(Press-News.org) Scientists claim to have found the 'missing link' in the process that leads to an ice age on Earth.
Melting icebergs in the Antarctic are the key, say the team from Cardiff University, triggering a series of chain reactions that plunges Earth into a prolonged period of cold temperatures.
The findings have been published today in Nature from an international consortium of scientists from universities around the world.
It has long been known that ice age cycles are paced by periodic changes to Earth's orbit of the sun, which subsequently changes the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface.
However, up until now it has been a mystery as to how small variations in solar energy can trigger such dramatic shifts in the climate on Earth.
In their study, the team propose that when the orbit of Earth around the sun is just right, Antarctic icebergs begin to melt further and further away from Antarctica, shifting huge volumes of freshwater away from the Southern Ocean and into the Atlantic Ocean.
As the Southern Ocean gets saltier and the North Atlantic gets fresher, large-scale ocean circulation patterns begin to dramatically change, pulling CO2 out of the atmosphere and reducing the so-called greenhouse effect.
This in turn pushes the Earth into ice age conditions.
As part of their study the scientists used multiple techniques to reconstruct past climate conditions, which included identifying tiny fragments of Antarctic rock dropped in the open ocean by melting icebergs.
The rock fragments were obtained from sediments recovered by the International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) Expedition 361, representing over 1.6 million years of history and one of the longest detailed archives of Antarctic icebergs.
The study found that these deposits, known as Ice-Rafted Debris, appeared to consistently lead to changes in deep ocean circulation, reconstructed from the chemistry of tiny deep-sea fossils called foraminifera.
The team also used new climate model simulations to test their hypothesis, finding that huge volumes of freshwater could be moved by the icebergs.
Lead author of the study Aidan Starr, from Cardiff University's School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, said: "We were astonished to find that this lead-lag relationship was present during the onset of every ice age for the last 1.6 million years. Such a leading role for the Southern Ocean and Antarctica in global climate has been speculated but seeing it so clearly in geological evidence was very exciting".
Professor Ian Hall, co-author of the study and co-chief scientist of the IODP Expedition, also from the School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, said: "Our results provide the missing link into how Antarctica and the Southern Ocean responded to the natural rhythms of the climate system associated with our orbit around the sun."
Over the past 3 million years the Earth has regularly plunged into ice age conditions, but at present is currently situated within an interglacial period where temperatures are warmer.
However, due to the increased global temperatures resulting from anthropogenic CO2 emissions, the researchers suggest the natural rhythm of ice age cycles may be disrupted as the Southern Ocean will likely become too warm for Antarctic icebergs to travel far enough to trigger the changes in ocean circulation required for an ice age to develop.
Professor Hall believes that the results can be used to understand how our climate may respond to anthropogenic climate change in the future.
"Likewise as we observe an increase in the mass loss from the Antarctic continent and iceberg activity in the Southern Ocean, resulting from warming associated with current human greenhouse-gas emissions, our study emphasises the importance of understanding iceberg trajectories and melt patterns in developing the most robust predictions of their future impact on ocean circulation and climate," he said.
Professor Grant Bigg, from the University of Sheffield's Department of Geography, who contributed to the iceberg model simulations, said: "The groundbreaking modelling of icebergs within the climate model is crucial for identifying and supporting the ice-rafted debris hypothesis of Antarctic iceberg meltwater impacts which are leading glacial cycle onsets."
INFORMATION:
The Cardiff University-led study was funded by NERC.
Notes to editors
1). For more information, please contact:
Michael Bishop
Cardiff University
02920 874499
Bishopm1@cardiff.ac.uk
2). Cardiff University is recognised in independent government assessments as one of Britain's leading teaching and research universities and is a member of the Russell Group of the UK's most research intensive universities. The 2014 Research Excellence Framework ranked the University 5th in the UK for research excellence. Among its academic staff are two Nobel Laureates, including the winner of the 2007 Nobel Prize for Medicine, Professor Sir Martin Evans. Founded by Royal Charter in 1883, today the University combines impressive modern facilities and a dynamic approach to teaching and research. The University's breadth of expertise encompasses: the College of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences; the College of Biomedical and Life Sciences; and the College of Physical Sciences and Engineering, along with a longstanding commitment to lifelong learning.
KU Leuven researchers have identified the biological mechanism that explains why some people experience abdominal pain when they eat certain foods. The finding paves the way for more efficient treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and other food intolerances. The study, carried out in mice and humans, was published in Nature.
Up to 20% of the world's population suffers from the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which causes stomach pain or severe discomfort after eating. This affects their quality of life. Gluten-free and other diets can provide some relief, but why this works is a mystery, since the patients are not allergic to the foods in question, nor do they ...
Researchers have shown that the link between physical and mental illness is closer than previously thought. Certain changes in physical health, which are detectable in childhood, are linked with the development of mental illness in adulthood.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, used a sample of over 10,000 people to study how insulin levels and body mass index (BMI) in childhood may be linked with depression and psychosis in young adulthood.
