Breakthrough on diarrhea virus opens up for new vaccines
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) "The findings provide an increased understanding of how the virus gets through the stomach and intestinal system. Continued research can provide answers to whether this property can also be used to create vaccines that ride 'free rides' and thus be given in edible form instead of as syringes," says Lars-Anders Carlson, researcher at Umeå University.
The virus that the researchers have studied is a so-called enteric adenovirus. It has recently been clarified that enteric adenoviruses are one of the most important factors behind diarrhea among infants, and they are estimated to kill more than 50,000 children under the age of five each year, mainly in developing countries.
Most adenoviruses are respiratory, that is, they cause respiratory disease, while the lesser-known enteric variants of adenovirus instead cause gastrointestinal disease. The enteric adenoviruses therefore need to be equipped to pass through the acidic environment of the stomach without being broken down, so that they can then infect the intestines.
With the help of the advanced cryo-electron microscope available in Umeå, the researchers have now managed to take such detailed images of an enteric adenovirus that it has been possible to put a three-dimensional puzzle that shows what the virus looks like right down to the atomic level. The virus is one of the most complex biological structures studied at this level. The shell that protects the virus' genome when it is spread between humans consists of two thousand protein molecules with a total of six million atoms.
The researchers were able to see that the enteric adenovirus manages to keep its structure basically unchanged at the low pH value found in the stomach. They could also see other differences compared to respiratory adenoviruses in how a particular protein is altered in the shell of the virus as well as new clues to how the virus packs its genome inside the shell. All in all, it provides an increased understanding of how the virus manages to move on to create disease and death.
"The hope is that you will be able to turn the ability that this unpleasant virus has to get to something that can instead be used as a tool to fight disease, perhaps even COVID-19. This is a step in the right direction, but it is still a long way off," says Lars-Anders Carlson.
Several of the new vaccines being tested against COVID-19 are based on genetically modified adenovirus. Today, these adenovirus-based vaccines must be injected to work in the body. If a vaccine could instead be based on enteric adenovirus, the vaccine might be given in edible form. This would, of course, facilitate large-scale vaccination.
INFORMATION:
The virus that the researchers have studied is called HAdV-F41. The study is published in the scientific journal Science Advances. It is a collaboration between Lars-Anders Carlson's and Niklas Arnberg's research groups at Umeå University.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have discovered a key mechanism underlying bacterial skin colonisation in atopic dermatitis, which affects millions around the globe.
Atopic dermatitis (AD, also called commonly eczema) is the most common chronic inflammatory skin disorder in children, affecting 15-20% of people in childhood. During disease flares, patients experience painful inflamed skin lesions accompanied by intense itch and recurrent skin infection.
The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) thrives on skin affected by AD, increasing inflammation and worsening AD symptoms. Although a small number of therapies are available at present for patients with moderate ...
2021-01-11
Leading research at Newcastle University has been used to shape how dentistry can be carried out safely during the Covid-19 pandemic by mitigating the risks of dental aerosols.
It is well known that coronavirus can spread in airborne particles, moving around rooms to infect people, and this has been a major consideration when looking into patient and clinician safety.
Research, published in the Journal of Dentistry, has led the way in helping shape national clinical guidance for the profession to work effectively under extremely challenging circumstances.
The findings have been used by the Dental Schools' Council, Association of Dental Hospitals and the Scottish Dental Clinical Effectiveness ...
2021-01-11
Micro-CT scanning and digital reconstructions have been used to compare the skulls of the Tasmanian tiger (thylacine) and wolf across their early development and into adulthood, establishing that not only did the thylacine resemble the wolf as adults, but also as newborns and juveniles.
"Remarkably, the Tasmanian tiger pups were more similar to wolf pups than to other closely related marsupials," Professor Andrew Pask from the University of Melbourne said.
The collaborative study with Flinders University and Museums Victoria complement earlier findings that thylacine and wolf have evolved ...
2021-01-11
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already an integral part of our everyday lives online. For example, search engines such as Google use intelligent ranking algorithms and video streaming services such as Netflix use machine learning to personalize movie recommendations.
As the demands for AI online continue to grow, so does the need to speed up AI performance and find ways to reduce its energy consumption.
Now a University of Washington-led team has come up with a system that could help: an optical computing core prototype that uses phase-change material. This system is fast, energy efficient and capable of accelerating ...
2021-01-11
Topological materials are characterised by unique electronic and physical properties that are determined by the underlying topology of their electronic systems. Scientists from the Max Planck Institutes for Microstructure Physics (Halle) and for Chemical Physics of Solids (Dresden) have now discovered that (TaSe4)2I is the first material in which a charge density wave induces a phase transition between the semimetal to insulator state.
An international team of scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Microstructure Physics, Halle (Saale), the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids ...
2021-01-11
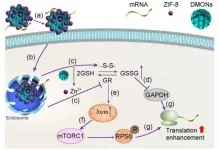
Delivery of genetic molecules such as mRNA into cells is vital with important applications such as vaccine development. Various agents have been developed for mRNA delivery. However, conventional mRNA nanocarriers mainly focus on their physical interaction with mRNA molecules, or protection / delivery of mRNA, such as adjusting physical properties of nanocarriers to control binding with mRNA or cellular uptake. Moreover, effective mRNA delivery in hard-to-transfect APCs remains a challenge. The hard-to-transfect nature in APCs is partly attributed to the suppressed mRNA translation associated with the intrinsic high intracellular glutathione (GSH) level. Thus, ...
2021-01-11
Photorespiration is a highly energy consuming process in plants that leads to the release of previously fixed CO2. Thus, engineering this metabolic process is a key approach for improvement of crop yield and for meeting the challenge of ever-rising CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Researchers led by Tobias Erb from the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Marburg, Germany, have now succeeded in engineering the TaCo pathway, a synthetic photorespiratory bypass. This new-to-nature metabolic connection opens up new possibilities of CO2 fixation ...
2021-01-11
With the rapid development of smart portable electronics and electric vehicles, the consumption of lithium resource will increase dramatically and the cost of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) may increase significantly in the future. In addition, the shortage (0.0017 wt% in the earth's crust) and uneven crustal distribution of lithium also limit its further development and application. As potassium (2.7 wt% in the earth's crust) have properties similar to lithium and abundant reserves. Therefore, as an alternative to LIBs, potassium ion batteries (PIBs) have become the focus of research. Potassium (2.92 V vs. ...
2021-01-11
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry, led by Nikolaos Koutsouleris, combined psychiatric assessments with machine-learning models that analyse clinical and biological data. Although psychiatrists make very accurate predictions about positive disease outcomes, they might underestimate the frequency of adverse cases that lead to relapses. The algorithmic pattern recognition helps physicians to better predict the course of disease.
The results of the study show that it is the combination of artificial and human intelligence that optimizes the prediction ...
2021-01-11
The spiky structure that erupts from the smooth surface of a ferrofluid when a magnet is brought close can be predicted more accurately than previously thought. KAUST researchers have shown that computational algorithms can calculate the ferrofluid's bristling response to a magnet by simulating only the liquid's surface layer.
Ferrofluids are liquid suspensions of iron-based particles that behave like a regular fluid, but once a magnet is present, the ferrofluid rapidly shape-shifts to form spikes that align with the magnetic field. Originally developed by NASA, ferrofluids have numerous uses ranging from advanced electronics to nanomedicine and have the potential for even broader use, if their magnetic responses could be predicted more accurately.
Dominik Michels and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough on diarrhea virus opens up for new vaccines