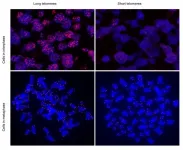
SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrated in a human lung bronchioalveolar tissue model
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) Heidelberg/Germany, 11 January 2021 - Development of an in vitro human-derived tissue model for studying virus infection and disease progression in the alveolar cells of the lungs responsible for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange with the blood might enable the study of possible therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) triggered by SARS-CoV-2. Researchers in the Netherlands have demonstrated that the SARS-CoV-2 replicates efficiently in their model resembling the human bronchioalveolar system that is thought to play a critical role in progression of infection towards pneumonia and ARDS.
It is already established that in people infected with COVID-19 or some other respiratory viruses, alveolar injury can trigger a cascade of events that leads to ARDS, restricting transport of oxygen into the blood to dangerously low levels. There is also mounting evidence that the epithelium lining the alveoli plays a major role in progression of COVID-19. However, in vitro models for replicating disease progression in the alveoli of human lungs have proven difficult to establish, especially models that are also permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection. This has greatly limited our understanding of COVID-19.
The Dutch team has now remedied this deficiency through application of self-renewing organoid models containing stem cells capable of differentiating into relevant cell types for study of disease processes. Organoids are tiny 3D tissues typically around 2 mm in diameter across derived from stem cells to mirror the complex structures of an organ, or at least to express selected aspects of it to meet a given biomedical research objective. Such organoids can then provide continuous sources of 2D tissues that mimic more accurately the geometry or cellular alignment of the structures under study.
A self-renewing organoid model for the epithelium of the airways conducting the gases, has already been developed by the same team, but the alveolar epithelium has proven a greater challenge to generate so far. The Dutch team has overcome this challenge and developed a 2D "air interface" system comprising a basal layer of stem cells in contact with the culture media and a top layer exposed to the air just as it would be in the lungs.
Multiple cultures were generated and infected successfully by SARS-CoV-2 targeting primarily alveolar type-II-like cells, known as ATII-L, confirmed by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), surface marker stainings and single-cell sequencing. The study then shed light on the sequence of events following infection.
The study also identified through messenger RNA expression analysis a cellular immune response to the virus by infected cells. When the cultures were treated with the antiviral signaling molecule interferon lambda early in infection, SARS-CoV-2 replication was almost completely blocked, indicating that - when timed right - interferon lambda could be an effective treatment. These results also indicate that these cultures could be helpful for the development of a therapeutic intervention against acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) from COVID-19.
INFORMATION:
The EMBO Journal
An Organoid-derived Bronchioalveolar Model for SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Alveolar-type II-like Cells
Mart M. Lamers, Jelte van der Vaart, Kèvin Knoops, Samra Riesebosch, Tim I. Breugem, Anna Z. Mykytyn, Joep Beumer, Debby Schipper, Karel Bezstarosti, Charlotte D. Koopman, Nathalie Groen, Raimond B.G. Ravelli, Hans Q. Duimel, Jeroen A.A. Demmers, Georges M.G.M. Verjans, Marion P.G. Koopmans, Mauro J. Muraro, Peter J. Peters, Hans Clevers, Bart L. Haagmans
DOI:10.15252/embj.2020105912
Read the paper: http://www.embopress.org/doi/abs/10.15252/embj.2020105912
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
Two billion years after the Big Bang, the Universe was still very young. However, thousands of huge galaxies, rich in stars and dust, were already formed. An international study, led by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, now explains how this was possible. Scientists combined observational and theoretical methods to identify the physical processes behind their evolution and, for the first time, found evidence for a rapid growth of dust due to a high concentration of metals in the distant Universe. The study, published in Astronomy&Astrophysics, offers a new approach to investigate the evolutionary phase of massive objects.
Since their initial discovery 20 years ago, very distant and massive galaxies that form prodigious amount of ...
2021-01-11
Patients with severe COVID-19 disease have significantly shorter telomeres, according to a study conducted by researchers at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) in collaboration with the COVID-IFEMA Field Hospital, published in the journal Aging. The study, led by Maria A. Blasco and whose first authors are Raúl Sánchez and Ana Guío-Carrión, postulates that telomere shortening as a consequence of the viral infection impedes tissue regeneration and that this is why a significant number of patients suffer prolonged sequelae.
