Healthcare Nutrition Council leads the way on medical food discussions
Announcement of publication of workshop proceedings
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) While most people are able to eat a normal diet, many of those managing distinct nutritional requirements related to a disease or health condition rely on medical foods. Medical foods help patients meet their nutritional needs, often improving nutritional and health outcomes and quality of life. A recent publication in Current Developments in Nutrition, titled "Medical Foods: Science, Regulation, and Practical Aspects. Summary of a Workshop," shares the historical and regulatory context of medical foods and perspectives on their role in the future.
Medical foods help patients manage their nutritional needs, yet it can be very difficult for patients to have access to them. In August 2019, the Healthcare Nutrition Council (HNC), in partnership with the American Society for Nutrition (ASN), held the Medical Foods Workshop: Science, Regulation, and Practical Aspects. The workshop discussions focused on:
Patient and healthcare professional considerations for and benefits from medical foods.
Opportunities for product innovation and future research. Real-world examples were discussed for enteral tube feeding, surgery and trauma, intractable epilepsy, diabetes, renal disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The role of clinical guidelines for developing and use of medical foods.
The use of medical foods in clinical practice under medical supervision.
The statutory term distinctive nutritional requirements.
The regulatory term modification of the diet alone.
Differentiation of medical foods from foods for special dietary use.
"The objectives of our workshop were to advance the dialogue on the scientific and regulatory status of medical foods in the U.S., drive consensus on terms and definitions for medical foods, and ultimately help improve patient access to these important products," said Robert Rankin, Executive Director of HNC. "It was extremely important that the workshop included a variety of stakeholders, encompassing patients, clinicians, government officials, and the medical food industry. We have more work ahead to improve the landscape for medical foods, assuring that the regulatory framework fosters research, innovation, and development for these important products as well as assuring patients have access to products which improve their clinical care."
INFORMATION:
The workshop proceedings are available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/cdn/nzaa172.
About the Healthcare Nutrition Council (HNC): HNC is an organization representing the manufacturers of nutrition support products, specifically enteral nutrition (EN) formulas, parenteral nutrition (PN) solutions, supplies and equipment. HNC member companies are committed to improving health by advancing policies that address and raise awareness of nutrition and its impact on patient outcomes and healthcare costs. This includes promoting nutritional screenings, diagnoses, assessments, and appropriate and timely clinical nutrition interventions while maintaining patients' access to specialized nutrition support products and services throughout the continuum of care. For more information about HNC, please visit healthcarenutrition.org.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
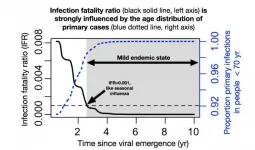
What is the endgame for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that is causing worldwide devastation? If it becomes endemic -- circulating in the general population -- and most people are exposed in childhood, SARS-CoV-2 may join the ranks of mild cold-causing coronaviruses that currently circulate in humans, according to a model developed by Emory and Penn State scientists.
The model, published January 12 in Science, draws upon studies of the four common cold coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-1. For those viruses, the term "herd immunity" is incomplete and possibly misleading, says ...
2021-01-12
Antibodies are an important weapon in the immune system's defense against infections. They bind to the surface structures of bacteria or viruses and prevent their replication. One strategy in the fight against disease is therefore to produce effective antibodies in large quantities and inject them into the patients. The outgoing US President Donald Trump probably owes his rapid recovery to this method. However, the antibodies used to treat him have a complex structure, do not penetrate very deeply into the tissue and may cause unwanted complications. Moreover, producing antibodies is difficult and time-consuming. They are therefore probably not suitable for widespread use.
Mass production in yeast or bacteria
"We focus on another group of molecules, the nanobodies," ...
2021-01-12
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed, in collaboration with researchers in Germany and the U.S., new small antibodies, also known as nanobodies, which prevent the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus from entering human cells. The research study, published in Science, shows that a combined nanobody had a particularly good effect - even if the virus mutated. According to the researchers, the nanobodies have the potential to be developed into a treatment for COVID-19.
