Modulating helical nanostructures in liquid crystal phase by molecular design
The ester bond direction in liquid crystal dimers impacts the helical pitch in the twist-bend nematic phase
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Overview:
A team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Yuki Arakawa (Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan) has successfully developed sulfur-containing liquid crystal (LC) dimer molecules1) with oppositely directed ester bonds, which exhibit a helical liquid crystal phase, viz. twist-bend nematic (NTB) phase, 2) over a wide temperature range, including room temperature. Collaboration with a team at the Advanced Light Source research facility (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, USA) revealed that the ester bond direction in the molecular structures largely impacts the pitch lengths of helical nanostructures in the NTB phase. It is expected that this molecular design can be used to tune the resultant physical properties of LC materials that would contribute to new LC technologies, such as LC laser, photo-alignment, and display technologies.
Details:
The NTB is a newly identified fluidic LC phase, which possesses a helical nanostructure with a pitch ranging from several to tens of nanometers, becoming a hot topic in the LC science community. Recently, various approaches were explored to apply the NTB materials to wavelength-tunable LC laser and photo-alignment technologies. In terms of practicality, LC materials must be devised by forming LC phases over a broad temperature range and at room temperature. However, molecules that exhibit the NTB phase over a wide temperature range, including room temperature, remain exceptionally rare. This has impeded deep evaluations of various properties and the development of new applications.
Assistant Professor Yuki Arakawa and his team in the Toyohashi University of Technology have been taking interest in developing novel sulfur-containing LC materials, especially for high-birefringence materials and twist-bend nematic LCs, based on thioether (R-S-R) linkages that contain sulfur, which is a component of hot springs and one of the few surplus resources in Japan. Sulfur or thioether bonds have high polarizability and are expected to be useful functional moieties for improving physical properties, such as refractive index and birefringence, compared with other bonds based on conventional atoms, such as methylene (carbon) and ether (oxygen).
Previously, Assistant Professor Yuki Arakawa and his team had successfully developed thioether-based bent molecules that exhibit the NTB phase. In this study, we attempted to devise new LC dimers by introducing oppositely directed ester bonds (i.e., -C=OO- and -O=CO-) to the thioether-based bent dimeric molecules and elucidate the influence of the ester bond direction on the NTB phase behaviors. The team succeeded in developing new molecules that exhibit NTB phases over a wide temperature range, including room temperature.
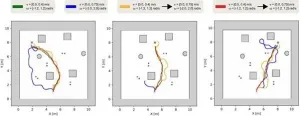
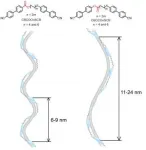
Furthermore, the team observed a phenomenon, in which the helical pitches (6-9 nm) of the molecules with O=CO ester were approximately double (11-24 nm) of those with C=OO ester (Figure 1). This is because the C=OO-ester dimers have more bent molecular geometries than the O=CO-ester dimers, resulting in enhanced molecular precession in the helical structure for the former than for the latter. Finely tuning the molecular design (i.e., the ester bond direction) enables the manipulation of helical nanostructures, which is particularly important for optical applications.
According to Assistant Professor Arakawa, "LC molecules that exhibit the helical NTB phase over a broad temperature range, including room temperature, remain rare. No studies have clearly revealed the structure-property relationship between molecular design and the resultant helical structure, i.e. how the helical nano-structures can be controlled by molecular design. We believe that our studies provide insight into it."
INFORMATION:
This paper was selected in Materials Advances HOT Article Collection, 2020.
Funding Agency:
This work was partly supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI grant numbers 17K14493 and 20K15351, the Naito Research Grant, and research grants from the Toukai Foundation for Technology and Toyohashi University of Technology.
Reference:
Yuki Arakawa, Kenta Komatsu, Jun Feng, Chenhui Zhu, Hideto Tsuji. "Distinct twist-bend nematic phase behaviors associated with the ester-linkage direction of thioether-linked liquid crystal dimers." Materials Advances, 2020.
DOI: 10.1039/D0MA00746C
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00746C
Technical terms:
1) A structure type of LC molecules in which two rigid structures are connected with a flexible alkyl chain spacer.
2) A helical liquid crystal phase in which bent molecules heliconically assemble to make a helical nano-structure.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
Overview:
A research group from the Active Intelligent System Laboratory (AISL) at Toyohashi University of Technology (TUT) has proposed a new framework for training mobile robots to quickly navigate while maintaining low collision rates. The framework combines deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and curriculum learning in the training process for robots to learn a fast but safe navigation policy.
Details:
One of the basic requirements of autonomous mobile robots is their navigation capability. The robot must be able to navigate from its current position to the specified target position ...
