(Press-News.org) While most children need to show immunization records to attend school, the same may not be true for camps, a new study suggests.
Nearly half of summer camps surveyed by researchers didn't have official policies requiring campers be vaccinated, according to findings led by Michigan Medicine C.S. Mott Children's Hospital in END
Study: Many summer camps don't require childhood immunizations
Study suggests that camps, which draw in 14 million children a year, may be an overlooked group when addressing communicable disease spread
2021-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
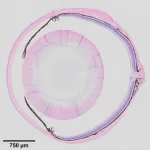
A niche for the eye
2021-01-13
KANSAS CITY, MO--What if the degenerative eye conditions that lead to glaucoma, corneal dystrophy, and cataracts could be detected and treated before vision is impaired? Recent findings from the lab of Investigator Ting Xie, PhD, at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research point to the ciliary body as a key to unlocking this possibility.
Previous work from the lab showed that when mouse stem cells were differentiated into light-sensing photoreceptor cells in vitro, and then transplanted back into mice with a degenerative condition of the retina, they could partially restore vision. However, the transplanted photoreceptors only lasted three to four months.
"You cannot cure the condition in a diseased eye if you don't know what ...
The compound that makes chili peppers spicy also boosts perovskite solar cell performance
2021-01-13
Scientists in China and Sweden have determined that a pinch of capsaicin, the chemical compound that gives chili peppers their spicy sting, may be a secret ingredient for more stable and efficient perovskite solar cells. The research, published January 13 in the journal Joule, determined that sprinkling capsaicin into the precursor of methylammonium lead triiodide (MAPbI3) perovskite during the manufacturing process led to a greater abundance of electrons (instead of empty placeholders) to conduct current at the semiconductor's surface. The addition resulted in polycrystalline MAPbI3 solar cells with the most efficient charge transport to date.
"In the future, green and sustainable forest-based biomaterial ...
Asian butterfly mimics other species to defend against predators
2021-01-13
NEW YORK, January 13, 2021 -- Many animal and insect species use Batesian mimicry -- mimicking a poisonous species -- as a defense against predators. The common palmfly Elymnias hypermnestra -- a species of satyrine butterfly that is found throughout wide areas of tropical and subtropical Asia -- adds a twist to this evolutionary strategy. The females evolved two distinct forms, either orange or dark brown, imitating two separate poisonous model species, Danaus or Euploea. The males are uniformly brown. A population group is either entirely brown (both males and females) or mixed (brown males and orange females).
David Lohman, ...
The dire wolf was a distinct species, different from the gray wolf, biologists discover
2021-01-13
The iconic, prehistoric dire wolf, which prowled through Los Angeles and elsewhere in the Americas over 11 millennia ago, was a distinct species from the slightly smaller gray wolf, an international team of scientists reports today in the journal Nature.
The study, which puts to bed a mystery that biologists have pondered for more than 100 years, was led by researchers from UCLA, along with colleagues from Durham University in the U.K., Australia's Adelaide University and Germany's Ludwig Maximilian University.
"The terrifying dire wolf, a legendary symbol of Los Angeles and the La Brea Tar Pits, has earned its place among the many large, unique species that went extinct at the end of the Pleistocene ...
Study finds neglected mutations may play important role in autism spectrum disorder
2021-01-13
Mutations that occur in certain DNA regions, called tandem repeats, may play a significant role in autism spectrum disorders, according to research led by Melissa Gymrek, assistant professor in the UC San Diego Department of Computer Science and Engineering and School of Medicine. The study, which was published in Nature on Jan. 14, was co-authored by UCLA professor of human genetics Kirk Lohmueller and highlights the contributions these understudied mutations can make to disease.
"Few researchers really study these repetitive regions because they're generally non-coding--they do not make proteins; their function is ...
Ancient DNA reveals secrets of Game of Thrones wolves
2021-01-13
Extinct dire wolves split off from other wolves nearly six million years ago and were only a distant relative of today's wolves, according to new research published in Nature today (13 January).
Dire wolves, made famous in the TV show Game of Thrones, were common across North America until around 13,000 years ago, after which they went extinct.
The study shows that dire wolves were so different from other canine species like coyotes and grey wolves that they were not able to breed with each other. Previous analyses, based on morphology alone, had led scientists to believe that dire wolves were closely related to grey wolves.
The research was led by Durham University in the UK alongside scientists at the University of Oxford, Ludwig Maximilian University in ...
Columbia engineers first to observe avalanches in nanoparticles
2021-01-13
New York, NY--January 13, 2021--Researchers at Columbia Engineering report today that they have developed the first nanomaterial that demonstrates "photon avalanching," a process that is unrivaled in its combination of extreme nonlinear optical behavior and efficiency. The realization of photon avalanching in nanoparticle form opens up a host of sought-after applications, from real-time super-resolution optical microscopy, precise temperature and environmental sensing, and infrared light detection, to optical analog-to-digital conversion and quantum sensing.
"Nobody has seen avalanching behavior like this in nanomaterials before," said James Schuck, associate professor of mechanical engineering, who led the study published today by Nature. "We ...
Error protected quantum bits entangled
2021-01-13
Even computers can miscalculate. Already small disturbances change stored information and corrupt results. That is why computers use methods to continuously correct such errors. In quantum computers, the vulnerability to errors can be reduced by storing quantum information in more than a single quantum particle. These logical quantum bits are less sensitive to errors. In recent years, theorists have developed many different error correction codes and optimized them for different tasks. "The most promising codes in quantum error correction are those defined on a two-dimensional lattice," ...
Asian butterfly populations show different mimicry patterns thanks to genetic 'switch'
2021-01-13
A new study by researchers at the University of Chicago and the City College of New York (CCNY) has identified a unique, genetic "mimicry switch" that determines whether or not male and female Elymnias hypermnestra palmflies mimic the same or different species of butterflies. The results indicate that sexual dimorphism has repeatedly emerged in different palmfly populations, and linked the trait to a gene associated with melanin localization and regulation.
Published on Jan. 13 in the journal END ...
Red and green snow algae increase snowmelt in the Antarctic Peninsula
2021-01-13
Red and green algae that grow on snow in the Antarctic Peninsula (AP) cause significant extra snowmelt on par with melt from dust on snow in the Rocky Mountains, according to a first-of-its-kind scientific research study led by Alia Khan, affiliate research scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and assistant professor at Western Washington University. Algal blooms are likely to increase in Antarctica as the planet continues to warm, which will further exacerbate seasonal snowmelt and contribute to the expansion of ice-free areas in the AP region. This could have serious impacts on regional climate, snow and ice melt, freshwater availability and ecosystems, yet is not accounted for in current global climate models. Results of the research were published on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Study: Many summer camps don't require childhood immunizationsStudy suggests that camps, which draw in 14 million children a year, may be an overlooked group when addressing communicable disease spread