(Press-News.org) Reza Shahbazian-Yassar, professor of mechanical and industrial engineering at the University of Illinois Chicago.
Shahbazian-Yassar and colleagues facilitated the development of a cutting edge "Swiss Army knife" catalyst made up of 10 different elements - each of which on its own has the ability to reduce the combustion temperature of methane - plus oxygen. This unique catalyst can bring the combustion temperature of methane down by about half - from above 1400 degrees Kelvin down to 600 to 700 degrees Kelvin.
Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Catalysis.
In previously-published research, Shahbazian-Yassar and colleagues demonstrated the ability to create multi-element nanoparticle catalysts, known as high entropy alloys using a unique shock-wave technique. Before this, materials scientists didn't make serious attempts to create nanoparticles out of more than three elements because of the tendency of each elements' atoms to separate from each other and become useless.
Taking advantage of the unique real-time, high-temperature electron microscopy system at UIC, Shahbazian-Yassar's team showed that high entropy nanoparticles made up of 10 metal oxides were highly stable at temperatures up to 1,073 degrees Kelvin and the individual elements were distributed evenly throughout each nanoparticle forming a single, solid-state stable crystalline structure.
Their metal oxide alloy contained various mixtures of transition metals, which are rare-earth elements, and noble metals plus oxygen.
"It is almost impossible to maintain a perfect mix of these elements in a solid phase due to the differences in atomic radius, crystal structure, oxidation potential, and electronic properties of the elements," said Zhennan Huang, a Ph.D. student in Shahbazian-Yassar's lab and co-first author in the paper. "But we were able to show that this is possible."
"Among multiple alloys with multiple elements that we created, the particles made of 10 elements not only were most effective in reducing the combustion point of methane gas but also the most stable at those temperatures," said Shahbazian-Yassar, who is a corresponding author on the paper.
The researchers believe the catalyst could be used to reduce the output of harmful greenhouse gases produced by burning natural gas in individual households, to power turbines and even in cars that run on compressed natural gas.
INFORMATION:
Tangyuan Li, Yonggang Yao, Menghao Yang, Jinglong Gao, Alexandra Brozena, Liangbing Hu, Yifei Mo, Glenn Pastel, Miaolun Jiao, Qi Dong, Jiaqi Dai and Shuke Li of the University of Maryland; Pengfei Xie, Kaizhu Zeng, Han Zong and Chao Wang of Johns Hopkins University; Zhenyu Liu and Guofeng Wang of the University of Pittsburgh; Miaofang Chi of Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Jian Luo of the University of California, San Diego, are co-authors on the paper.
Tales of post-apocalyptic landscapes in which few survivors emerge into a new and much different world have long been popular tales woven by screenwriters and authors. While many enjoy these stories, thinking of them as nothing but a guilty pleasure, they may not realize that immersing themselves in fiction has prepared them for the reality of 2020, according to a team of researchers.
John Johnson, professor emeritus of psychology at Penn State, recently conducted research with several colleagues revealing that an individual's enjoyment of horror films could have better prepared them for the COVID-19 pandemic as opposed to others who do not enjoy frightening entertainment. Their findings are documented in Personality and Individual Differences.
"My latest ...
The first-ever study of the levels of the stress hormone cortisol in the saliva of newborn white-tailed deer fawns yielded thought-provoking results that have Penn State researchers suggesting predation is not the only thing in the wild killing fawns.
"We think the hormone offers a way to evaluate factors in the environment that affect fawns, such as disease, but are difficult to evaluate when just looking at a carcass that has been picked over by predators," said researcher Duane Diefenbach, adjunct professor of wildlife ecology. "By then, it's impossible to be certain what ...
University of Wyoming researchers headed a study that shows nonnative birds in Oahu, Hawaii, have taken over the role of seed dispersal networks on the island, with most of the seeds coming from nonnative plants.
