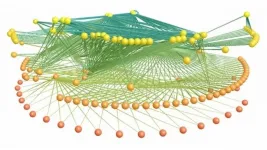
(Press-News.org) Genome analysis can provide information on genes and their location on a strand of DNA, but such analysis reveals little about their spatial location in relation to one another within chromosomes -- the highly complex, three-dimensional structures that hold genetic information.
Chromosomes resemble a fuzzy "X" in microscopy images and can carry thousands of genes. They are formed when DNA winds around proteins -- called histones -- which are further folded into complexes called chromatin, which make up individual chromosomes.
Knowing which genes are located in spatial proximity within the chromatin is important because genes that are near each other generally work together.
Now, researchers at the END
Reverse engineering 3D chromosome models for individual cells
Distant genes can be neighbors
2021-01-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Borrowing from birds, experts reduce search times for novel high-entropy alloys to seconds
2021-01-14
Computational materials science experts at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory enhanced an algorithm that borrows its approach from the nesting habits of cuckoo birds, reducing the search time for new high-tech alloys from weeks to mere seconds.
The scientists are investigating a type of alloys called high-entropy alloys, a novel class of materials that are highly sought after for a host of unusual and potentially beneficial properties. They are lightweight in relation to their strength, fracture-resistant, highly corrosion and oxidation resistant, and stand up well in high-temperature and high-pressure environments -- making them attractive materials for aerospace industry, space exploration, nuclear energy, and defense applications.
While the promise of these ...
New PTSD biotypes enables improved tests, sheds light on divergent treatments efficacy
2021-01-14
Researchers from the PTSD Systems Biology Consortium, led by scientists from the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, have identified distinct biotypes for post-traumatic stress disorder, the first of their kind for any psychological disorder. "These biotypes can refine the development of screening tools and may explain the varying efficacy of PTSD treatments", said Dr. Marti Jett, leader of the consortium and WRAIR chief scientist.
Publishing their work in Molecular Psychiatry in a manuscript first authored by WRAIR's Dr. Ruoting Yang, researchers used blood tests from male, combat-exposed veterans across a three year period to identify two PTSD biotypes, G1--characterized ...
Cancer models created by mechanical engineers offer new insight into tumor growth
2021-01-14
TROY, N.Y. -- As cancer and tumor cells move inside the human body, they impart and are subject to mechanical forces. In order to understand how these actions affect cancer cell growth, spread, and invasion, a team of engineers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is developing new models that mimic aspects of the mechanical environment within the body, providing new insight into how and why tumors develop in certain ways.
In research published today in Integrative Biology, a team of engineers from Rensselaer developed an in vitro -- in the lab -- lymphatic vessel model to study the growth of tumor emboli, collections of ...
Keeping the costs of superconducting magnets down using ultrasound
2021-01-14
Superconductivity already has a variety of practical applications, such as medical imaging and levitating transportation like the ever-popular maglev systems. However, to ensure that the benefits of applied superconductors keep spreading further into other technological fields, we need to find ways of not only improving their performance, but also making them more accessible and simpler to fabricate.
In this regard, magnesium diboride (MgB2) has attracted the attention of researchers since its discovery as a superconductor with multiple advantages. It is a lightweight, easily processible material made from widely abundant ...
Discrimination may increase risk of anxiety disorders regardless of genetics, study finds
2021-01-14
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (Jan. 14, 2021)-- Exposure to discrimination plays a significant role in the risk of developing anxiety and related disorders, even - in a first - after accounting for potential genetic risks, according to a multidisciplinary team of health researchers led by Tufts University and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
Researchers determined that even after controlling for genetic risk for anxiety, depression, and neuroticism, greater reports of discrimination experiences remained associated with higher scores of anxiety and related disorders. The findings, recently ...
Rare lichen unique to Florida discovered in museum collections, may be extinct
2021-01-14
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Scientists have found a new species of fleshy verdigris lichen, thanks to DNA analysis of museum specimens. Misidentified by its original collectors, the lichen is only known from 32 specimens collected in North and Central Florida scrubland between 1885 and 1985. Now the hunt is on to find it in the wild - if it still exists.
The lichen, named Cora timucua in honor of Florida's Timucua people, is critically endangered, even more so than the federally protected Florida perforate reindeer lichen, and possibly extinct. Researchers are holding out hope that C. timucua may persist in undisturbed pockets of the state's dwindling pine scrub habitat, though recent searches came up empty.
"The million-dollar question is 'Where is this lichen?'" said Laurel Kaminsky, a digitization ...
New study: Without right messaging, masks could lead to more COVID-19 spread
2021-01-14
A novel new study suggests that the behavior public officials are now mandating or recommending unequivocally to slow the spread of surging COVID-19--wearing a face covering--should come with a caveat. If not accompanied by proper public education, the practice could lead to more infections.
The finding is part of an unique study, just published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance, that was conducted by a team of health economists and public health faculty at the University of Vermont's Larner College of Medicine in partnership with public health officials for the state of Vermont.
The study combines survey data gathered from adults living in northwestern Vermont with test results that showed whether a subset of them had contracted COVID-19, a dual research ...
Researchers show Irish soil can offer more hope in fight against antibiotic resistance
2021-01-14
Scientists who highlighted the bug-busting properties of bacteria in Northern Irish soil have made another exciting discovery in the quest to discover new antibiotics.
The Traditional Medicine Group, an international collaboration of scientists from Swansea University, Brazil and Northern Ireland, have discovered more antibiotic-producing species and believe they may even have identified new varieties of antibiotics with potentially life-saving consequences.
Antibiotic resistant superbugs could kill up to 1.3 million people in Europe by 2050 - the World Health Organisation (WHO) describes the problem as "one of the biggest threats to global health, food security, and development today".
The search for replacement antibiotics to combat ...
Accounting for the gaps in ancient food webs
2021-01-14
If you want to understand an ecosystem, look at what the species within it eat. In studying food webs -- how animals and plants in a community are connected through their dietary preferences -- ecologists can piece together how energy flows through an ecosystem and how stable it is to climate change and other disturbances. Studying ancient food webs can help scientists reconstruct communities of species, many long extinct, and even use those insights to figure out how modern-day communities might change in the future. There's just one problem: only some species left enough of a trace for scientists to find eons later, leaving large gaps in the fossil record -- and researchers' ability to piece together the food webs from the past.
"When things die and get preserved as fossils, all the ...
Galaxies hit single, doubles, and triple (growing black holes)
2021-01-14
When three galaxies collide, what happens to the huge black holes at the centers of each? A new study using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and several other telescopes reveals new information about how many black holes are furiously growing after these galactic smash ups.
Astronomers want to learn more about galactic collisions because the subsequent mergers are a key way that galaxies and the giant black holes in their cores grow over cosmic time.
"There have been many studies of what happens to supermassive black holes when two galaxies merge," said Adi Foord of Stanford University, who led the study. "Ours is one of the first to systematically look at what happens to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
[Press-News.org] Reverse engineering 3D chromosome models for individual cellsDistant genes can be neighbors