New videos show RNA as it's never been seen
First-ever data-driven videos illuminate RNA's mysterious folding process
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) A new Northwestern University-led study is unfolding the mystery of how RNA molecules fold themselves to fit inside cells and perform specific functions. The findings could potentially break down a barrier to understanding and developing treatments for RNA-related diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy and perhaps even the novel coronavirus.
"RNA folding is a dynamic process that is fundamental for life," said Northwestern's Julius B. Lucks, who led the study. "RNA is a really important piece of diagnostic and therapeutic design. The more we know about RNA folding and complexities, the better we can design treatments."
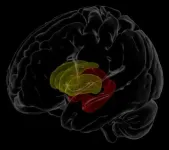
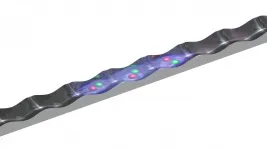
Using data from RNA-folding experiments, the researchers generated the first-ever data-driven movies of how RNA folds as it is made by cellular machinery. By watching their videos of this folding occur, the researchers discovered that RNA often folds in surprising, perhaps unintuitive ways, such as tying itself into knots -- and then immediately untying itself to reach its final structure.
"Folding takes place in your body more than 10 quadrillion times a second," Lucks said. "It happens every single time a gene is expressed in a cell, yet we know so little about it. Our movies allow us to finally watch folding happen for the first time."
The research will be published Jan. 15 in the journal Molecular Cell.
Lucks is an associate professor of chemical and biological engineering at Northwestern's McCormick School of Engineering and a member of Northwestern's Center for Synthetic Biology. He co-led the work with Alan Chen, an associate professor of chemistry at the University of Albany.
Although videos of RNA folding do exist, the computer models that generate them are full of approximations and assumptions. Lucks' team has developed a technology platform that captures data about RNA folding as the RNA is being made. His group then uses computational tools to mine and organize the data, revealing points where the RNA folds and what happens after it folds. Angela Yu, a former student of Lucks, inputted this data into computer models to generate accurate videos of the folding process.
"The information that we give the algorithms helps the computer models correct themselves," Lucks said. "The model makes accurate simulations that are consistent with the data."
Lucks and his collaborators used this strategy to model the folding of an RNA called SRP, an ancient RNA found in all kingdoms of life. The molecule is well-known for its signature hairpin shape. When watching the videos, the researchers discovered that the molecule ties itself into a knot and unties itself very quickly. Then it suddenly flips into the correct hairpin-like structure using an elegant folding pathway called toehold mediated strand displacement.
"To the best of our knowledge, this has never been seen in nature," Lucks said. "We think the RNA has evolved to untie itself from knots because if knots persist, it can render the RNA nonfunctional. The structure is so essential to life that it had to evolve to find a way to get out of a knot."
INFORMATION:
The study, "Computationally reconstructing cotranscriptional RNA folding pathways from experimental data reveals rearrangement of non-native folding intermediates," was supported by the National Institutes of Health (award numbers T32GM083937, 1DP2GM110838 and GM120582), the National Science Foundation (award numbers MCB1651877 and 1914567) and the Searle Funds at The Chicago Community Trust.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
Nearly 38 million people around the world are living with HIV, which, with access to treatment, has become a lifelong chronic condition. Understanding how infection changes the brain, especially in the context of aging, is increasingly important for improving both treatment and quality of life.
In January, researchers at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (USC Stevens INI), part of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, and other international NeuroHIV researchers, published one of the largest-ever neuroimaging studies of HIV. The researchers pooled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data from 1,203 HIV-positive individuals across Africa, ...
2021-01-15
The White-lipped peccary Tayassu pecari is a boar-like hoofed mammal found throughout Central and South America. These animals roam the forest in bands of 50 to 100 individuals, eating a wide variety of foods. In Brazil's Atlantic Rainforest, they prefer the fruit of the jussara palm Euterpe edulis.
The jussara is very abundant in this biome, probably thanks to vast amounts of dung, urine, and soil trampling by peccaries as well as tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) and other fruit-eating animals, or frugivores. This behavior releases forms of nitrogen, a key element in plant growth.
A study supported ...
