US fishing and seafood industries saw broad declines last summer due to COVID-19
New analysis by NOAA Fisheries provides insights into the pandemic's early economic impact
2021-01-15
(Press-News.org) The U.S. fishing and seafood sector generated more than $200 billion in annual sales and supported 1.7 million jobs in recent years. It experienced broad declines in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 public health crisis, according to a new NOAA Fisheries analysis released today. While losses vary by sector, by region and by industry, data and information from this report may help businesses and communities assess losses and inform long-term recovery and resilience strategies.
According to analysts, COVID-19 protective measures instituted in March across the United States and globe contributed to an almost-immediate impact on seafood sector sales. There was a strong start to the year, with a 3 percent increase in commercial fish landings revenue in January and February. However, revenues declined each month from a 19 percent decrease in March to a 45 percent decrease by July. This translates to a 29 percent decrease across those 7 months, as compared to 5-year averages and adjusted for inflation.
Restaurant closures, social distancing protocols, and other safety measures also contributed to losses in other sectors of the seafood economy. By the end of second quarter 2020, 78 percent of aquaculture, aquaponics, and allied businesses reported COVID-19 impacts with 74 percent experiencing lost sales. The analysis noted outdoor seating at restaurants in warm months and a pivot to direct delivery at some supermarkets provided an outlet for some aquaculture sales. Also, the recreational charter/for-hire fishing industry was completely shut down in the spring with some phased reopenings in the early summer. The new analysis contains regional snapshots to help industries understand local impacts to key fisheries.
"In the coming months and years, scientists and economists will work to obtain a more complete picture of COVID-19's impact on U.S. seafood and the Blue Economy. It is our hope that this initial analysis provides a foundation that the industry researchers and planners can draw upon as they plan for the future," said NOAA Fisheries Assistant Administrator Chris Oliver.
On the trade front, international markets were negatively affected by disruptions in harvesting, processing and shipping. U.S. seafood exports declined 18 percent in value in the January to June period, when compared to the past five years. Fresh product exports experienced steeper declines when compared to frozen product exports. The value of seafood imports into the United States declined 4 percent in value in this period. These declines were offset by U.S. consumer demand for tuna imports (canned and in pouches), which increased 25 percent in this 6-month period, peaking to 49 percent in June.
The report notes that some U.S. industry losses may be offset by the infusion of emergency federal relief funding. In May, NOAA allocated $300 million in fisheries aid to states, territories, and tribes as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act. They, with the help of interstate commissions, are distributing these much-needed funds to eligible fishery participants. Furthermore, in September, the Secretary of Agriculture made $530 million available through the Seafood Trade Relief Program to support fishermen and industries impacted by retaliatory tariffs from foreign governments.
"NOAA Fisheries stands with our fishermen, seafood industries, and coastal communities who have suffered great economic hardship this year due to COVID-19," added Oliver. "The United States is a global leader in sustainable, world class fisheries. Our goal is to help all those up and down the U.S. seafood supply chain rebound, recover and strengthen resilience as we plan strong returns to sea in 2021 and beyond."
INFORMATION:
Read the report and regional snapshots: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/feature-story/us-fishing-and-seafood-industries-saw-broad-declines-last-summer-due-covid-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-15
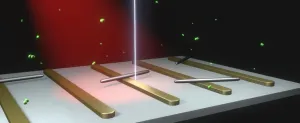
Like a person breaking up a cat fight, the role of catalysts in a chemical reaction is to hurry up the process - and come out of it intact. And, just as not every house in a neighborhood has someone willing to intervene in such a battle, not every part of a catalyst participates in the reaction. But what if one could convince the unengaged parts of a catalyst to get involved? Chemical reactions could occur faster or more efficiently.
Stanford University material scientists led by Jennifer Dionne have done just that by using light and advanced fabrication and characterization techniques to endow catalysts with new abilities.
In a proof-of-concept experiment, rods of palladium that were approximately 1/200th the width of a human hair served as catalysts. ...
2021-01-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. - When he was in middle school, teachers would give Sam Curran a list of words to type in a computer to practice his vocabulary. But Sam, who has autism, was unable to stay focused on the task and required a significant amount of one-to-one direction from a teacher to complete his work. After his mother, Alicia, persuaded his teachers to allow Sam to change the colors of the words, he was able to complete work more independently and began making remarkable progress.
Now 20 years old, Sam's mother continues to ensure his special interests are leveraged in an effort to continue to help him grow and develop. A new survey from the MU Thompson Center for Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders has found that similar strategies for children with disabilities can help reduce anxiety ...
