INFORMATION:
Other members of the research team were graduate student Keely Shaw, research assistant John Ko, and undergraduate summer student Dalton Deprez.
USask study finds COVID isolation worsens student diets, inactivity, and alcohol intake
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) A University of Saskatchewan study has found that the COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant worsening of already poor dietary habits, low activity levels, sedentary behaviour, and high alcohol consumption among university students.
The findings of the study--the first to assess changes in students' dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour before and during the pandemic--are published today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition and Metabolism.
"Our findings are important because university students, especially those most vulnerable for poor nutrition and sedentary behaviour, should be targeted for interventions aimed at maintaining and improving physical activity and dietary practices during this pandemic and beyond," said lead author and nutrition professor Gordon Zello.
The four-month study involved 125 graduate and undergraduate students at USask and the University of Regina who were the most vulnerable as they were living independently or had roommates or partners, and were responsible for buying and preparing their own meals.
The students responded to an online questionnaire about their food and drink consumption, physical activity and sedentary behaviour before and during the pandemic.
The study began just as Saskatchewan was imposing pandemic restrictions, so details of what students were eating prior to the pandemic and during it were fresh on the minds of students, said Zello.
"With pre-pandemic research already showing university students to be a vulnerable group for inadequate diet and physical activity, the measures imposed to curb the COVID pandemic presented a unique opportunity to examine further impact on their lives," Zello said.
The study found that the students consumed less food every day during the pandemic compared to before. For instance, they ate 20 per cent less meat, 44 per cent less dairy, and 45 per cent fewer vegetables. While they also drank considerably fewer beverages such as coffee and tea, their alcohol consumption increased significantly, said Zello.
"This dietary inadequacy combined with long hours of sedentary behaviour and decreased physical activity could increase health risks in this unique population during COVID-19 confinement and once the pandemic ends," Zello said.
Several reasons could explain the dietary shift, said Zello and co-investigators kinesiology professor Phil Chilibeck and post-doctoral fellow Leandy Bernard. Psychological distress has been linked to poor diet quality, particularly increased consumption of alcohol. As well, students could be eating less to offset their lack of exercise and increased sedentariness.
Zello said measures implemented to fight COVID spread, such as reduced store and restaurant hours, may have limited students' shopping frequency and at-home availability of food.
While only 16 per cent of participants were meeting Canadian guidelines of 150 minutes of moderate to intense physical activity per week before the pandemic, that further decreased to 9.6 per cent during the pandemic.
Of those who were meeting Canadian activity guidelines before the pandemic, 90 per cent became less active. Meanwhile, the number of hours spent in sedentary behaviour rose by three hours, to about 11 hours a day.
"There's no doubt that measures such as the closures of gyms and other recreational facilities by the universities and other private and public establishments within the province resulted in reductions in the level of physical activity," the study states.
Another reason for the reduction in physical activity may be that many students were no longer walking to school after the universities moved to remote learning, it says.
About 55 per cent were employed before the pandemic, dropping to 49 per cent during the pandemic.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
45% of adults over 65 lack online medical accounts, which could affect COVID vaccination
2021-01-15
As the vaccination of older adults against COVID-19 begins across the country, new poll data suggests that many of them don't yet have access to the "patient portal" online systems that could make it much easier for them to schedule a vaccination appointment.
The poll finds that 45% of adults aged 65 to 80, and 42% of all adults aged 50 to 80, said they had not set up an account with their health provider's portal system. That's according to the newly analyzed data from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at the University of Michigan's Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
The new number actually represents some progress: 49% of adults in the same age range hadn't set up patient portal access the last time the ...
COVID-19 deaths really are different. But best practices for ICU care should still apply
2021-01-15
Exactly what kills a person with COVID-19?
How do those deaths differ from the deaths of people whose lungs fail rapidly because of other infections or injuries?
And what can hospital teams pressed into service on overtaxed COVID-19 wards do to try to keep patients from dying, despite strained circumstances?
All of these questions have sparked discussion - and even conspiracy theories - since the pandemic began. Now, two studies from Michigan Medicine may help answer them.
The bottom line: COVID-19 deaths are indeed different from other lung failure deaths. But, the researchers conclude, the kind of care needed to help sustain people through the worst cases of all forms of lung failure is highly similar. It just needs to be fine-tuned to focus on the ...
T cells linked to myelin implicated in MS-like disease in monkeys
2021-01-15
Scientists have uncovered new clues implicating a type of herpes virus as the cause of a central nervous system disease in monkeys that's similar to multiple sclerosis in people.
The findings, published in the Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, expand on previous work to understand the cause of the disease and potentially develop antiviral therapies. The work was led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University.
"This gives us a better understanding of the model," said Scott Wong, Ph.D., senior author of the study and a scientist at the OHSU Vaccine and Gene Therapy Institute and the Oregon National Primate Research Center. "It draws more parallels to MS in people."
