Better diet and glucose uptake in the brain lead to longer life in fruit flies
Improved neuronal glucose uptake plus healthier eating might have anti-aging effects
2021-01-16
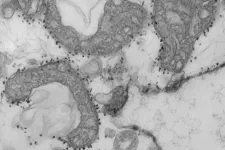
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that fruit flies with genetic modifications to enhance glucose uptake have significantly longer lifespans. Looking at the brain cells of aging flies, they found that better glucose uptake compensates for age-related deterioration in motor functions, and led to longer life. The effect was more pronounced when coupled with dietary restrictions. This suggests healthier eating plus improved glucose uptake in the brain might lead to enhanced lifespans.
The brain is a particularly power-hungry part of our bodies, consuming 20% of the oxygen we take in and 25% of the glucose. That's why it's so important that it can stay powered, using the glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "energy courier" of the body. This chemical process, known as glycolysis, happens in both the intracellular fluid and a part of cells known as the mitochondria. But as we get older, our brain cells become less adept at making ATP, something that broadly correlates with less glucose availability. That might suggest that more food for more glucose might actually be a good thing. On the other hand, it is known that a healthier diet actually leads to longer life. Unravelling the mystery surrounding these two contradictory pieces of knowledge might lead to a better understanding of healthier, longer lifespans.
A team led by Associate Professor Kanae Ando studied this problem using Drosophila fruit flies. Firstly, they confirmed that brain cells in older flies tended to have lower levels of ATP, and lower uptake of glucose. They specifically tied this down to lower amounts of the enzymes needed for glycolysis. To counteract this effect, they genetically modified flies to produce more of a glucose-transporting protein called hGut3. Amazingly, this increase in glucose uptake was all that was required to significantly improve the amount of ATP in cells. More specifically, they found that more hGut3 led to less decrease in the production of the enzymes, counteracting the decline with age. Though this did not lead to an improvement in age-related damage to mitochondria, they also suffered less deterioration in locomotor functions.
But that's not all. In a further twist, the team put the flies with enhanced glucose uptake under dietary restrictions, to see how the effects interact. Now, the flies had even longer lifespans. Curiously, the increased glucose uptake did not actually improve the levels of glucose in brain cells. The results point to the importance of not just how much glucose there is, but how efficiently it is used once taken into cells to make the energy the brain needs.
Though the anti-aging benefits of a restricted diet have been shown in many species, the team were able to combine this with improved glucose uptake to leverage the benefits of both for even longer lifespans in a model organism. Further study may provide vital clues to how we might keep our brains healthier for longer.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by a research award from the Japan Foundation for Aging and Health, a JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Challenging Research (Exploratory) (19K21593), NIG-JOINT (71A2018, 25A2019), a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Research Fellows (18J21936) and Research Funding for Longevity Science (19-7) from the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology, Japan.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-16
The spread of COVID-19 in Brazil overwhelmed the health systems in all the country's regions, particularly in areas where they were already fragile, according to a collaborative effort involving the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, the University of Sao Paulo, the Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro, the D'Or Institute of Research and Education and the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation. The findings, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, reveal that a large percentage of COVID-19 patients that were hospitalised in Brazil required intensive care and respiratory support, and many did not survive.
The COVID-19 pandemic has put an enormous strain on healthcare ...
2021-01-16
BOSTON - The Study on Stress, Spirituality and Health (SSSH), a cutting-edge proteomics analysis, suggests that religious beliefs modulate protein expression associated with cardiovascular disease in South Asians in the United States. The research, published by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) in Scientific Reports, demonstrates that spiritual struggles, in particular, significantly modify the impact of unique proteins on risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in U.S. South Asians, a community that has especially ...
2021-01-16
One of the most vexing aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic is doctors' inability to predict which newly hospitalized patients will go on to develop severe disease, including complications that require the insertion of a breathing tube, kidney dialysis or other intensive care. Knowledge of a patient's age and underlying medical conditions can help predict such outcomes, but there are still surprises when younger, seemingly healthier patients suffer severe complications that can lead to death.
Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown that a relatively simple and rapid blood test can predict -- within a day of a hospital admission -- which patients with ...
