(Press-News.org) The higher a person's income, the more likely they were to protect themselves at the early stages of the Covid-19 pandemic in the United States, Johns Hopkins University economists find.
When it comes to adopting behaviors including social distancing and mask wearing, the team detected a striking link to their financial well-being. People who made around $230,000 a year were as much as 54% more likely to increase these types of self-protective behaviors compared to people making about $13,000.
"We need to understand these differences because we can wring our hands, and we can blame and shame, but in a way it doesn't matter," said Nick Papageorge, the Broadus Mitchell Associate Professor of Economics. "Policymakers just need to recognize who is going to socially distance, for how long, why and under what circumstances to give us accurate predictions of how the disease will spread and help us establish policies that will be useful."
The findings, that could contribute to more accurate predictions of how the disease will spread, appear in the latest Journal of Population Economics.
As part of a six-country survey, 1,000 people in the United States, from Texas, Florida, California and New York, were asked a series of questions in April 2020 to determine if and how their behavior had changed as Covid-19 cases were beginning to spike across the country. The resulting data includes information on income, gender and race along with unique variables relevant to the pandemic, such as work arrangements and housing quality.
The team, which included economics graduate student Matthew Zahn, found that while almost everyone changed their behavior in some way to try to stay safe, people making the most money made the most changes. The highest earners were 13% more likely to change their behaviors, 32% more likely to increase social distancing and 30% more likely to increase hand washing and mask wearing.
But the team found it was also much easier for people with more money to take extra safety measures.
Higher-income individuals were more likely to report being able to work from home and more likely to have transitioned to telework instead of losing their job. The researchers found the ability to telework emerged as a huge predictor of whether someone would social distance. Compared to somebody who continued to work, people able to telework were 24% more likely to social distance.
"The whole messaging of this pandemic is you're stuck at home teleworking, that must be really tough so here are some recipes for sourdough starter, and here's what you should catch up on Netflix," Papageorge said. "But what about the people who aren't teleworking? What are they going to do?"
The team found lower-income respondents faced increased chances of job and income losses due to the pandemic and limited access to remote work. They were also more likely to live in homes with no access to the outdoors - access to outdoor space was a very strong predictor of social distancing, the researchers found. People with access to open air at home were 20% more likely to social distance.
All of these burdens ensured those earning the least would have a harder time adopting social-distancing behaviors, which could have prolonged the pandemic, the team found. Social distancing was simply more practical, comfortable and feasible for people with more income.
"It's not shocking that if you don't live in a comfortable house you're going to be leaving your house more often. But the point we want to push is that if I'm a policy maker maybe I really need to think about opening city parks in a dense neighborhood during a pandemic. Maybe that's something that's worth the risk. This is why we want to understand these details - they can eventually suggest policies," Papageorge said.
The data showed that women were 23% more likely than men to social distance. Surprisingly, the researchers did not find any meaningful patterns between pre-existing health conditions and people's self-protective actions.
The team is now expanding this research with even more extensive surveys that look into how events such as the Black Lives Matter protests affected behavior during the pandemic, the pandemic's possible effects on addictive behaviors and, more broadly, how to build tools to better understand the unequal burdens the pandemic.
INFORMATION:
Authors also included: Michele Belot of Cornell University; Eline van den Broek-Altenburg of University of Vermont; Syngjoo Choi of Seoul National University; Julian C. Jamison of University of Exeter; and Egon Tripodi of University of Essex.
This work was supported by funding from the Creative-Pioneering Researchers Program at Seoul National University and the European University Institute.
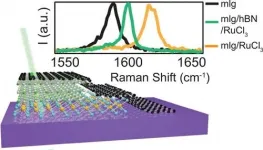
Physicists at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered how to locally add electrical charge to an atomically thin graphene device by layering flakes of another thin material, alpha-RuCl3, on top of it.
A paper published in the journal Nano Letters describes the charge transfer process in detail. Gaining control of the flow of electrical current through atomically thin materials is important to potential future applications in photovoltaics or computing.
"In my field, where we study van der Waals heterostructures made by custom-stacking atomically ...
ATLANTA--Compared to standard machine learning models, deep learning models are largely superior at discerning patterns and discriminative features in brain imaging, despite being more complex in their architecture, according to a new study in Nature Communications led by Georgia State University.