Specific proteins, spike proteins, on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus help the virus infect host cells. Therefore, antibodies that block the spike proteins and prevent them from binding to the cell can be a way to stop infection.
From the perspective ...
2021-01-12
What will the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak look like ten years from now as it passes from pandemic to endemic, maintained at a constant baseline level in populations without being fueled by outside infections? Data from four endemic human coronaviruses, which circulate globally and cause only mild symptoms, may hold some answers, say Jennie Lavine and colleagues. Their analysis of the immunological and epidemiological data for these viruses helped them develop a model to predict the trajectory of SARS-CoV-2 as it becomes endemic. Most importantly, the authors say, their model incorporates distinct components of immunological protection--susceptibility to reinfection, weakening of the disease after reinfection, and transmissibility of the virus after reinfection--that each wane differently. Lavine ...
2021-01-12
An immunization strategy tested in mice protects against infection from SARS-CoV-2, as well as from potentially emerging animal coronaviruses, researchers say. The approach could be "used as described or easily adapted" to provide defense against newly discovered zoonotic coronaviruses. In the last 20 years, three betacoronaviruses have caused devastating disease in humans. The global pandemic caused by the latest such virus, SARS-CoV-2, highlights the need to protect against other strains that could present a threat to humans, possibly through a pan-coronavirus vaccine. To support related efforts, ...
2021-01-12
Thanks to major progress in the understanding and management of rare congenital diseases and syndromes, many patients with these rare disorders are now living longer lives. With this progress it has become apparent that many non-skeletal rare diseases have an impact on bone mass, bone quality and/or bone metabolism, with potentially severe repercussions for quality of life in adults.
The new paper 'Bone fragility in patients affected by congenital diseases non skeletal in origin', published in Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) Skeletal Rare Diseases Working Group (SRDWG), provides ...
2021-01-12
Most people experience turbulence primarily from the experience of flying in an airplane. However, turbulence is a key feature of nature and is found everywhere, from rivers to galaxies.
Turbulent-like dynamics are difficult to capture in a still image. However, Leonardo da Vinci did everything possible to identify the underlying order of the phenomenon, which he observed in eddy currents forming randomly in water. In fact, he was fascinated by trying to understand and describe the generating principles governing such complicated dynamics. This is so much ...
2021-01-12
Scientists are combining artificial intelligence and advanced computer technology with biological know how to identify insects with supernatural speed. This opens up new possibilities for describing unknown species and for tracking the life of insects across space and time
Insects are the most diverse group of animals on Earth and only a small fraction of these have been found and formally described. In fact, there are so many species that discovering all of them in the near future is unlikely.
This enormous diversity among insects also means that they have very different life histories and roles in the ecosystems.
For ...
2021-01-12
A new study conducted at the New England Aquarium finds that as climate change causes the ocean to warm, baby sharks are born smaller, exhausted, undernourished, and into environments that are already difficult for them to survive in.
In a recently published paper in the journal Scientific Reports, lead author Carolyn Wheeler, a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Massachusetts Boston and at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University, examined the effects of increased temperatures on the growth, development and physiological performance of epaulette ...
2021-01-12
It's been more than a year since the first cases were identified in China, yet the exact origins of the COVID-19 pandemic remain a mystery. Though strong evidence suggests that the responsible coronavirus originated in bats, how and when it crossed from wildlife into humans is unknown.
In a study published online Jan.12 in the journal mBio, an international team of 15 biologists say this lack of clarity has exposed a glaring weakness in the current approach to pandemic surveillance and response worldwide.
In most recent studies of animal-borne pathogens with the potential to spread to humans, known as zoonotic pathogens, physical specimens of suspected wildlife ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Healthcare Nutrition Council leads the way on medical food discussions
Announcement of publication of workshop proceedings