2D compound shows unique versatility
Multifunctional nanomaterial proposed by Rice could enhance solar energy, quantum computing
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (Jan. 11, 2021) - An atypical two-dimensional sandwich has the tasty part on the outside for scientists and engineers developing multifunctional nanodevices.
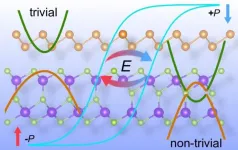
An atom-thin layer of semiconductor antimony paired with ferroelectric indium selenide would display unique properties depending on the side and polarization by an external electric field.
The field could be used to stabilize indium selenide's polarization, a long-sought property that tends to be wrecked by internal fields in materials like perovskites but would be highly useful for solar energy applications.
Calculations by Rice materials theorist Boris Yakobson, lead author and researcher Jun-Jie Zhang and graduate student Dongyang Zhu shows switching the material's polarization with an external electric field makes it either a simple insulator with a band gap suitable for visible light absorption or a topological insulator, a material that only conducts electrons along its surface.
Turning the field inward would make the material good for solar panels. Turning it outward could make it useful as a spintronic device for quantum computing.
The lab's study appears in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
"The ability to switch at will the material's electronic band structure is a very attractive knob," Yakobson said. "The strong coupling between ferroelectric state and topological order can help: the applied voltage switches the topology through the ferroelectric polarization, which serves as an intermediary. This provides a new paradigm for device engineering and control."
Weakly bound by the van der Waals force, the layers change their physical configuration when exposed to an electric field. That changes the compound's band gap, and the change is not trivial, Zhang said.
"The central selenium atoms shift along with switching ferroelectric polarization," he said. "This kind of switching in indium selenide has been observed in recent experiments."
Unlike other structures proposed and ultimately made by experimentalists -- boron buckyballs are a good example -- the switching material may be relatively simple to make, according to the researchers.
"As opposed to typical bulk solids, easy exfoliation of van der Waals crystals along the low surface energy plane realistically allows their reassembly into heterobilayers, opening new possibilities like the one we discovered here," Zhang said.
INFORMATION:
Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry at Rice.
The Army Research Office, the Office of Naval Research and the Robert Welch Foundation supported the research.
Read the abstract at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04531.
This news release can be found online at https://news.rice.edu/2021/01/11/2d-compound-shows-unique-versatility/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Yakobson Research Group: https://biygroup.blogs.rice.edu
Rice Department of Materials Science and Nanoengineering: https://msne.rice.edu
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
Image for download:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/01/0111_FERRO-1a-WEB.jpg
Rice University materials theorists show how a unique two-dimensional compound of antimony and indium selenide can have distinct properties on each side, depending on polarization by an external electric field, with possible applications in solar energy and quantum computing. The figure indicates that two states for nonvolatile memory devices can be flipped by the polarization of the ferroelectric layer. (Credit: Illustration by Jun-Jie Zhang/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-11
MDC researchers have developed a new approach to CAR T-cell therapy. The team has shown in Nature Communications that the procedure is very effective, especially when it comes to fighting follicular lymphomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the most common type of blood cancer in adults.
The body's defense system generally does not recognize cancer cells as dangerous. To correct this sometimes fatal error, researchers are investigating a clever new idea, one that involves taking a handful of immune cells from cancer patients and "upgrading" them in the laboratory so that they recognize certain surface proteins in the malignant cells. The researchers then multiply ...
2021-01-11
Stress on an expectant mother could affect her baby's chance of developing disease - perhaps even over the course of the child's life, UC researchers have found.
Psychosocial factors creating stress -- such as lack of social support, loneliness, marriage status or bereavement -- may be mutating their child's mitochondrial DNA and could be a precursor to a host of diseases, according to a University of Cincinnati study.
"There are a lot of conditions that start in childhood that have ties to mitochondrial dysfunction including asthma, obesity, attention deficit hyperactivity ...
2021-01-11
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- University at Buffalo researchers are reporting an advancement of a chemical sensing chip that could lead to handheld devices that detect trace chemicals -- everything from illicit drugs to pollution -- as quickly as a breathalyzer identifies alcohol.
The chip, which also may have uses in food safety monitoring, anti-counterfeiting and other fields where trace chemicals are analyzed, is described in a study that appears on the cover of the Dec. 17 edition of the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
"There is a great need for portable and cost-effective chemical sensors ...
