Pillar-like molecules as biosensors for metabolites
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) Metabolites are organic molecules that take part in or are created during the biochemical reactions constantly taking place in an organism. For the human body, more than 110,000 metabolites have been identified. Metabolites play a role in metabolic syndrome, which is the situation in which several medical conditions occur simultaneously; the conditions include obesity, high blood pressure and high blood sugar. Metabolic syndrome is associated with a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, type-2 diabetes and different kinds of cancer. The presence of certain metabolites can be an indicator for particular pathological conditions related to metabolic syndrome. Efficiently measuring and monitoring the presence is therefore important for early diagnosis. Now, Tomoki Ogoshi*, Atsushi Hirao*, and Masaya Ueno (*correspondence authors) from Kanazawa University and colleagues have developed a biosensor for a low-molecular-weight metabolite known as 1-MNA. The sensor relies on the physicochemical properties of pillar[6]arene, a channel-like molecule.
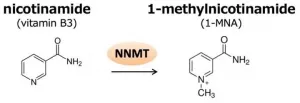
The researchers investigated the metabolite 1-MNA (1-methylnicotinamide), recently discovered to be present in higher levels in aggressive cancer cell lines. These cancers have increased NNMT (nicotinamide N-methyltransferase) activity in which 1-MNA is a byproduct. Detecting 1-MNA could be therefore crucial for the timely diagnosis and treatment of such cancers.
Ogoshi and colleagues hypothesized that pillar[n]arenes could be used as biosensors for metabolites like 1-MNA. Pillar[n]arenes are pillar-shaped macrocyclic compounds with a polygonal cross-section (pentagonal and hexagonal for n = 5 and 6, respectively). The researchers found that pillar[6]arene (P6A) forms host-guest a complex with 1-MNA; the metabolite can bind to it because the hexagonal cavity inside P6A offers just the right environment for doing so. They also found that when 1-MNA is bound to P6A, the fluorescent response of the latter significantly decreases -- an effect that can be exploited as an indicator for the presence or absence of 1-MNA (strong or weak fluorescent response, respectively).
Importantly, the scientists could show that the P6A fluorescence detection mechanism works for biological samples. Specifically, they were able to detect 1-MNA in urine, albeit with a low sensitivity. Ogoshi and colleagues conclude that additional experiments "will help to improve the sensitivity and specificity of the biosensors", and that their work "should contribute to the development of low-cost, easy, and rapid methods for the detection of human metabolites for diagnosis".
[Background]
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome refers to the combination of diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension) and obesity. Patients with metabolic syndrome are at a greater risk for developing certain cardiovascular diseases as well as different types of cancer. Metabolic syndrome is often associated with being overweight and a lack of physical activity, and is also linked to insulin resistance (a key feature of type-2 diabetes).
Now, Tomoki Ogoshi from Kanazawa University and colleagues have developed a biosensor for a metabolite known as 1-MNA. Being able to efficiently detect metabolites associated with certain pathologies is an important step forward towards the development of treatments for pathologies associated with metabolic syndrome.
Pillar[n]arenes
Pillar[n]arenes, collectively named pillararenes (and sometimes pillarenes), are cyclic organic molecules consisting of n so-called hydroquinone units, which can be substituted. Hydroquinone, also known as quinol, has the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It consists of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl (OH) groups bound to it at opposite sides of the benzene hexagon.
The first pillararene was synthesized in 2008 by Tomoki Ogoshi and colleagues from Kanazawa University. The name pillararene was chosen since the molecules are cylindrical (pillar-like) in shape and composed of aromatic moieties (arenes).
Now, Ogoshi, Hirao and colleagues have shown that pillar[6]arene (n = 6) can be used as biosensors for the metabolite 1-MNA -- an important result given that detecting low-molecular-weight metabolites is challenging.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
This most likely explains the augmented response of the immune system and the more severe disease progression. However, certain hypertension-reducing drugs known as ACE inhibitors can have a beneficial effect. They not only lower blood pressure, but also counteract immune hyperactivation. The scientists have now published their findings in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
More than one billion people worldwide suffer from high blood pressure, or hypertension. Of the more than 75 million people around the world who have become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide so far, more than 16 million also have hypertension. These patients are more likely to become severely ill, which in turn results in an increased ...
2021-01-11
NEW YORK, NY (Jan. 11, 2021)--Thousands of different genetic mutations have been implicated in cancer, but a new analysis of almost 10,000 patients found that regardless of the cancer's origin, tumors could be stratified in only 112 subtypes and that, within each subtype, the Master Regulator proteins that control the cancer's transcriptional state were virtually identical, independent of the specific genetic mutations of each patient.