2021-01-15
Boston - A national group of pediatric addiction medicine experts have released newly-established principles of care for young adults with substance use disorder. Led by the Grayken Center for Addiction at Boston Medical Center, the collection of peer-reviewed papers was developed to guide providers on how to treat young adults with substance use disorder given their age-specific needs, as well as elevate national discussions on addressing these challenges more systematically.
Published in Pediatrics, the 11-paper supplement is the result of a convening of national experts in the treatment of young adults to determine the most important principles to address when caring for this unique population of patients with substance use disorder. ...
2021-01-15
Liquids are ubiquitous in Nature: from the water that we consume daily to superfluid helium which is a quantum liquid appearing at temperatures as low as only a few degrees above the absolute zero. A common feature of these vastly different liquids is being self-bound in free space in the form of droplets. Understanding from a microscopic perspective how a liquid is formed by adding particles one by one is a significant challenge.
Recently, a new type of quantum droplets has been experimentally observed in ultracold atomic systems. These ones ...
2021-01-15
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Texas Medical Branch (US) have shown how optoacoustics can be used for monitoring skin water content, a technique which is promising for medical applications such as tissue trauma management and in cosmetology. The paper outlining these results was published in the Journal of Biophotonics.
(swelling caused by fluid accumulation) or dehydration, which can also have cosmetic impacts. Right now, electrical, mechanical and spectroscopic methods can be used to monitor water content in tissues, but there is no accurate and noninvasive technique that would also provide a high resolution and significant probing depth required for potential clinical applications.
Sergei Perkov of the Skoltech Center for Photonics ...
2021-01-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - "Buy low and sell high" says the old adage about investing in the stock market.
But a relatively new type of investment fund is luring unsophisticated investors into buying when values are at their highest, resulting in losses almost immediately, a new study has found.
The lure? Buying into trendy investment areas like cannabis, cybersecurity and work-from-home businesses.
"As soon as people buy them, these securities underperform as the hype around them vanishes," said Itzhak Ben-David, co-author of the study and professor of finance at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"They appeal to people who are not sophisticated ...
2021-01-15
New Rochelle, NY, January 15, 2021--The biodistribution of adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene transfer vectors can be measured in nonhuman primates using a new method. The method quantifies whole-body and organ-specific AAV capsids from 1 to 72 hours after administration. Study design and results are presented in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website through February 15, 2021.
AAV capsids were labeled with I-124 and delivered using two routes of administration: intravenous and directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Biodistribution was measured by quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) at 1, 24, 48, and 72 hours after AAV administration. Two AAV vectors - AAVrsh.10 and AAV9 - were compared.
"Following ...
2021-01-15
HAMILTON, ON, Jan. 15, 2021 -- A team of neuroscientists and engineers at McMaster University has created a nasal spray to deliver antipsychotic medication directly to the brain instead of having it pass through the body.
The leap in efficiency means patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and other conditions could see their doses of powerful antipsychotic medications cut by as much as three quarters, which is expected to spare them from sometimes-debilitating side effects while also significantly reducing the frequency of required treatment.
The new method delivers medication in a spray that reaches the brain directly through ...
2021-01-15
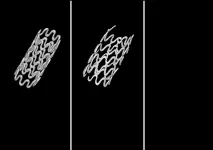
Pediatric laryngotracheal stenosis (LTS), a narrowing of the airway in children, is a complex medical condition. While it can be something a child is born with or caused by injury, the condition can result in a life-threatening emergency if untreated.
Treatment, however, is challenging. Depending on the severity, doctors will use a combination of endoscopic techniques, surgical repair, tracheostomy, or deployment of stents to hold the airway open and enable breathing.
While stents are great at holding the airway open and simultaneously allowing the trachea to continue growing, they can move around, ...
2021-01-15
There is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, but a group of scientists believe they've discovered a method through which a simple knee injection could potentially stop the disease's effects. These researchers showed that they could target a specific protein pathway in mice, put it into overdrive and halt cartilage degeneration over time. Building on that finding, they were able to show that treating mice with surgery-inducedknee cartilage degeneration through the same pathway via the state of the art of nanomedicine could dramatically reduce the cartilage degeneration and knee pain. These findings were published in Science Translational Medicine.
"Our lab is one of the few in the world studying epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New videos show RNA as it's never been seen
First-ever data-driven videos illuminate RNA's mysterious folding process