Posidonia marine seagrass can catch and remove plastics from the sea
A trap for plastics in coastal areas
2021-01-14
(Press-News.org) Posidonia oceanica seagrass -an endemic marine phanerogam with an important ecological role in the marine environment- can take and remove plastic materials that have been left at the sea, according to a study published in the journal Scientific Reports. The article's first author is the tenure-track 2 lecturer Anna Sànchez-Vidal, from the Research Group on Marine Geosciences of the Faculty of Earth Sciences of the University of Barcelona (UB).
The study describes for the first time the outstanding role of the Posidonia as a filter and trap for plastics in the coastal areas, and it is pioneer in the description of a natural mechanism to take and remove these materials from the sea. Other authors of the study are the experts Miquel Canals, William P. de Haan and Marta Veny, from the Research Group on Marine Geosciences of the UB, and Javier Romero, from the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the UB.
A trap for plastics in coastal areas
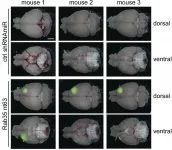
The Posidonia oceanica makes dense prairies that make a habitat with a great ecological value (nutrition, shelter, reproduction, etc.) for marine biodiversity. As part of the study, the team analysed the trapping and extraction of plastic in great seagrasses of the Posidonia in the coasts of Majorca. "Everything suggests that plastics are trapped in the Posidonia seagrass. In the grasslands, the plastics are incorporated to agglomerates of natural fiber with a ball shape -aegagropila or Posidonia Neptune balls- which are expulsed from the marine environment during storms", notes Anna Sànchez-Vidal, member of the Department of Ocean and Earth Dynamics of the UB.
"According to the analyses -she continues- the trapped microplastics in the prairies of the Posidonia oceanica are mainly filaments, fibers and fragments of polymers which are denser than the sea water such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
How are Posidonia Neptune balls made?
This marine phanerogam has a vegetative structure made by a modified stem with a rhizome shape from which the roots and leaves appear. When the leaves fall, its bases (pods) are added to rhizomes and give them a feather-like appearance. "As a result of the mechanical erosion in the marine environment, those pods under the seafloors are progressively releasing lignocellulosic fibres which are slowly added and intertwined until they make agglomerates in a ball-shape, known as aegagropilae. Aegagropilae are expulsed from prairies during periods of strong waves and a certain part ends up in the beaches", says Professor Javier Romero, from the Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology and Environmental Sciences and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the UB.
Posidonia aegagropilae are expelled from the prairies during periods of strong waves and a part ends up piled in the beaches. Although there are no studies that quantify the amount of aegagropilae expelled from the marine environment, it is estimated that about 1,470 plastics are taken per kilogram of plant fibre, amounts which are significantly higher than those captured through leaves or sand. As researcher Anna Sànchez-Vidal says, "we cannot completely know the magnitude of this plastic export to the land. However, first estimations reveal that Posidonia balls could catch up to 867 million plastics per year".
Plastic-free oceans: everyone's responsibility
The polluting footprint of plastics that come from human activity is a serious environmental problem affecting coastal and ocean ecosystems worldwide. Since plastics were created massively in the 20th century fifties, these materials have been left and accumulated at the sea -seafloors act as a sink for microplastics-- and are transported by ocean currents, wind and waves. "The plastics we find floating in the sea are only a small percentage of everything we have thrown onto the marine environment", warns Anna Sànchez-Vidal.
The paper published in the journal Scientific Reports has been carried out within the frame of the subject of the EHEA bachelor's degree final project of the degree in Marine Sciences of the Faculty of Earth Sciences, and counted on the support from the Scientific and Technological Centers of the UB (CCiTUB). The new ecosystemic service of the Posidonia described in the article has a significant value in a marine area such as the Mediterranean -with high quantities of floating plastic and in the seafloors-- and with Posidonia seagrass that can occupy large areas up to forty meters deep.
"This is why we need to protect and preserve these vulnerable ecosystems. However, the best environmental protection strategy to keep oceans free of plastic is to reduce landfills, an action that requires to limit its use by the population", conclude the experts.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-14
Both past and present-day scientists have suspected the intestines of playing a role in various diseases. Present-day studies focus on the intestinal flora's role in physical diseases such as diabetes and overweight, while others seek to establish a connection between the intestinal flora and e.g. autism, schizophrenia and depression. But even modern-day scientists have difficulties studying the around 500-1000 different species among the approx. 100 billion active bacteria in our intestines.
Therefore, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have developed a ground-breaking technique that ...
