(Press-News.org) Extinct dire wolves split off from other wolves nearly six million years ago and were only a distant relative of today's wolves, according to new research published in Nature today (13 January).
Dire wolves, made famous in the TV show Game of Thrones, were common across North America until around 13,000 years ago, after which they went extinct.
The study shows that dire wolves were so different from other canine species like coyotes and grey wolves that they were not able to breed with each other. Previous analyses, based on morphology alone, had led scientists to believe that dire wolves were closely related to grey wolves.
The research was led by Durham University in the UK alongside scientists at the University of Oxford, Ludwig Maximilian University in Germany, the University of Adelaide in Australia and the University of California Los Angeles in the US.
For the first time, the international team has sequenced the ancient DNA of five dire wolf sub-fossils from Wyoming, Idaho, Ohio, and Tennessee, dating back to over 50,000 years ago. Their analyses showed that dire wolves and grey wolves were in fact very distant cousins.
This is the first time ancient DNA has been taken from dire wolves revealing a complex history of these ice age predators.
The collaboration of 49 researchers across nine countries analysed the genomes of dire wolves alongside those of many different wolf-like canid species. Their analyses suggest that unlike many canid species who apparently migrated repeatedly between North America and Eurasia over time, dire wolves evolved solely in North America for millions of years.
Although dire wolves overlapped with coyotes and grey wolves in North America for at least 10,000 years before their extinction, they found no evidence that they interbred with these species. The researchers suggest that their deep evolutionary differences meant that they were likely ill equipped to adapt to changing conditions at the end of the ice age.
Lead author, Dr Angela Perri from Durham University's Archaeology Department, said: "Dire wolves have always been an iconic representation of the last ice age in the Americas and now a pop culture icon thanks to Game of Thrones, but what we know about their evolutionary history has been limited to what we can see from the size and shape of their bones and teeth.
"With this first ancient DNA analysis of dire wolves we have revealed that the history of dire wolves we thought we knew - particularly a close relationship to grey wolves - is actually much more complicated than we previously thought.
"Instead of being closely related to other North American canids, like grey wolves and coyotes, we found that dire wolves represent a branch that split off from others millions of years ago, representing the last of a now extinct lineage."
Co-lead author, Dr Alice Mouton, from the University of California Los Angeles, added: "We have found the dire wolf is not closely related to the grey wolf. Further we show that the dire wolf never interbred with the grey wolf. In contrast, grey wolves, African wolves, dogs, coyotes and jackals can and do interbreed. Dire wolves likely diverged from grey wolves more than five million years ago, which was a great surprise that this divergence occurred so early. This finding highlights how special and unique the dire wolf was."
The dire wolf is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores from Pleistocene America which became extinct around 13,000 years ago. Known scientifically as Canis dirus, meaning 'fearsome dog', they preyed on large mammals like bison. The team suggests the dire wolves' stark evolutionary divergence from grey wolves places them in an entirely different genus - Aenocyon dirus ('terrible wolf')- as first proposed by palaeontologist John Campbell Merriam over 100 years ago.
Co-lead author, Dr Kieren Mitchell, from the University of Adelaide, commented: "Dire wolves are sometimes portrayed as mythical creatures - giant wolves prowling bleak frozen landscapes - but reality turns out to be even more interesting.
"Despite anatomical similarities between grey wolves and dire wolves - suggesting that they could perhaps be related in the same way as modern humans and Neanderthals - our genetic results show these two species of wolf are much more like distant cousins, like humans and chimpanzees.
"While ancient humans and Neanderthals appear to have interbred, as do modern grey wolves and coyotes, our genetic data provided no evidence that dire wolves interbred with any living canine species. All our data point to the dire wolf being the last surviving member of an ancient lineage distinct from all living canines."
Senior author, Dr Laurent Frantz, from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, added: "When we first started this study we thought that dire wolves were just beefed up grey wolves, so we were surprised to learn how extremely genetically different they were, so much so that they likely could not have interbred. Hybridisation across Canis species is thought to be very common, this must mean that dire wolves were isolated in North America for a very long time to become so genetically distinct."
Dire wolves became extinct around 13,000 years ago but thanks to fossil remains, DNA analysis and a little bit of help from Game of Thrones, their legend lives on.
INFORMATION:
New York, NY--January 13, 2021--Researchers at Columbia Engineering report today that they have developed the first nanomaterial that demonstrates "photon avalanching," a process that is unrivaled in its combination of extreme nonlinear optical behavior and efficiency. The realization of photon avalanching in nanoparticle form opens up a host of sought-after applications, from real-time super-resolution optical microscopy, precise temperature and environmental sensing, and infrared light detection, to optical analog-to-digital conversion and quantum sensing.
