(Press-News.org) A loss of biodiversity and accelerating climate change in the coming decades coupled with ignorance and inaction is threatening the survival of all species, including our very own, according to the experts from institutions including Stanford University, UCLA, and Flinders University.
The researchers state that world leaders need a 'cold shower' regarding the state of our environment, both to plan and act to avoid a ghastly future.
Lead author Professor Corey Bradshaw of Flinders University in Australia says he and his colleagues have summarised the state of the natural world in stark form to help clarify the gravity of the human predicament.
"Humanity is causing a rapid loss of biodiversity and, with it, Earth's ability to support complex life. But the mainstream is having difficulty grasping the magnitude of this loss, despite the steady erosion of the fabric of human civilization" Professor Bradshaw says.
"In fact, the scale of the threats to the biosphere and all its lifeforms is so great that it is difficult to grasp for even well-informed experts.
"The problem is compounded by ignorance and short-term self-interest, with the pursuit of wealth and political interests stymying the action that is crucial for survival" he says.
Professor Paul Ehrlich of Stanford University says that no political or economic system, or leadership, is prepared to handle the predicted disasters, or even capable of such action.
"Stopping biodiversity loss is nowhere close to the top of any country's priorities, trailing far behind other concerns such as employment, healthcare, economic growth, or currency stability.
"While it is positive news that President-elect Biden intends to reengage the US in Paris Climate accord within his first 100 days of office, it is a minuscule gesture given the scale of the challenge.
"Humanity is running an ecological Ponzi scheme in which society robs nature and future generations to pay for short-term economic enhancement today".
"Most economies operate on the basis that counteraction now is too costly to be politically palatable. Combined with disinformation campaigns to protect short-term profits it is doubtful that the scale of changes we need will be made in time" Professor Ehrlich says.
Professor Dan Blumstein from UCLA says the scientists are choosing to speak boldly and fearlessly because life literally depends on it.
"What we are saying might not be popular, and indeed is frightening. But we need to be candid, accurate, and honest if humanity is to understand the enormity of the challenges we face in creating a sustainable future.
"Without political will backed by tangible action that scales to the enormity of the problems facing us, the added stresses to human health, wealth, and well-being will perversely diminish our political capacity to mitigate the erosion of the Earth's life-support system upon which we all depend.
"Human population growth and consumption continues to escalate, and we're still more focused on expanding human enterprise than we are on devising and implementing solutions to critical issues such as biodiversity loss. By the time we fully comprehend the impact of ecological deterioration, it will be too late.
"Without fully appreciating and broadcasting the scale of the problems and the enormity of the solutions required, society will fail to achieve even modest sustainability goals, and catastrophe will surely follow" Professor Blumstein concludes.
The experts say their 'perspective' paper, which cites more than 150 studies, seeks to outline clearly and unambiguously the likely future trends in biodiversity decline, mass extinction, climate disruption, planetary toxification, all tied to human consumption and population growth to demonstrate the near certainty that these problems will worsen over the coming decades, with negative impacts for centuries to come. It also explains the impact of political impotence and the ineffectiveness of current and planned actions to address the ominous scale of environmental erosion.
INFORMATION:
The perspective paper "Underestimating the challenges of avoiding a ghastly future" is published in
Frontiers in Conservation Science 1:615419 [Jan 2021 DOI:10.3389/fcosc.2020.615419]
Tsukuba, Japan - Work causes so much stress that it's become a global public health issue. Stress's impact on mental and physical health can also hurt productivity and result in economic loss. A new study now finds that working people who regularly take walks in forests or greenspaces may have higher stress-coping abilities.
In a study published in Public Health in Practice, researchers led by Professor Shinichiro Sasahara at the University of Tsukuba analyzed workers' "sense of coherence" (SOC) scores, demographic attributes, and their forest/greenspace walking habits. SOC comprises the triad of meaningfulness (finding a sense of meaning in life), comprehensibility (recognizing and understanding stress), and ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Jan. 13, 2021)--If you're a bit more forgetful or having more difficulty processing complex concepts than in the past, the problem may be your menopause stage. A new study claims that menopause stage is a key determinant of cognition and, contrary to previous studies, shows that certain cognitive declines may continue into the postmenopause period. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
It's commonly assumed that people's memories decline with age, as does their ability to learn new things and grasp challenging concepts. ...