Advanced biomedical technologies such as structural and functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI and fMRI) or genomic sequencing have produced an enormous volume of data about the human body. By extracting patterns from this information, scientists can glean ...
Philadelphia, January 14, 2021--Based on preclinical studies of an investigational drug to treat peripheral nerve tumors, researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) as part of the Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium have shown that the drug, cabozantinib, reduces tumor volume and pain in patients with the genetic disorder neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). The results of the Phase 2 clinical trial, co-chaired by Michael J. Fisher, MD at CHOP, were published recently in Nature Medicine.
"This is the second class of drugs to demonstrate ...
Many animal and insect species use Batesian mimicry - mimicking a poisonous species - as a defense against predators. The common palmfly, Elymnias hypermnestra (a species of satyrine butterfly), which is found throughout wide areas of tropical and subtropical Asia, adds a twist to this evolutionary strategy: the females evolved two distinct forms, either orange or dark brown, imitating two separate poisonous model species, Danaus or Euploea. The males are uniformly brown. A population group is either entirely brown (both males and females) or mixed (brown males and orange females).
City College of New York entomologist David Lohman and his collaborators studied the genome of 45 samples representing 18 subspecies across Asia to determine ...
While new research from West Virginia University economists finds that presidential inaugurations have gained popularity as must-see tourist events in recent years, major security threats will keep visitors away for the inauguration of President-Elect Joe Biden.
Published in "Tourism Economics," the study, by Joshua Hall, chair and professor of economics, and economic doctoral student Clay Collins, examined the impact of the inaugurations of Barack Obama and Donald Trump on hotel occupancy in the Washington, D.C.-area.
Daily occupancy rates around the inaugurations were four-to-six times higher than the next largest event in the sample. The research team also concluded ...
To achieve full occupancy, hotels used to rely exclusively on experience, concentration and human abilities. Then came online booking, which made the reservation collection process faster, but did not solve the risk of turning down long stays because of rooms previously booked for short stays.
To avoid overbooking (accepting more reservations than there is room for) in some cases online sales are blocked before hotels are completely booked. The solution that the University of Trento has just discovered could change the life of hotels by increasing the number of occupied rooms and, therefore, in the revenue of hotel owners.
For an average Italian hotel (50 rooms), ...
More than half of all university students in the United States have experienced high levels of psychological impact from the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Matthew Browning of Clemson University, US, and colleagues.
University students are increasingly recognized as a psychologically vulnerable population, suffering from higher levels of depression, anxiety, substance abuse and disordered eating compared to the general population. Moreover, college students have been among the most strongly affected by COVID-19 because of uncertainty regarding academic success, future careers and social life during college, among other concerns.
In the new study, researchers collected data on 2,534 students ...
Investors who bet on tropical forest conservation and reforestation to solve global warming by storing carbon in wood face huge uncertainties because the science behind predicting carbon stocks is still shaky. Even the best Earth Systems Models fail to predict how carbon stored by tropical forests varies from place to place. The New Phytologist invites scientists doing the "most-exciting, ground-breaking research" to review timely topics in a way that non-scientists can understand. Helene Muller-Landau, staff scientist at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) was chosen to write the authoritative Tansley Review ...
MIAMI--Scientists used a 600-year-old marine sponge to reconstruct a record of ocean temperature in the North Atlantic revealing past volcanic activity as well as the current global warming trend from the release of carbon dioxide and other heat trapping gasses into Earth's atmosphere and absorbed by the oceans.
The University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science-led research team used geochemical proxies to reconstruct a 600 year-long record of Atlantic Ocean temperatures from the skeleton of a sclerosponge (Ceratoporella nicholsoni).
The basketball-sized sclerosponge was ...
These findings validate the significance of the previously described first threshold - the point when the damage to the acinar cells of the pancreas is sufficient to trigger the infamous inflammatory cascade (Barreto and Saccone, 2010) - while highlighting the importance of a second threshold, namely the point when a person develops clinical symptoms of the disease sufficient to warrant going to hospital.
"This transcontinental collaboration of pancreatologists drew on their vast clinical and research experience spanning decades investigating the pathophysiology and treatments ...