2021-01-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- The fossilized insect is tiny and its genital capsule, called a pygophore, is roughly the length of a grain of rice. It is remarkable, scientists say, because the bug's physical characteristics - from the bold banding pattern on its legs to the internal features of its genitalia - are clearly visible and well-preserved. Recovered from the Green River Formation in present-day Colorado, the fossil represents a new genus and species of predatory insects known as assassin bugs.
The find is reported in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Discovered in 2006 by breaking open ...
2021-01-19
Simple vision tests can predict which people with Parkinson's disease will develop cognitive impairment and possible dementia 18 months later, according to a new study by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Movement Disorders, adds to evidence that vision changes precede the cognitive decline that occurs in many, but not all, people with Parkinson's.
In another new study published today in Communications Biology, the same research team found that structural and functional connections of brain regions become decoupled throughout the entire brain in people with Parkinson's disease, particularly among people with vision problems.
The ...
2021-01-19
There are high hopes for the next generation of high energy-density lithium metal batteries, but before they can be used in our vehicles, there are crucial problems to solve. An international research team led by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has now developed concrete guidelines for how the batteries should be charged and operated, maximising efficiency while minimising the risk of short circuits.
Lithium metal batteries are one of several promising concepts that could eventually replace the lithium-ion batteries which are currently widely used - particularly in various types of electric vehicles.
The big advantage of this new battery type is that the energy density can be significantly ...
2021-01-19
New research suggests a unique program called Moms2B at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center shows a reduction in adverse pregnancy outcomes in communities disproportionately affected by these public health issues.
The study, led by researchers Courtney Lynch and Erinn Hade and published in the Journal of Maternal and Child Health, indicates that women who attended at least two Moms2B sessions may have lower rates of preterm birth, low birth weight and infant mortality compared to women who only received individual care.
"When we started the program 10 years ago, ...
2021-01-19
New study identifies a bizarre new species suggesting that giant marine lizards thrived before the asteroid wiped them out 66 million years ago.
A new species of mosasaur - an ancient sea-going lizard from the age of dinosaurs - has been found with shark-like teeth that gave it a deadly slicing bite.
Xenodens calminechari, from the Cretaceous of Morocco, had knifelike teeth that were packed edge to edge to make a serrated blade and resemble those of certain sharks. The cutting teeth let the small, agile mosasaur, about the size of a small porpoise, punch above its weight, cutting fish in half and taking large bites from bigger animals.
Dr Nick Longrich, Senior Lecturer at the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University of Bath and lead author on ...
2021-01-19
Clumsy kids can be as aerobically fit as their peers with better motor skills, a new Finnish study shows. The results are based on research conducted at the Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences of the University of Jyväskylä and the Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Eastern Finland, and they were published in Translational Sports Medicine.
Aerobic fitness doesn't go hand in hand with motor skills
According to the general perception, fit kids also have good motor skills, while low aerobic fitness has been thought to be a link ...
2021-01-19
A group of international scientists, including an Australian astrophysicist, has used knowhow from gravitational wave astronomy (used to find black holes in space) to study ancient marine fossils as a predictor of climate change.
The research, published in the journal Climate of the Past, is a unique collaboration between palaeontologists, astrophysicists and mathematicians - to improve the accuracy of a palaeo-thermometer, which can use fossil evidence of climate change to predict what is likely to happen to the Earth in coming decades.
Professor Ilya Mandel, from the ARC Centre of Excellence in Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav), and colleagues, studied biomarkers left behind by tiny single-cell organisms called archaea in the distant past, including the Cretaceous period ...
2021-01-19
In the strawberry nursery industry, a nursery's reputation relies on their ability to produce disease- and insect-free plants. The best way to produce clean plants is to start with clean planting stock. Many nurseries struggle with angular leaf spot of strawberry, a serious disease that can result in severe losses either by directly damaging the plant or indirectly through a violation of quarantine standards within the industry.
Angular leaf spot is caused by the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas fragariae. Current management strategies rely primarily ...
2021-01-19
Chemotherapy and radiation treatments are known to cause harsh side effects that patients can see or feel throughout their bodies. Yet there are additional, unseen and often undiscussed consequences of these important therapies: the impacts on their future pregnancies and hopes for healthy children.
Extensive evidence shows that chemotherapy and radiation treatments are genotoxic, meaning they can mutate the DNA and damage chromosomes in patients' cancerous and noncancerous cells alike. When this occurs in a germline cell - which are egg cells in women and sperm in men - it can lead to serious fetal and birth ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Modulating helical nanostructures in liquid crystal phase by molecular design
The ester bond direction in liquid crystal dimers impacts the helical pitch in the twist-bend nematic phase