The new study reveals the presence of two kinds of T cells, a type of ...
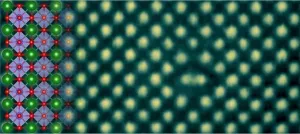
Conductive nature in crystal structures revealed at magnification of 10 million times
2021-01-15
In groundbreaking materials research, a team led by University of Minnesota Professor K. Andre Mkhoyan has made a discovery that blends the best of two sought-after qualities for touchscreens and smart windows--transparency and conductivity.
The researchers are the first to observe metallic lines in a perovskite crystal. Perovskites abound in the Earth's center, and barium stannate (BaSnO3) is one such crystal. However, it has not been studied extensively for metallic properties because of the prevalence of more conductive materials on the planet like metals or semiconductors. The ...
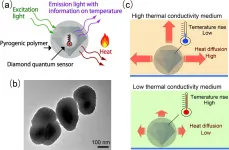
Nanodiamonds feel the heat
2021-01-15
Osaka, Japan - A team of scientists from Osaka University, The University of Queensland, and the National University of Singapore's Faculty of Engineering used tiny nanodiamonds coated with a heat-releasing polymer to probe the thermal properties of cells. When irradiated with light from a laser, the sensors acted both as heaters and thermometers, allowing the thermal conductivity of the interior of a cell to be calculated. This work may lead to a new set of heat-based treatments for killing bacteria or cancer cells.
Even though the cell is the fundamental unit of all living organisms, some physical properties have remained difficult to study in vivo. For example, a cell's thermal conductivity, as well as the rate that heat can flow through an object if ...
Glass frogs living near roaring waterfalls wave hello to attract mates
2021-01-15
Berkeley -- Most frogs emit a characteristic croak to attract the attention of a potential mate. But a few frog species that call near loud streams -- where the noise may obscure those crucial love songs -- add to their calls by visually showing off with the flap of a hand, a wave of a foot or a bob of the head. Frogs who "dance" near rushing streams have been documented in the rainforests of India, Borneo, Brazil and, now, Ecuador.
Conservation ecologist Rebecca Brunner, a Ph.D. candidate at the University of California, Berkeley, has discovered that the glass frog ...
New study compiles four years of corn loss data from 26 states and Ontario, Canada
2021-01-15
Plant pathologists working at universities across 26 corn-producing states in the United States and in Ontario, Canada, compiled data about annual corn reductions caused by diseases. Estimated loss from each disease varied greatly by region.
"This group of plant pathologists takes a step back to estimate what has gone wrong in corn fields in each of their states," said Iowa State University plant pathologist Daren Mueller, who was involved in this project. "Collectively, and across years, corn disease loss estimates provide folks a zoomed out view of what diseases are affecting corn in the U.S. and Canada."
To Mueller, these data represent one of the pieces of a good research project. Researchers can use these data to justify new research projects that can help mitigate the impacts ...
US fishing and seafood industries saw broad declines last summer due to COVID-19
2021-01-15
The U.S. fishing and seafood sector generated more than $200 billion in annual sales and supported 1.7 million jobs in recent years. It experienced broad declines in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 public health crisis, according to a new NOAA Fisheries analysis released today. While losses vary by sector, by region and by industry, data and information from this report may help businesses and communities assess losses and inform long-term recovery and resilience strategies.
According to analysts, COVID-19 protective measures instituted in March across the United States and globe contributed to an almost-immediate impact on seafood sector sales. There was a strong start to the year, with ...
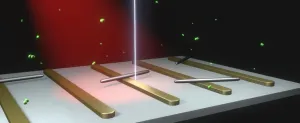
Controlling chemical catalysts with sculpted light
2021-01-15
Like a person breaking up a cat fight, the role of catalysts in a chemical reaction is to hurry up the process - and come out of it intact. And, just as not every house in a neighborhood has someone willing to intervene in such a battle, not every part of a catalyst participates in the reaction. But what if one could convince the unengaged parts of a catalyst to get involved? Chemical reactions could occur faster or more efficiently.
Stanford University material scientists led by Jennifer Dionne have done just that by using light and advanced fabrication and characterization techniques to endow catalysts with new abilities.
In a proof-of-concept experiment, rods of palladium that were approximately 1/200th the width of a human hair served as catalysts. ...
Special interests can be assets for youth with autism
2021-01-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. - When he was in middle school, teachers would give Sam Curran a list of words to type in a computer to practice his vocabulary. But Sam, who has autism, was unable to stay focused on the task and required a significant amount of one-to-one direction from a teacher to complete his work. After his mother, Alicia, persuaded his teachers to allow Sam to change the colors of the words, he was able to complete work more independently and began making remarkable progress.
Now 20 years old, Sam's mother continues to ensure his special interests are leveraged in an effort to continue to help him grow and develop. A new survey from the MU Thompson Center for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders has found that similar strategies for children with disabilities can help reduce anxiety ...