2021-01-15
MIAMI--A group of more than 60 scientists have provided recommendations to improve the Indian Ocean Observing System (IndOOS), a basin-wide monitoring system to better understand the impacts of human-caused climate change in a region that has been warming faster than any other ocean.
The group, led by Lisa Beal, professor of ocean sciences at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, provides a road map for an enhanced IndOOS to better meet the scientific and societal needs for more reliable environmental forecasts in the next decade. The 136 actionable recommendations from the three-year, internationally coordinated review were published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
The scientists call for four major ...
2021-01-15
A University of Saskatchewan study has found that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant worsening of already poor dietary habits, low activity levels, sedentary behaviour, and high alcohol consumption among university students.
The findings of the study--the first to assess changes in students' dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour before and during the pandemic--are published today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism.
"Our findings are important because university students, especially those most vulnerable for poor nutrition and sedentary behaviour, should be targeted for interventions aimed at maintaining and improving physical activity and dietary practices during this pandemic and beyond," said lead author ...
2021-01-15
As the vaccination of older adults against COVID-19 begins across the country, new poll data suggests that many of them don't yet have access to the "patient portal" online systems that could make it much easier for them to schedule a vaccination appointment.
The poll finds that 45% of adults aged 65 to 80, and 42% of all adults aged 50 to 80, said they had not set up an account with their health provider's portal system. That's according to the newly analyzed data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at the University of Michigan's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
The new number actually represents some progress: 49% of adults in the same age range hadn't set up patient portal access the last time the ...
2021-01-15
Exactly what kills a person with COVID-19?
How do those deaths differ from the deaths of people whose lungs fail rapidly because of other infections or injuries?
And what can hospital teams pressed into service on overtaxed COVID-19 wards do to try to keep patients from dying, despite strained circumstances?
All of these questions have sparked discussion - and even conspiracy theories - since the pandemic began. Now, two studies from Michigan Medicine may help answer them.
The bottom line: COVID-19 deaths are indeed different from other lung failure deaths. But, the researchers conclude, the kind of care needed to help sustain people through the worst cases of all forms of lung failure is highly similar. It just needs to be fine-tuned to focus on the ...
2021-01-15
Scientists have uncovered new clues implicating a type of herpes virus as the cause of a central nervous system disease in monkeys that's similar to multiple sclerosis in people.
The findings, published in the Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, expand on previous work to understand the cause of the disease and potentially develop antiviral therapies. The work was led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University.
"This gives us a better understanding of the model," said Scott Wong, Ph.D., senior author of the study and a scientist at the OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute and the Oregon National Primate Research Center. "It draws more parallels to MS in people."
The new study reveals the presence of two kinds of T cells, a type of ...
2021-01-15
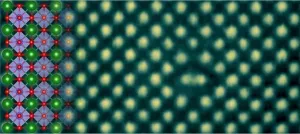
In groundbreaking materials research, a team led by University of Minnesota Professor K. Andre Mkhoyan has made a discovery that blends the best of two sought-after qualities for touchscreens and smart windows--transparency and conductivity.
The researchers are the first to observe metallic lines in a perovskite crystal. Perovskites abound in the Earth's center, and barium stannate (BaSnO3) is one such crystal. However, it has not been studied extensively for metallic properties because of the prevalence of more conductive materials on the planet like metals or semiconductors. The ...
2021-01-15
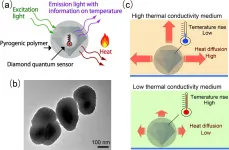
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists from Osaka University, The University of Queensland, and the National University of Singapore's Faculty of Engineering used tiny nanodiamonds coated with a heat-releasing polymer to probe the thermal properties of cells. When irradiated with light from a laser, the sensors acted both as heaters and thermometers, allowing the thermal conductivity of the interior of a cell to be calculated. This work may lead to a new set of heat-based treatments for killing bacteria or cancer cells.
Even though the cell is the fundamental unit of all living organisms, some physical properties have remained difficult to study in vivo. For example, a cell's thermal conductivity, as well as the rate that heat can flow through an object if ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Better diet and glucose uptake in the brain lead to longer life in fruit flies
Improved neuronal glucose uptake plus healthier eating might have anti-aging effects