The study, published Jan. 11 in Cell, confirms that Master Regulators provide the molecular logic that integrates the effect ...
2021-01-11
Philadelphia, January 11, 2021 - Children and adolescents with a family history of suicide attempts have lower executive functioning, shorter attention spans, and poorer language reasoning than those without a family history, according to a new study by researchers from the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania. The study is the largest to date to examine the neurocognitive functioning of youth who have a biological relative who made a suicide attempt.
The findings, which were first published online last March, were published in the January 2021 edition of The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Researchers looked at 3,507 youth aged 8 to 21. Of those, ...
2021-01-11
Russian researchers have proposed a new method for synthesizing high-quality graphene nanoribbons -- a material with potential for applications in flexible electronics, solar cells, LEDs, lasers, and more. Presented in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, the original approach to chemical vapor deposition, offers a higher yield at a lower cost, compared with the currently used nanoribbon self-assembly on noble metal substrates.
Silicon-based electronics are steadily approaching their limits, and one wonders which material could give our devices the next big push. Graphene, the 2D sheet of carbon atoms, comes to mind but for all its celebrated electronic properties, it does not have what it takes: Unlike silicon, graphene does not have the ability to switch between ...
2021-01-11
CHICAGO (January 11, 2021): A new study of liver transplant centers confirms that non-Hispanic white patients get placed on liver transplant waitlists at disproportionately higher rates than non-Hispanic Black patients. However, researchers went a step further as they identified key reasons for that disparity: disproportionate access to private health insurance, travel distance to transplant centers, and a potential lack of knowledge among both practitioners and patients about available options. The study was selected for the 2020 Southern Surgical Association Program and published as an "article in press" on the website of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons in advance of print.
"We found that the Black population was underrepresented at the vast majority of centers, ...
2021-01-11
All-solid-state batteries are the next-generation batteries that can simultaneously improve the stability and capacity of existing lithium batteries. The use of non-flammable solid cathodes and electrolytes in such batteries considerably reduces the risk of exploding or catching fire under high temperatures or external impact and facilitates high energy density, which is twice that of lithium batteries. All-solid-state batteries are expected to become a game changer in the electric vehicle and energy storage device markets. Despite these advantages, the low ionic conductivity of solid electrolytes combined with their high interfacial resistance and rapid deterioration reduce battery performance and life, thus limiting their commercialization.
The ...
2021-01-11
Special Issue: Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Delivery
Guest Editors: Huile Gao, West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China; Zhiqing Pang, Fudan University, Shanghai, China and Wei He, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is a monthly journal, in English, which publishes significant original research articles, rapid communications and high quality reviews of recent advances in all areas of pharmaceutical sciences -- including pharmacology, pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, natural products, ...
2021-01-11
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is a monthly journal, in English, which publishes significant original research articles, rapid communications and high quality reviews of recent advances in all areas of pharmaceutical sciences -- including pharmacology, pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, natural products, pharmacognosy, pharmaceutical analysis and pharmacokinetics.
Featured papers in this issue are:
Berberine diminishes cancer cell PD-L1 expression and facilitates antitumor immunity via inhibiting the deubiquitination activity of CSN5 by authors Yang Liu, Xiaojia Liu, Na Zhang, Mingxiao Yin, Jingwen Dong, Qingxuan ...
2021-01-11
"The findings provide an increased understanding of how the virus gets through the stomach and intestinal system. Continued research can provide answers to whether this property can also be used to create vaccines that ride 'free rides' and thus be given in edible form instead of as syringes," says Lars-Anders Carlson, researcher at Umeå University.
The virus that the researchers have studied is a so-called enteric adenovirus. It has recently been clarified that enteric adenoviruses are one of the most important factors behind diarrhea among infants, and they are estimated to kill more than 50,000 children under the age of five each year, ...
2021-01-11
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have discovered a key mechanism underlying bacterial skin colonisation in atopic dermatitis, which affects millions around the globe.
Atopic dermatitis (AD, also called commonly eczema) is the most common chronic inflammatory skin disorder in children, affecting 15-20% of people in childhood. During disease flares, patients experience painful inflamed skin lesions accompanied by intense itch and recurrent skin infection.
The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) thrives on skin affected by AD, increasing inflammation and worsening AD symptoms. Although a small number of therapies are available at present for patients with moderate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pillar-like molecules as biosensors for metabolites