"Nobody has seen avalanching behavior like this in nanomaterials before," said James Schuck, associate professor of mechanical engineering, who led the study published today by Nature. "We ...
Even computers can miscalculate. Already small disturbances change stored information and corrupt results. That is why computers use methods to continuously correct such errors. In quantum computers, the vulnerability to errors can be reduced by storing quantum information in more than a single quantum particle. These logical quantum bits are less sensitive to errors. In recent years, theorists have developed many different error correction codes and optimized them for different tasks. "The most promising codes in quantum error correction are those defined on a two-dimensional lattice," ...
A new study by researchers at the University of Chicago and the City College of New York (CCNY) has identified a unique, genetic "mimicry switch" that determines whether or not male and female Elymnias hypermnestra palmflies mimic the same or different species of butterflies. The results indicate that sexual dimorphism has repeatedly emerged in different palmfly populations, and linked the trait to a gene associated with melanin localization and regulation.
Published on Jan. 13 in the journal END ...
Red and green algae that grow on snow in the Antarctic Peninsula (AP) cause significant extra snowmelt on par with melt from dust on snow in the Rocky Mountains, according to a first-of-its-kind scientific research study led by Alia Khan, affiliate research scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and assistant professor at Western Washington University. Algal blooms are likely to increase in Antarctica as the planet continues to warm, which will further exacerbate seasonal snowmelt and contribute to the expansion of ice-free areas in the AP region. This could have serious impacts on regional climate, snow and ice melt, freshwater availability and ecosystems, yet is not accounted for in current global climate models. Results of the research were published on ...
Scientists claim to have found the 'missing link' in the process that leads to an ice age on Earth.
Melting icebergs in the Antarctic are the key, say the team from Cardiff University, triggering a series of chain reactions that plunges Earth into a prolonged period of cold temperatures.
The findings have been published today in Nature from an international consortium of scientists from universities around the world.
It has long been known that ice age cycles are paced by periodic changes to Earth's orbit of the sun, which subsequently changes the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface.
However, ...
KU Leuven researchers have identified the biological mechanism that explains why some people experience abdominal pain when they eat certain foods. The finding paves the way for more efficient treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and other food intolerances. The study, carried out in mice and humans, was published in Nature.
Up to 20% of the world's population suffers from the irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which causes stomach pain or severe discomfort after eating. This affects their quality of life. Gluten-free and other diets can provide some relief, but why this works is a mystery, since the patients are not allergic to the foods in question, nor do they ...
Researchers have shown that the link between physical and mental illness is closer than previously thought. Certain changes in physical health, which are detectable in childhood, are linked with the development of mental illness in adulthood.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, used a sample of over 10,000 people to study how insulin levels and body mass index (BMI) in childhood may be linked with depression and psychosis in young adulthood.
They found that persistently high insulin levels from mid-childhood were linked with a higher chance of developing psychosis in adulthood. In addition, they found that an increase in BMI around the onset of puberty, was linked with a higher chance of developing depression in adulthood, ...
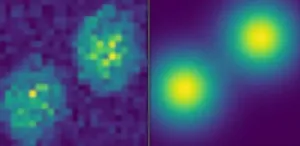
Since the earliest microscopes, scientists have been on a quest to build instruments with finer and finer resolution to image a cell's proteins - the tiny machines that keep cells, and us, running. But to succeed, they need to overcome the diffraction limit, a fundamental property of light that long prevented optical microscopes from bringing into focus anything smaller than half the wavelength of visible light (around 200 nanometers or billionths of a meter) - far too big to explore many of the inner-workings of a cell.
For over a century, scientists have experimented with different approaches - from intensive calculations to special lasers and microscopes - to resolve cellular features at ever smaller scales. And ...
TORONTO, Jan. 13, 2021 - Close to 5,700 lakes in the Northern Hemisphere may permanently lose ice cover this century, 179 of them in the next decade, at current greenhouse gas emissions, despite a possible polar vortex this year, researchers at York University have found.
Those lakes include large bays in some of the deepest of the Great Lakes, such as Lake Superior and Lake Michigan, which could permanently become ice free by 2055 if nothing is done to curb greenhouse gas emissions or by 2085 with moderate changes.
Many of these lakes that are ...
SILVER SPRING, Md.--A new study confirms that treatment with Bimagrumab, an antibody that blocks activin type II receptors and stimulates skeletal muscle growth, is safe and effective for treating excess adiposity and metabolic disturbances of adult patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
"These exciting results suggest that there may be a novel mechanism for achieving weight loss with a profound loss of body fat and an increase in lean mass, along with other metabolic benefits," said Steve Heymsfield, MD, FTOS, past president of The Obesity Society and corresponding author of the study. Heymsfield is professor and director of the Metabolism and Body Composition Laboratory at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge, La.
A ...