They found that persistently high insulin levels from mid-childhood were linked with a higher chance of developing psychosis in adulthood. In addition, they found that an increase in BMI around the onset of puberty, was linked with a higher chance of developing depression in adulthood, ...
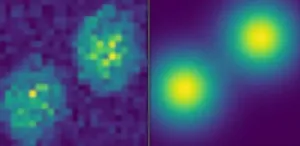
Since the earliest microscopes, scientists have been on a quest to build instruments with finer and finer resolution to image a cell's proteins - the tiny machines that keep cells, and us, running. But to succeed, they need to overcome the diffraction limit, a fundamental property of light that long prevented optical microscopes from bringing into focus anything smaller than half the wavelength of visible light (around 200 nanometers or billionths of a meter) - far too big to explore many of the inner-workings of a cell.
For over a century, scientists have experimented with different approaches - from intensive calculations to special lasers and microscopes - to resolve cellular features at ever smaller scales. And ...
TORONTO, Jan. 13, 2021 - Close to 5,700 lakes in the Northern Hemisphere may permanently lose ice cover this century, 179 of them in the next decade, at current greenhouse gas emissions, despite a possible polar vortex this year, researchers at York University have found.
Those lakes include large bays in some of the deepest of the Great Lakes, such as Lake Superior and Lake Michigan, which could permanently become ice free by 2055 if nothing is done to curb greenhouse gas emissions or by 2085 with moderate changes.
Many of these lakes that are ...
SILVER SPRING, Md.--A new study confirms that treatment with Bimagrumab, an antibody that blocks activin type II receptors and stimulates skeletal muscle growth, is safe and effective for treating excess adiposity and metabolic disturbances of adult patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
"These exciting results suggest that there may be a novel mechanism for achieving weight loss with a profound loss of body fat and an increase in lean mass, along with other metabolic benefits," said Steve Heymsfield, MD, FTOS, past president of The Obesity Society and corresponding author of the study. Heymsfield is professor and director of the Metabolism and Body Composition Laboratory at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, La.
A ...
LAWRENCE -- Parents around the world have long told us that breakfast is the most important meal of the day. Soon, basketball coaches may join them.
Researchers at the University of Kansas have published a study showing that eating breakfast can improve a basketball player's shooting performance, sometimes by significant margins. The study, along with one showing that lower body strength and power can predict professional basketball potential, is part of a larger body of work to better understand the science of what makes an elite athlete.
Breakfast and better basketball shooting
Dimitrije Cabarkapa left his native Novi Sad, Serbia, to play basketball at James Madison University. Never a fan of 6 a.m. workouts, he was discussing ...
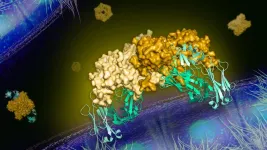
A team of researchers led by the University of California, Berkeley and the University of Michigan has discovered an antibody that blocks the spread within the body of the dengue virus, a mosquito-borne pathogen that infects between 50 and 100 million people a year. The virus causes what is known as dengue fever, symptoms of which include fever, vomiting and muscle aches, and can lead to more serious illnesses, and even death.
"Protein structures determined at the APS have played a critical role in the development of drugs and vaccines for several diseases, and these new results are key to the development of a potentially effective treatment against flaviviruses." -- Bob Fischetti, group leader with Argonne's X-ray Sciences Division and life sciences ...
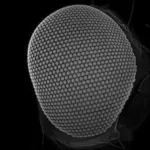
The fascinating compound eyes of insects consist of hundreds of individual eyes known as "facets". In the course of evolution, an enormous variety of eye sizes and shapes has emerged, often representing adaptations to different environmental conditions. Scientists, led by an Emmy Noether research group at the University of Göttingen, together with scientists from the Andalusian Centre for Developmental Biology (CABD) in Seville, have now shown that these differences can be caused by very different changes in the genome of fruit flies. The study was published ...
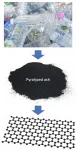
HOUSTON - (Jan. 13, 2021) - Pyrolyzed plastic ash is worthless, but perhaps not for long.
Rice University scientists have turned their attention to Joule heating of the material, a byproduct of plastic recycling processes. A strong jolt of energy flashes it into graphene.
The technique by the lab of Rice chemist James Tour produces turbostratic graphene flakes that can be directly added to other substances like films of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) that better resist water in packaging and cement paste and concrete, dramatically increasing their compressive strength. ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A dramatic decline in bees and other pollinating insects presents a threat to the global food supply, yet it's getting little attention in mainstream news.
That's the conclusion of a study from researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, published this week in a special issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study was based on a search of nearly 25 million news items from six prominent U.S. and global news sources, among them The New York Times, The Washington Post and The Associated Press.
The study found "vanishingly low levels of attention to pollinator population topics" over several decades, even compared with ...