Blasco was already developing a therapy to regenerate lung tissue in pulmonary fibrosis patients; she now believes that this treatment -which should still take at least a year and a half to become available- ...
2021-01-11
NEW YORK, NY (Jan. 11, 2021)--A new study has found that up to 20% of glioblastomas--an aggressive brain cancer--are fueled by overactive mitochondria and may be treatable with drugs currently in clinical trials.
Mitochondria are responsible for creating the energy that fuels all cells. Though they are usually less efficient at producing energy in cancer, tumor cells in this newly identified type of glioblastoma rely on the extra energy provided by overactive mitochondria to survive.
The study, by cancer scientists at Columbia University's Vagelos College ...
2021-01-11
For some years, an active substance from the leaves of an ornamental plant has been regarded as a possible forerunner of a new group of potent drugs. So far, however, it has been very laborious to manufacture it in large quantities. That could now change: Researchers at the University of Bonn (Germany) have identified a bacterium that produces the substance and can also be easily cultivated in the laboratory. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The coralberry currently once again adorns many living rooms: In winter it bears bright red fruits, which make it a popular ornamental plant at this time of year. For pharmacists, however, it is interesting for a different reason: It contains ...
2021-01-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- For years, researchers have worked to repurpose excess atmospheric carbon dioxide into new chemicals, fuels and other products traditionally made from hydrocarbons harvested from fossil fuels. The recent push to mitigate the climactic effects of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has chemists on their toes to find the most efficient means possible. A new study introduces an electrochemical reaction, enhanced by polymers, to improve CO2-to-ethylene conversion efficiency over previous attempts.
The results of the study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign chemistry ...
2021-01-11
Metabolites are organic molecules that take part in or are created during the biochemical reactions constantly taking place in an organism. For the human body, more than 110,000 metabolites have been identified. Metabolites play a role in metabolic syndrome, which is the situation in which several medical conditions occur simultaneously; the conditions include obesity, high blood pressure and high blood sugar. Metabolic syndrome is associated with a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, type-2 diabetes and different kinds of cancer. The presence of certain metabolites can be an indicator for particular pathological ...
2021-01-11
This most likely explains the augmented response of the immune system and the more severe disease progression. However, certain hypertension-reducing drugs known as ACE inhibitors can have a beneficial effect. They not only lower blood pressure, but also counteract immune hyperactivation. The scientists have now published their findings in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
More than one billion people worldwide suffer from high blood pressure, or hypertension. Of the more than 75 million people around the world who have become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide so far, more than 16 million also have hypertension. These patients are more likely to become severely ill, which in turn results in an increased ...
2021-01-11
NEW YORK, NY (Jan. 11, 2021)--Thousands of different genetic mutations have been implicated in cancer, but a new analysis of almost 10,000 patients found that regardless of the cancer's origin, tumors could be stratified in only 112 subtypes and that, within each subtype, the Master Regulator proteins that control the cancer's transcriptional state were virtually identical, independent of the specific genetic mutations of each patient.
The study, published Jan. 11 in Cell, confirms that Master Regulators provide the molecular logic that integrates the effect ...
2021-01-11
Philadelphia, January 11, 2021 - Children and adolescents with a family history of suicide attempts have lower executive functioning, shorter attention spans, and poorer language reasoning than those without a family history, according to a new study by researchers from the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania. The study is the largest to date to examine the neurocognitive functioning of youth who have a biological relative who made a suicide attempt.
The findings, which were first published online last March, were published in the January 2021 edition of The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Researchers looked at 3,507 youth aged 8 to 21. Of those, ...
2021-01-11
Russian researchers have proposed a new method for synthesizing high-quality graphene nanoribbons -- a material with potential for applications in flexible electronics, solar cells, LEDs, lasers, and more. Presented in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, the original approach to chemical vapor deposition, offers a higher yield at a lower cost, compared with the currently used nanoribbon self-assembly on noble metal substrates.
Silicon-based electronics are steadily approaching their limits, and one wonders which material could give our devices the next big push. Graphene, the 2D sheet of carbon atoms, comes to mind but for all its celebrated electronic properties, it does not have what it takes: Unlike silicon, graphene does not have the ability to switch between ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrated in a human lung bronchioalveolar tissue model