2021-01-11
Pregnant women who exercise more during the first trimester of pregnancy may have a lower risk of developing gestational diabetes, according to a new study led by Samantha Ehrlich, an assistant professor in the Department of Public Health at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and adjunct investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research. The analysis found that lower risk was associated with at least 38 minutes of moderate intensity exercise each day--a bit more than current recommendations of at least 30 minutes a day five days a week.
Gestational diabetes refers to diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy. It can pose serious health problems including pregnancy and delivery complications as well as increased future risk for diabetes ...
2021-01-11
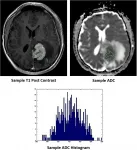
The cover for issue 45 of Oncotarget features Figure 3, "Representative images of whole tumor volume segmentation of the co-registered T1 post-contrast sequence and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map, yielding the corresponding ADC histogram distribution utilized for data analysis," recently published in "Diffusion-weighted MR imaging histogram analysis in HIV positive and negative patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma as a predictor of outcome and tumor proliferation" by Khan, et al.
This authors reported that the aim of this study is to investigate the correlation between ...
2021-01-11
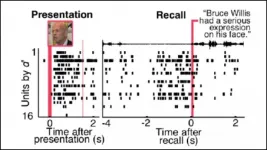
Face-sensitive neurons in humans employ distinct activity patterns to encode individual faces; those patterns reactivate when imagining the face, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
Human social interaction hinges on faces. In fact, faces are so important that the brain contains entire regions in the ventral temporal cortex devoted to facial recognition. In humans, the fusiform facial area activates in response to faces, and monkeys have single neurons that fire when shown a face. However, experimental limitations have prevented us from knowing how the human brain responds to and processes faces at the level of the single neuron.
To close this gap, Khuvis et al. measured the electrical activity of neurons in the ventral temporal ...
2021-01-11
HOUSTON - (Jan. 11, 2021) - Rice University engineers hope to make life better for those with replacement joints by modeling how artificial hips are likely to rub them the wrong way.
The computational study by the Brown School of Engineering lab of mechanical engineer Fred Higgs simulates and tracks how hips evolve, uniquely incorporating fluid dynamics and roughness of the joint surfaces as well as factors clinicians typically use to predict how well implants will stand up over their expected 15-year lifetime.
The team's immediate goal is to advance the design of more robust prostheses.
Ultimately, they say the model could help clinicians personalize hip joints for patients depending on gender, ...
2021-01-11
In most animal species, if a major artery is cut off from the heart, the animal will struggle to survive. The same can be said for many of our critical infrastructure systems, such as electric power, water and communications. They are networked systems with vulnerable connections.
This vulnerability was on display in September 2017 when Hurricane Maria wrecked Puerto Rico's electric power grid, leaving almost all of the island's 3.3 million people without electricity. The months-long blackout that followed was the worst in U.S. history.
Claire Trevisan, ...
2021-01-11
Oncotarget recently published "PD-1/PD-L1 expression in anal squamous intraepithelial lesions" which reported that the presence and distribution of CD8 lymphocytes and the presence of PD-1 lymphocytes and PD-L1 epithelial cells were assessed.
CD8 lymphocytes were observed more frequently in HSIL versus LSIL in the lamina propria or intra epithelial.
PD-1 lymphocytes were observed more frequently in HSIL versus LSIL.
There was no difference between HSIL and LSIL for PD-L1 epithelial cells.
Anal dysplastic lesions are accompanied by an inflammatory lymphocytic infiltrate expressing CD8 and PD-1, more frequent in high-grade lesions.
Dr. ...
2021-01-11
A team led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers has discovered a groundbreaking one-step process for creating materials with unique properties, called metamaterials. Their results show the realistic possibility of designing similar self-assembled structures with the potential of creating "built-to-order" nanostructures for wide application in electronics and optical devices.
The research was published and featured on the cover of Nano Letters, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society.
In general, metamaterials are materials made in the lab so as to provide specific physical, chemical, electrical, and optical properties otherwise impossible to find in naturally occurring materials. These materials can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 2D compound shows unique versatility
Multifunctional nanomaterial proposed by Rice could enhance solar energy, quantum computing