2021-01-14
Roughly 8,200 years ago, the island of Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov in Lake Onega in the Republic of Karelia, Russia, housed a large burial ground where men, women and children of varying ages were buried. Many of the graves contain an abundance of objects and red ochre, signifying the wish to ensure the comfort of the buried also after death. Pendants made of elk incisors were apparently attached to clothing and accessories, such as dresses, coats, cloaks, headdresses and belts. Although no clothing material has been preserved, the location of the elk teeth sheds light on the possible type of these outfits.
A people of grooved elk tooth pendants
A study headed by archaeologist Kristiina Mannermaa, University of Helsinki, aimed to determine who ...
2021-01-14
Bacteria are likely triggering greater melting on the Greenland ice sheet, possibly increasing the island's contribution to sea-level rise, according to Rutgers scientists.
That's because the microbes cause sunlight-absorbing sediment to clump together and accumulate in the meltwater streams, according to a Rutgers-led study - the first of its kind - in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. The findings can be incorporated in climate models, leading to more accurate predictions of melting, scientists say.
"These streams can be seen all over Greenland ...
2021-01-14
In patients with bladder cancer, chemotherapy effectiveness is partially determined by the body's immune system response to the malignancy. This is the conclusion of research conducted by a team of scientists from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Berlin Institute of Health. The findings, which have been published in Science Translational Medicine*, can be used to predict treatment success and may increase survival in patients with bladder cancer.
Bladder cancer is one of the ten most common types of cancer in Germany, and one of the five most common cancers in men. Nationwide, the disease affects approximately 30,000 people a year. The risk of the cancer ...
2021-01-14
TAMPA, Fla. -- The hallmarks of cancer include rapid cell reproduction and metabolic activity. But these processes also lead to increased cellular stress and oxidation, and the risk of cell death. To circumvent these negative consequences of supercharged growth, cancer cells stimulate pathways to reduce oxidative stress and avoid cell death. In an article published in Cell Metabolism, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers report on a newly discovered biochemical pathway that protects cells from a type of cell death called ferroptosis.
Ferroptosis is a specialized type of cell death that is caused ...
2021-01-14
Scientists at the Walter Reed Army Institute for Research have shown that microRNA biomarkers related to Alzheimer's disease play a role in brain damage caused by traumatic brain injury.
TBI or brain trauma results from blows to the head, leading to chronic disruption of the brain and a cascade of long-term health conditions. Patients who suffer from TBI are at much higher risk of developing neurodegenerative disease or dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. The mechanism behind this relationship remains understudied, making the development effective therapeutics challenging.
MiRNAs are small pieces of genetic material that play a critical role in normal gene expression. Yet, studies have also linked abnormal miRNA levels, or dysregulation, to a range of diseases including neurodegenerative ...
2021-01-14
Recently, the research team led by academician GUO Guangcan from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has made security analysis and improvement of source independent quantum random number generators with imperfect devices.
By studying the actual characteristics of the measurement devices of the source-independent quantum random number generation, the researchers pointed out that the security issues were caused by afterpulse, detection efficiency mismatching, poor sensitivity to photon number distribution ...
2021-01-14
Researchers at McGill University have identified a new cellular pathway that limits the growth and spread of brain tumors by controlling the recycling of cell surface receptor proteins. The study, which will be published January 14 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), suggests that the pathway, which involves a protein called Rab35, is defective in many patients with glioblastoma and that restoring Rab35's activity could be a new therapeutic strategy for this deadly form of brain cancer.
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive type of brain cancer, and because it is largely untreatable, the average patient dies within 14 months of diagnosis. Like in other cancers, the proliferation and spread of glioblastoma cells depends on various receptor proteins on the outside of the cell. The ...
2021-01-14
While humans may struggle to navigate a murky, turbid underwater environment, weakly electric fish can do so with ease. These aquatic animals are specially adapted to traverse obscured waters without relying on vision; instead, they sense their environment via electric fields. Now, researchers are attempting to adapt these electrosensing techniques to improve underwater robotics.
Scientists have spent years studying how weakly electric fish--including the knife fish and elephantnose fish--utilize electricity for navigation. These fish have specialized electric organs that discharge small voltages into the surrounding water, creating their own personal electric fields. Nearby objects cause slight disruptions to these fields, which the fish detect with sensitive organs ...
2021-01-14
There is a growing consensus among scientists as well as national and local governments representing hundreds of millions of people, that humanity faces a climate crisis that demands a crisis response. New research from the University of California San Diego explores one possible mode of response: a massively funded program to deploy direct air capture (DAC) systems that remove CO2 directly from the ambient air and sequester it safely underground.
The findings reveal such a program could reverse the rise in global temperature well before 2100, but only with immediate and sustained investments from governments and firms to scale up the new technology.
Despite the enormous undertaking explored in the study, the research also reveals the need ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Posidonia marine seagrass can catch and remove plastics from the sea
A trap for plastics in coastal areas