2021-01-15
A new Northwestern University-led study is unfolding the mystery of how RNA molecules fold themselves to fit inside cells and perform specific functions. The findings could potentially break down a barrier to understanding and developing treatments for RNA-related diseases, including spinal muscular atrophy and perhaps even the novel coronavirus.
"RNA folding is a dynamic process that is fundamental for life," said Northwestern's Julius B. Lucks, who led the study. "RNA is a really important piece of diagnostic and therapeutic design. The more we know about RNA folding and complexities, the better we can design treatments."
Using data from RNA-folding experiments, the researchers generated the first-ever data-driven movies of how RNA folds as it is made by cellular ...
2021-01-15
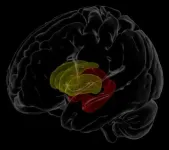
Nearly 38 million people around the world are living with HIV, which, with access to treatment, has become a lifelong chronic condition. Understanding how infection changes the brain, especially in the context of aging, is increasingly important for improving both treatment and quality of life.
In January, researchers at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (USC Stevens INI), part of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, and other international NeuroHIV researchers, published one of the largest-ever neuroimaging studies of HIV. The researchers pooled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data from 1,203 HIV-positive individuals across Africa, ...
2021-01-15
The White-lipped peccary Tayassu pecari is a boar-like hoofed mammal found throughout Central and South America. These animals roam the forest in bands of 50 to 100 individuals, eating a wide variety of foods. In Brazil's Atlantic Rainforest, they prefer the fruit of the jussara palm Euterpe edulis.
The jussara is very abundant in this biome, probably thanks to vast amounts of dung, urine, and soil trampling by peccaries as well as tapirs (Tapirus terrestris) and other fruit-eating animals, or frugivores. This behavior releases forms of nitrogen, a key element in plant growth.
A study supported ...
2021-01-15
Boston - A national group of pediatric addiction medicine experts have released newly-established principles of care for young adults with substance use disorder. Led by the Grayken Center for Addiction at Boston Medical Center, the collection of peer-reviewed papers was developed to guide providers on how to treat young adults with substance use disorder given their age-specific needs, as well as elevate national discussions on addressing these challenges more systematically.
Published in Pediatrics, the 11-paper supplement is the result of a convening of national experts in the treatment of young adults to determine the most important principles to address when caring for this unique population of patients with substance use disorder. ...
2021-01-15
Liquids are ubiquitous in Nature: from the water that we consume daily to superfluid helium which is a quantum liquid appearing at temperatures as low as only a few degrees above the absolute zero. A common feature of these vastly different liquids is being self-bound in free space in the form of droplets. Understanding from a microscopic perspective how a liquid is formed by adding particles one by one is a significant challenge.
Recently, a new type of quantum droplets has been experimentally observed in ultracold atomic systems. These ones ...
2021-01-15
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Texas Medical Branch (US) have shown how optoacoustics can be used for monitoring skin water content, a technique which is promising for medical applications such as tissue trauma management and in cosmetology. The paper outlining these results was published in the Journal of Biophotonics.
(swelling caused by fluid accumulation) or dehydration, which can also have cosmetic impacts. Right now, electrical, mechanical and spectroscopic methods can be used to monitor water content in tissues, but there is no accurate and noninvasive technique that would also provide a high resolution and significant probing depth required for potential clinical applications.
Sergei Perkov of the Skoltech Center for Photonics ...
2021-01-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - "Buy low and sell high" says the old adage about investing in the stock market.
But a relatively new type of investment fund is luring unsophisticated investors into buying when values are at their highest, resulting in losses almost immediately, a new study has found.
The lure? Buying into trendy investment areas like cannabis, cybersecurity and work-from-home businesses.
"As soon as people buy them, these securities underperform as the hype around them vanishes," said Itzhak Ben-David, co-author of the study and professor of finance at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"They appeal to people who are not sophisticated ...
2021-01-15
New Rochelle, NY, January 15, 2021--The biodistribution of adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene transfer vectors can be measured in nonhuman primates using a new method. The method quantifies whole-body and organ-specific AAV capsids from 1 to 72 hours after administration. Study design and results are presented in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website through February 15, 2021.
AAV capsids were labeled with I-124 and delivered using two routes of administration: intravenous and directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Biodistribution was measured by quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) at 1, 24, 48, and 72 hours after AAV administration. Two AAV vectors - AAVrsh.10 and AAV9 - were compared.
"Following ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] US fishing and seafood industries saw broad declines last summer due to COVID-19
New analysis by NOAA Fisheries provides insights into the pandemic's early economic impact