Hubble pinpoints supernova blast
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has observed the supernova remnant named 1E 0102.2-7219. Researchers are using Hubble's imagery of the remnant object to wind back the clock on the expanding remains of this exploded star in the hope of understanding the supernova event that caused it 1700 years ago.
The featured star that exploded long ago belongs to the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way located roughly 200 000 light-years away. The doomed star left behind an expanding, gaseous corpse -- a supernova remnant -- known as 1E 0102.2-7219.
Because the gaseous knots in this supernova remnant are moving at different speeds and directions from the supernova explosion, those moving toward Earth are colored blue in this composition and the ones moving away are shown in red. This new Hubble image shows these ribbons of gas speeding away from the explosion site at an average speed of 3.2 million kilometers per hour. At that speed, you could travel to the Moon and back in 15 minutes.
Researchers have studied the Hubble archive looking for visible-light images of the supernova remnant and they have analysed the data to calculate a more accurate estimate of the age and centre of the supernova blast.
According to their new estimates [1], light from this blast arrived at Earth 1700 years ago, during the decline of the Roman Empire. This supernova would only have been visible to inhabitants of Earth's southern hemisphere. Unfortunately, there are no known records of this titanic event. Earlier studies proposed explosion dates of 2000 and 1000 years ago, but this new analysis is believed to be more robust.
To pinpoint when the explosion occurred, researchers studied the tadpole-shaped, oxygen-rich clumps of ejecta flung out by this supernova blast. Ionised oxygen is an excellent tracer because it glows brightest in visible light. By using Hubble's powerful resolution to identify the 22 fastest moving ejecta clumps, or knots, the researchers determined that these targets were the least likely to have been slowed down by passage through interstellar material. They then traced the knots' motion backward until the ejecta coalesced at one point, identifying the explosion site. Once that was known, they could calculate how long it took the speedy knots to travel from the explosion centre to their current location.
Hubble also measured the speed of a suspected neutron star -- the crushed core of the doomed star -- that was ejected from the blast. Based on the researchers' estimates, itmust be moving at more than 3 million kilometres per hour from the centre of the explosion to have arrived at its current position. The suspected neutron star was identified in observations with the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope in Chile, in combination with data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
INFORMATION:
Notes
[1] The international team of astronomers who carried out this study consists of J. Banovetz, D. Milisavljevic, N. Sravan, R. A. Fesen, D. J. Patnaude, P. P. Plucinsky, W. P. Blair, K. E. Weil, J. A. Morse, R. Margutti, and M. R. Drout.
The Hubble Space Telescope observations involved in this study are associated with programmes 6052 (Morse), 12001 (Green), 12858 (Madore), and 13378 (Milisavljevic).
These results have been presented at the 237th American Astronomical Society virtual meeting on 14 January 2021 and will be published in the Astrophysical Journal.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
The researchers published their report in the Journal Nature Communications from 15 January 2021.
When the communication breaks down
Spinal cord injuries caused by sports or traffic accidents often result in permanent disabilities such as paraplegia. This is caused by damage to nerve fibers, so-called axons, which carry information from the brain to the muscles and back from the skin and muscles. If these fibers are damaged due to injury or illness, this communication is interrupted. Since severed axons in the spinal cord can't grow back, the patients suffer from paralysis and numbness for life. To date, there are still no treatment options that could restore the lost functions ...
2021-01-15
El Niño or correctly El Niño - Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the strongest natural climate fluctuation on time scales of a few years. Through ocean and atmosphere interactions, El Niño (Spanish for The Christ Child) events cause significant warming of the eastern Pacific, accompanied by catastrophic rainfall over South America and droughts in the Indo-Pacific region. Powerful events have global effects that reach even into the extra-tropics. There is also an El Niño variant in the Atlantic, called the Atlantic Niño, which, for example, has effects on rainfall in West Africa as well as the development of tropical cyclones over the eastern tropical Atlantic. A better understanding of the poorly investigated little ...
2021-01-15
Philadelphia, January 14, 2021--In a large study of pediatric cancer patients, researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have analyzed the frequency, fusion partners, and clinical outcome of neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) fusions, which are clinical biomarkers that identify patients suitable for treatment with FDA-approved TRK inhibitors. The researchers found that NTRK fusions are more common in pediatric tumors and also involve a wider range of tumors than adult cancers, information that could help prioritize screening for NTRK fusions in pediatric cancer patients who might benefit from treatment with TRK inhibitors.
