-8; and as a translation regulator for (c) synergistic GSH depletion by tetrasulfide-induced GSH oxidation and zinc-mediated inhibition of GR and GSSG reduction; (d-f) deactivated GAPDH involved mRNA translation inhibition and increased mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) activated mTORC1 pathway; and consequently (g) enhanced mRNA translation. DMONs-ZIF-8 exhibited higher mRNA translation modulation and delivery efficiency compared to polymer modified control (DMONs-PEI) and commercial products (in vitro: lipofectamine, in vivo: in vivo-jetPEI). This research provides new understandings in the rational design of functional nanocarriers for mRNA delivery towards APCs and paves the way to advance mRNA applications such as the development of mRNA vaccines.
INFORMATION:
This research received funding from the Australian Research Council (DP200102962).
See the article:
Yue Wang, Hao Song, Chao Liu, Ye Zhang, Yueqi Kong, Jie Tang, Yannan Yang and Chengzhong Yu
Confined growth of ZIF-8 in dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles as bio-regulators for enhanced mRNA delivery in vivo
Natl Sci Rev, 2020, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa268
https://academic.oup.com/nsr/advancearticle/doi/10.1093/nsr/nwaa268/5936582#209340881
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
Photorespiration is a highly energy consuming process in plants that leads to the release of previously fixed CO2. Thus, engineering this metabolic process is a key approach for improvement of crop yield and for meeting the challenge of ever-rising CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Researchers led by Tobias Erb from the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Marburg, Germany, have now succeeded in engineering the TaCo pathway, a synthetic photorespiratory bypass. This new-to-nature metabolic connection opens up new possibilities of CO2 fixation ...
2021-01-11
With the rapid development of smart portable electronics and electric vehicles, the consumption of lithium resource will increase dramatically and the cost of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) may increase significantly in the future. In addition, the shortage (0.0017 wt% in the earth's crust) and uneven crustal distribution of lithium also limit its further development and application. As potassium (2.7 wt% in the earth's crust) have properties similar to lithium and abundant reserves. Therefore, as an alternative to LIBs, potassium ion batteries (PIBs) have become the focus of research. Potassium (2.92 V vs. ...
2021-01-11
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry, led by Nikolaos Koutsouleris, combined psychiatric assessments with machine-learning models that analyse clinical and biological data. Although psychiatrists make very accurate predictions about positive disease outcomes, they might underestimate the frequency of adverse cases that lead to relapses. The algorithmic pattern recognition helps physicians to better predict the course of disease.
The results of the study show that it is the combination of artificial and human intelligence that optimizes the prediction ...
2021-01-11
The spiky structure that erupts from the smooth surface of a ferrofluid when a magnet is brought close can be predicted more accurately than previously thought. KAUST researchers have shown that computational algorithms can calculate the ferrofluid's bristling response to a magnet by simulating only the liquid's surface layer.
Ferrofluids are liquid suspensions of iron-based particles that behave like a regular fluid, but once a magnet is present, the ferrofluid rapidly shape-shifts to form spikes that align with the magnetic field. Originally developed by NASA, ferrofluids have numerous uses ranging from advanced electronics to nanomedicine and have the potential for even broader use, if their magnetic responses could be predicted more accurately.
Dominik Michels and ...
2021-01-11
Co-culture: stimulate the metabolic potential and explore the molecular diversity of natural products from microorganisms
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Xiao-Yue Peng, Jin-Tao Wu, Chang?Lun Shao, Zhi-Yong Li, Min Chen and Chang-Yun Wang from the Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao, China and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China consider the metabolic potential and molecular diversity of natural products from microorganisms.
Microbial secondary metabolites have long ...
2021-01-11
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Caiwen Li, Meng Li and Qian Huang from Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China consider the impact of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium on aquaculture of marine crustaceans in China.
Hematodinium is a type of parasitic dinoflagellate that infects marine crustaceans globally. The parasite lives mainly in the hemolymph or hemocoels of affected hosts, and results in mortalities due to malfunction or loss of functions of major organs.
In recent years, the parasite has developed into an emerging epidemic pathogen not only affecting wild populations of economically valuable marine crustaceans ...
2021-01-11
Good news for those who need a cuppa to start the day. Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have created new probiotic coffee and tea drinks that are packed with gut-friendly live probiotics.
Supervised by Associate Professor Liu Shao Quan from the Department of Food Science and Technology at the NUS Faculty of Science, the two doctoral students who worked on these two new beverages assert that their drinks have a great taste, and can be stored chilled or at room temperature for more than 14 weeks without compromising on their probiotic viability.
Traditional probiotic carriers like yoghurts and cultured milks are dairy-based products. The rise in veganism, along with common health issues like lactose intolerance, high ...
2021-01-11
Today's electronic devices strive for new form factors - to make them foldable, stretchable, and deformable. To produce such devices that are highly stretchable or deformable, it is necessary to develop electrodes and circuit lines whose electrical properties can withstand harsh deformation or mechanical damage. To this, POSTECH-Yonsei University joint research team has recently developed liquid metal ink to accelerate printed electronic devices that can be changed into any shape.
Professor Unyong Jeong and Dr. Selvaraj Veerapandian of POSTECH's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, with Professor Aloysius Soon and Dr. Woosun Jang of Yonsei University's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, have developed liquid metal microparticles ...
2021-01-11
NIH-supported pilot study found team-based approach may improve buprenorphine care.
WHAT:
A collaborative approach to treating opioid use disorder that relies heavily on community pharmacists is feasible and may increase adherence and participant satisfaction, according to a pilot study published today in Addiction. The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, through the NIDA Center for the Clinical Trials Network.
Most people with opioid use disorder who would benefit from medication do not receive it. Buprenorphine is a safe and effective ...
2021-01-11
DALLAS - Jan. 11, 2021 - A set of biomarkers not traditionally associated with cell fate can accurately predict how genetically identical cells behave differently under stress, according to a UT Southwestern study. The findings, published by Cell Reports as a Dec. 1 cover story, could eventually lead to more predictable responses to pharmaceutical treatments.
Groups of the same types of cells exposed to the same stimuli often display different responses. Some of these responses have been linked to slight differences in genetics between individual cells. However, even genetically identical cells can diverge in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Confined growth of ZIF-8 in organosilica nanoparticles to regulate mRNA translation