"Hawaii is one of the most altered ecosystems in the world, and we are lucky enough to examine how these nonnative-dominated communities alter important processes, such as seed dispersal," says Corey Tarwater, an assistant professor in the UW Department of Zoology and Physiology. "What we have found is that not only do nonnative species dominate species ...
Boston, Mass. - As the number of COVID-19 infections continues to rise nationwide, more than 360,000 Americans have already died from the potentially deadly viral infection. But recent reports describe an increase in mortality during the pandemic that cannot be explained by COVID-19 deaths alone.
In a new study from the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), researchers analyzed data from the National Center for Health Statistics to compare the rate of cardiovascular-related deaths before and after the onset of the pandemic in ...
Mindfulness courses can reduce anxiety, depression and stress and increase mental wellbeing within most but not all non-clinical settings, say a team of researchers at the University of Cambridge. They also found that mindfulness may be no better than other practices aimed at improving mental health and wellbeing.
Mindfulness is typically defined as 'the awareness that emerges through paying attention on purpose, in the present moment, and nonjudgmentally to the unfolding of experience moment by moment'. It has become increasingly popular in recent years as a way of increasing wellbeing and ...
Deaths from ischemic heart disease and hypertensive diseases in the United States increased during the COVID-19 pandemic over the prior year, while globally, COVID-19 was associated with significant disruptions in cardiovascular disease testing. These findings are from two papers publishing in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology that examined the indirect effects of the pandemic on cardiovascular disease patients and their care.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has been substantial, but there are concerns about the indirect impact of the pandemic as well, particularly for heart disease patients. Many reports have suggested that large mortality increases during the pandemic cannot be explained by COVID-19 alone. During the height of stay-at-home orders in the U.S., hospitals ...
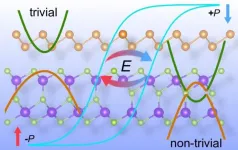
HOUSTON - (Jan. 11, 2021) - An atypical two-dimensional sandwich has the tasty part on the outside for scientists and engineers developing multifunctional nanodevices.
An atom-thin layer of semiconductor antimony paired with ferroelectric indium selenide would display unique properties depending on the side and polarization by an external electric field.
The field could be used to stabilize indium selenide's polarization, a long-sought property that tends to be wrecked by internal fields in materials like perovskites but would be highly useful for solar energy applications.
Calculations by Rice materials theorist Boris Yakobson, lead author and researcher Jun-Jie Zhang and graduate student Dongyang Zhu shows switching the material's polarization with an external electric field makes ...
MDC researchers have developed a new approach to CAR T-cell therapy. The team has shown in Nature Communications that the procedure is very effective, especially when it comes to fighting follicular lymphomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the most common type of blood cancer in adults.
The body's defense system generally does not recognize cancer cells as dangerous. To correct this sometimes fatal error, researchers are investigating a clever new idea, one that involves taking a handful of immune cells from cancer patients and "upgrading" them in the laboratory so that they recognize certain surface proteins in the malignant cells. The researchers then multiply ...
Stress on an expectant mother could affect her baby's chance of developing disease - perhaps even over the course of the child's life, UC researchers have found.
Psychosocial factors creating stress -- such as lack of social support, loneliness, marriage status or bereavement -- may be mutating their child's mitochondrial DNA and could be a precursor to a host of diseases, according to a University of Cincinnati study.
"There are a lot of conditions that start in childhood that have ties to mitochondrial dysfunction including asthma, obesity, attention deficit hyperactivity ...
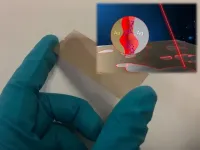
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- University at Buffalo researchers are reporting an advancement of a chemical sensing chip that could lead to handheld devices that detect trace chemicals -- everything from illicit drugs to pollution -- as quickly as a breathalyzer identifies alcohol.
The chip, which also may have uses in food safety monitoring, anti-counterfeiting and other fields where trace chemicals are analyzed, is described in a study that appears on the cover of the Dec. 17 edition of the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
"There is a great need for portable and cost-effective chemical sensors ...