The ability of our skin to protect us from chemicals is something we inherit. Some people are less well-protected which could imply an increased risk of being afflicted by skin disease or cancer. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden that has been published in Environmental Health Perspectives shows how the rate of uptake of common chemicals is faster in people with a genetically weakened skin barrier.
We are continually exposed to chemicals from many different sources, for example, food, hygiene products, cosmetics and textiles. Many people are also exposed to chemicals at their place of work which can constitute a work environment problem.
The protein filaggrin is important for the structure and moisture balance of the skin, properties that affect ...
January 13, 2021 - The element nitrogen is a double-edged sword. It is essential for growing plants and feeding people, but it is also a leading cause of pollution across the world. Only by using nitrogen more sustainably can the positive and harmful effects of nitrogen be balanced.
Xia (Emma) Liang, a member of the American Society of Agronomy, studies nitrogen loss during food production.
Liang and her team created a framework that accurately measures nitrogen loss across a wide variety of crops and food products. She recently presented their research at the virtual 2020 ASA-CSSA-SSSA Annual Meeting.
"This framework can capture the environmental impacts and societal costs of nitrogen ...
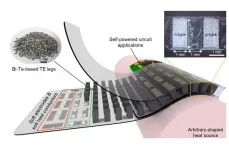
A thermoelectric device is an energy conversion device that utilizes the voltage generated by the temperature difference between both ends of a material; it is capable of converting heat energy, such as waste heat from industrial sites, into electricity that can be used in daily life. Existing thermoelectric devices are rigid because they are composed of hard metal-based electrodes and semiconductors, hindering the full absorption of heat sources from uneven surfaces. Therefore, recent studies were actively conducted on the development of flexible thermoelectric devices capable of generating energy in close contact with various heat sources such as human skins and hot water pipes.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced ...
A rare mineral that has allowed Roman concrete marine barriers to survive for more than 2,000 years has been found in the thick concrete walls of a decommissioned nuclear power plant in Japan. The formation of aluminous tobermorite increased the strength of the walls more than three times their design strength, Nagoya University researchers and colleagues report in the journal Materials and Design. The finding could help scientists develop stronger and more eco-friendly concrete.
"We found that cement hydrates and rock-forming minerals reacted in a way similar to what ...
Researchers from University of Hawaii and University of Florida published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that argues that a biological account of human behavior, especially undesirable behavior, will benefit human welfare. This biological perspective can complement traditional psychological, anthropological, and economic perspectives on consumption, particularly with respect to the vital topic of self-control.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Consumer Self-Control and the Biological Sciences: Implications for Marketing Stakeholders" and is authored by Yanmei Zheng and Joe Alba.
Society's understanding of human ills is constantly evolving. Many ill-advised consumer behaviors are conventionally viewed through a non-biological ...
CLEVELAND--The combined effectiveness of three COVID-prevention strategies on college campuses--mask-wearing, social distancing, and routine testing--are as effective in preventing coronavirus infections as the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), according to a new study co-authored by a Case Western Reserve University researcher.
The research, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, has immediate significance as college semesters are poised to start again--and as the distribution of approved vaccines lags behind goals.
The study found that a combination of just two common measures--distancing and mandatory masks--prevents 87% of campus COVID-19 infections and costs only $170 per infection prevented. ...
New research from King's College London shows nearly half of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) staff are likely to meet the threshold for PTSD, severe anxiety or problem drinking during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results from a study of ICU healthcare workers, published today in Occupational Medicine, shows the stark impact of working in critical care during the COVID-10 pandemic. The researchers found poor mental health was common in many ICU clinicians although they were more pronounced in nurses than in doctors or other healthcare professionals.
Lead author, Professor Neil Greenberg, from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King's College London said:
'Our results show a substantial burden of mental health symptoms being reported by ICU staff towards the end ...
As schools prepare to re-open to all pupils in February, experts warn that UK government plans for mass testing risks spreading covid-19 more widely.
Writing in The BMJ, Professor Jon Deeks and colleagues at the Royal Statistical Society argue that using the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to manage classroom outbreaks, without isolating close contacts, risks increasing disease spread and causing further disruption to children's education.
Before Christmas, schools limited pupil mixing and activities, and isolated pupil groups at home once a covid-19 case was identified, they explain. This year the government is relying on the INNOVA rapid lateral flow tests to mass screen staff and pupils, and test close contacts ...