The ...
2021-01-15
The experiment was performed at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) in Osaka. The research team, lead by scientists from TU Darmstadt and the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy-Ion Research, and from the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science, discuss the new findings in a contribution to the latest issue of the journal "Science".
The strong interaction binds neutrons and protons together to atomic nuclei. The knowledge of properties of nuclei and their theoretical description is basis for our understanding of nuclear matter and the development of the universe. Laboratory-based studies of reactions between atomic nuclei provide means to explore nuclear properties. These experiments ...
2021-01-15
Diabetes is characterized by elevated levels of sugar or glucose (hyperglycemia) in the blood. This occurs due to the lack of the hormone insulin in type 1 diabetes, and to reduced insulin levels in combination with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. A recent review of data supports stricter control of hemoglobin A1C levels (HbA1C) among pediatric patients with T1D. This review was led by Dr. Maria J. Redondo, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's Hospital and professor at Baylor College of Medicine, in collaboration with Dr. Sarah Lyons, pediatric endocrinologist at Texas Children's and assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, ...
2021-01-15
A refractive index of zero induces a wave vector with zero amplitude and undefined direction. Therefore, light propagating inside a zero-index medium does not accumulate any spatial phase advance, resulting in perfect spatial coherence. Such coherence brings several potential applications, including arbitrarily shaped waveguides, phase-mismatch-free nonlinear propagation, large-area single-mode lasers, and extended super radiance. A promising platform to achieve these applications is an integrated Dirac-cone material that features an impedance-matched zero index. However, although this platform eliminates ohmic losses via its purely dielectric structure, it still entails out-of-plane radiation loss (about 1 dB/μm), restricting the applications to a small scale.
In ...
2021-01-15
The development of ultrafast all-optical switches has long been a popular topic in photonics, while the speed of magnetization reversal triggered by means other than magnetic fields has recently attracted intense interest in spintronics. The discovery of all-optical helicity-dependent switching in metallic GdFeCo has promised a merger of the fields of photonics and spintronics, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient information processing technologies. However, the real potential of all-optical switching is still poorly understood because it is still unclear whether magnetic switching by light can keep up with the GHz frequencies required by photonics technologies. ...
2021-01-15
"The lotus roots may break, but the fiber remains joined" is an old Chinese saying that reflects the unique structure and mechanical properties of the lotus fiber. The outstanding mechanical properties of lotus fibers can be attributed to their unique spiral structure, which provides an attractive model for biomimetic design of artificial fibers.
In a new study published in Nano Letters, a team led by Prof. YU Shuhong from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a bio-inspired lotus-fiber-mimetic spiral structure bacterial cellulose (BC) hydrogel fiber with high strength, ...
2021-01-15
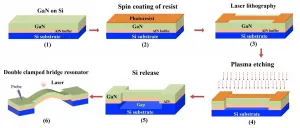
Liwen Sang, independent scientist at International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science (also JST PRESTO researcher) developed a MEMS resonator that stably operates even under high temperatures by regulating the strain caused by the heat from gallium nitride (GaN).
High-precision synchronization is required for the fifth generation mobile communication system (5G) with a high speed and large capacity. To that end, a high-performance frequency reference oscillator which can balance the temporal stability and temporal resolution is necessary as a timing device to generate signals ...
2021-01-15
PULLMAN, Wash. - Scientists have identified the presence of a non-tobacco plant in ancient Maya drug containers for the first time.
The Washington State University researchers detected Mexican marigold (Tagetes lucida) in residues taken from 14 miniature Maya ceramic vessels.
Originally buried more than 1,000 years ago on Mexico's Yucatán peninsula, the vessels also contain chemical traces present in two types of dried and cured tobacco, Nicotiana tabacum and N. rustica. The research team, led by anthropology postdoc Mario Zimmermann, thinks the Mexican marigold was mixed with the tobacco to make smoking more enjoyable.
The discovery of the vessels' contents paints a clearer picture of ancient Maya drug use practices. The research, which was published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hubble pinpoints supernova blast