(Press-News.org) Range anxiety, the fear of running out of power before being able to recharge an electric vehicle, may be a thing of the past, according to a team of Penn State engineers who are looking at lithium iron phosphate batteries that have a range of 250 miles with the ability to charge in 10 minutes.
"We developed a pretty clever battery for mass-market electric vehicles with cost parity with combustion engine vehicles," said Chao-Yang Wang, William E. Diefenderfer Chair of mechanical engineering, professor of chemical engineering and professor of materials science and engineering, and director of the Electrochemical Engine Center at Penn State. "There is no more range anxiety and this battery is affordable."
The researchers also say that the battery should be good for 2 million miles in its lifetime.
They report today (Jan. 18) in Nature Energy that the key to long-life and rapid recharging is the battery's ability to quickly heat up to 140 degrees Fahrenheit, for charge and discharge, and then cool down when the battery is not working.
"The very fast charge allows us to downsize the battery without incurring range anxiety," said Wang.
The battery uses a self-heating approach previously developed in Wang's center. The self-heating battery uses a thin nickel foil with one end attached to the negative terminal and the other extending outside the cell to create a third terminal. Once electrons flow it rapidly heats up the nickel foil through resistance heating and warm the inside of the battery. Once the battery's internal temperature is 140 degrees F, the switch opens and the battery is ready for rapid charge or discharge.
Wang's team modeled this battery using existing technologies and innovative approaches. They suggest that using this self-heating method, they can use low-cost materials for the battery's cathode and anode and a safe, low-voltage electrolyte. The cathode is thermally stable, lithium iron phosphate, which does not contain any of the expensive and critical materials like cobalt. The anode is made of very large particle graphite, a safe, light and inexpensive material.
Because of the self-heating, the researchers said they do not have to worry about uneven deposition of lithium on the anode, which can cause lithium spikes that are dangerous.
"This battery has reduced weight, volume and cost," said Wang. "I am very happy that we finally found a battery that will benefit the mainstream consumer mass market."
According to Wang, these smaller batteries can produce a large amount of power upon heating -- 40 kilowatt hours and 300 kilowatts of power. An electric vehicle with this battery could go from zero to 60 miles per hour in 3 seconds and would drive like a Porsche, he said.
"This is how we are going to change the environment and not contribute to just the luxury cars," said Wang. "Let everyone afford electric vehicles."
INFORMATION:
Other Penn State researchers working on this project were Xiao-Guang Yang, assistant research professor of mechanical engineering, and Teng Liu, doctoral student in mechanical engineering.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy and the William E Diefenderfer Endowment supported this research.
Targeted neuromodulation tailored to individual patients' distinctive symptoms is an increasingly common way of correcting misfiring brain circuits in people with epilepsy or Parkinson's disease. Now, scientists at UC San Francisco's Dolby Family Center for Mood Disorders have demonstrated a novel personalized neuromodulation approach that -- at least in one patient -- was able to provide relief from symptoms of severe treatment-resistant depression within minutes.
The approach is being developed specifically as a potential treatment for the significant fraction of people with debilitating depression ...
More than 3,000 animal species in the world today are considered endangered, with hundreds more categorized as vulnerable. Currently, ecologists don't have reliable tools to predict when a species may become at risk.
A new paper published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, "Management implications of long transients in ecological systems," focuses on the transient nature of species' and ecosystem stability and illustrates how management practices can be adjusted to better prepare for possible system flips. Some helpful modeling approaches are also offered, including one tool that may help identify potentially ...
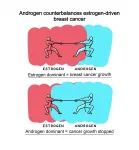
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have found new evidence about the positive role of androgens in breast cancer treatment with immediate implications for women with estrogen receptor-driven metastatic disease.
Published today in Nature Medicine, the international study conducted in collaboration with the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, looked at the role of androgens - commonly thought of as male sex hormones but also found at lower levels in women - as a potential treatment for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Watch a video explainer about the new ...
Some of the low-carbon policy options currently used by governments may be detrimental to the households and small businesses less able to manage added short-term costs from energy price hikes, according to a new study.
However, it also suggests that this menu of decarbonising policies, from quotas to feed-in tariffs, can be designed and balanced to benefit local firms and lower-income families - vital for achieving 'Net Zero' carbon and a green recovery.
University of Cambridge researchers combed through thousands of studies to create the most comprehensive analysis to date of widely used types of low-carbon policy, and compared how they perform in areas such as cost and competitiveness. ...
Some of the low-carbon policy options currently used by governments may be detrimental to the households and small businesses less able to manage added short-term costs from energy price hikes, according to a new study.
However, it also suggests that this menu of decarbonising policies, from quotas to feed-in tariffs, can be designed and balanced to benefit local firms and lower-income families - vital for achieving 'Net Zero' carbon and a green recovery.
University of Cambridge researchers combed through thousands of studies to create the most comprehensive analysis to date of widely used types of low-carbon policy, and compared how they perform in areas such ...
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health have discovered Jekyll and Hyde immune cells in the brain that ultimately help with brain repair but early after injury can lead to fatal swelling, suggesting that timing may be critical when administering treatment. These dual-purpose cells, which are called myelomonocytic cells and which are carried to the brain by the blood, are just one type of brain immune cell that NIH researchers tracked, watching in real-time as the brain repaired itself after injury. The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, ...
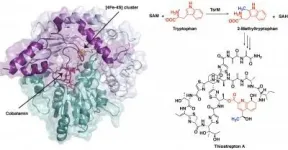
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Images of a protein involved in creating a potent antibiotic reveal the unusual first steps of the antibiotic's synthesis. The improved understanding of the chemistry behind this process, detailed in a new study led by Penn State chemists, could allow researchers to adapt this and similar compounds for use in human medicine.
"The antibiotic thiostrepton is very potent against Gram-positive pathogens and can even target certain breast cancer cells in culture," said Squire Booker, a biochemist at Penn State and investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. "While it has been used ...
HOUSTON — In an effort to address a major challenge when analyzing large single-cell RNA-sequencing datasets, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new computational technique to accurately differentiate between data from cancer cells and the variety of normal cells found within tumor samples. The work was published today in Nature Biotechnology.
The new tool, dubbed CopyKAT (copy number karyotyping of aneuploid tumors), allows researchers to more easily examine the complex data obtained from large single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments, which deliver gene expression data from ...
Mount Sinai researchers have published one of the first studies using a machine learning technique called "federated learning" to examine electronic health records to better predict how COVID-19 patients will progress. The study was published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - Medical Informatics on January 18.
The researchers said the emerging technique holds promise to create more robust machine learning models that extend beyond a single health system without compromising patient privacy. These models, in turn, can help triage patients and improve the quality of their care.
Federated ...
A research team from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) has developed a process for the electrolytic treatment of wastewater that degrades microplastics at the source. The results of this research have been published in the Environmental Pollution journal.
Wastewater can carry high concentrations of microplastics into the environment. These small particles of less than 5 mm can come from our clothes, usually as microfibers. Professor Patrick Drogui, who led the study, points out there are currently no established degradation methods to handle this contaminant during wastewater ...