(Press-News.org) University of South Australia scientists have developed the world's first test to accurately predict mood disorders in people, based on the levels of a specific protein found in the brain.
Links between low levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (mBDNF) and depression are well known but, until now, it hasn't been possible to distinguish between the three forms of the BDNF protein in blood samples.
The mature form promotes the growth of neurons and protects the brain, but the other two BDNF forms - its precursor and the prodomain of BDNF - bind to different receptors, causing nerve degeneration and inflammation.
An assay kit developed by researchers from UniSA can now precisely distinguish between these proteins, unlike other commercial kits in the market.
The finding, in collaboration with the University of Adelaide and Kunming Medical University in China, has been published in a new paper in the Journal of Psychiatric Research led by UniSA PhD student Liying Lin.
UniSA Professor Xin-Fu Zhou, one of the researchers, says there is strong evidence to suggest that psychological stress decreases mBDNF and a lack of mBDNF causes depression.
In a study of 215 people in China, including 90 patients with clinical depression and 15 with bipolar disorder, researchers found clear links with low levels of mBDNF in their blood. The more severe the depression, the lower the mBDNF level.
Mature BDNF levels in patients not on antidepressants was also lower than patients treated with antidepressants.
Surprisingly, there was no difference in mBDNF levels between 14 people with a history of suicide attempts and the control group of 96 people.
No significant gender differences were found.
"As mature BDNF and proBDNF have different biological activities, working in opposition to each other, it is essential that we can distinguish between these two proteins and detect changes in their levels," Prof Zhou says.
"The existing commercial BDNF ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) kits are not specific and can cross react with each other. The kit we have developed has an accuracy rate of 80-83 per cent."
The researchers say serum mBDNF levels less than 12.4 ng/ml could be used as a cut off point to diagnose depression and bipolar disorder.
"This could be an objective biomarker in addition to a clinical assessment by a doctor," Prof Zhou says.
"Growing evidence indicates that inflammation in brain cells is linked with depressive behaviours and proBDNF seems to activate the immune system. Therefore, we must separate it from mature BDNF to get an accurate reading.
"Interestingly, our recent studies in animals showed that proBDNF injected in both the brain and muscle can directly trigger depressive behaviours," Prof Zhou says.
The next step is to examine whether imbalances between proBDNF and mature BDNF can be restored in electric convulsion therapy. This project will be led by UniSA Associate Professor Larisa Bobrovskaya in collaboration with University of Adelaide psychiatrists Associate Professor Dennis Liu and Dr Oliver Schubert.
"Mood disorders affect millions of people worldwide. However, about one third of people with depression and bipolar disorder are resistant to antidepressants or alternative therapies. The reasons are not understood but it could have something to do with the imbalances between the different forms of BDNF, which we hope to investigate next," Prof Zhou says.
INFORMATION:
SINGAPORE, 19 January 2021 - Duke-NUS Medical School researchers, together with collaborators in Singapore, have designed armoured immune cells that can attack recurring cancer in liver transplant patients, while temporarily evading immunosuppressant drugs patients take to avoid organ rejection. The findings were published in the journal Hepatology.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer and the sixth most common cancer worldwide. It often develops in people with chronic liver disease following hepatitis B infection.
A common treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma is to completely ...
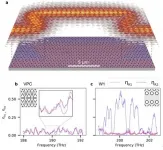
Topologically tailored photonic crystals (PhC) have opened up the possibility for attaining robust unidirectional transport of classical and quantum systems. The demand for unprecedented guiding capabilities that support unhindered transport around imperfections and sharp corners at telecom wavelengths, without the need for any optimization, is fundamental for efficient distribution of information through dense on-chip photonic networks. However, transport properties of experimental realizations of such topologically non-trivial states have been inferred by transmission measurements and even though robustness ...
Overview:
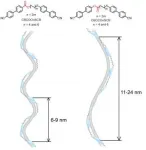
A team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Yuki Arakawa (Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan) has successfully developed sulfur-containing liquid crystal (LC) dimer molecules1) with oppositely directed ester bonds, which exhibit a helical liquid crystal phase, viz. twist-bend nematic (NTB) phase, 2) over a wide temperature range, including room temperature. Collaboration with a team at the Advanced Light Source research facility (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, USA) revealed that the ester bond direction in the molecular structures largely impacts the pitch lengths of helical nanostructures in the NTB phase. It is expected that this molecular design ...
Overview:
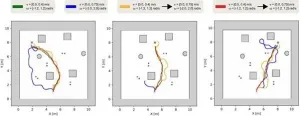
A research group from the Active Intelligent System Laboratory (AISL) at Toyohashi University of Technology (TUT) has proposed a new framework for training mobile robots to quickly navigate while maintaining low collision rates. The framework combines deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and curriculum learning in the training process for robots to learn a fast but safe navigation policy.
Details:
One of the basic requirements of autonomous mobile robots is their navigation capability. The robot must be able to navigate from its current position to the specified target position ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- The fossilized insect is tiny and its genital capsule, called a pygophore, is roughly the length of a grain of rice. It is remarkable, scientists say, because the bug's physical characteristics - from the bold banding pattern on its legs to the internal features of its genitalia - are clearly visible and well-preserved. Recovered from the Green River Formation in present-day Colorado, the fossil represents a new genus and species of predatory insects known as assassin bugs.
The find is reported in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Discovered in 2006 by breaking open ...
Simple vision tests can predict which people with Parkinson's disease will develop cognitive impairment and possible dementia 18 months later, according to a new study by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Movement Disorders, adds to evidence that vision changes precede the cognitive decline that occurs in many, but not all, people with Parkinson's.
In another new study published today in Communications Biology, the same research team found that structural and functional connections of brain regions become decoupled throughout the entire brain in people with Parkinson's disease, particularly among people with vision problems.
The ...
There are high hopes for the next generation of high energy-density lithium metal batteries, but before they can be used in our vehicles, there are crucial problems to solve. An international research team led by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has now developed concrete guidelines for how the batteries should be charged and operated, maximising efficiency while minimising the risk of short circuits.
Lithium metal batteries are one of several promising concepts that could eventually replace the lithium-ion batteries which are currently widely used - particularly in various types of electric vehicles.
The big advantage of this new battery type is that the energy density can be significantly ...
New research suggests a unique program called Moms2B at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center shows a reduction in adverse pregnancy outcomes in communities disproportionately affected by these public health issues.
The study, led by researchers Courtney Lynch and Erinn Hade and published in the Journal of Maternal and Child Health, indicates that women who attended at least two Moms2B sessions may have lower rates of preterm birth, low birth weight and infant mortality compared to women who only received individual care.
"When we started the program 10 years ago, ...
New study identifies a bizarre new species suggesting that giant marine lizards thrived before the asteroid wiped them out 66 million years ago.
A new species of mosasaur - an ancient sea-going lizard from the age of dinosaurs - has been found with shark-like teeth that gave it a deadly slicing bite.
Xenodens calminechari, from the Cretaceous of Morocco, had knifelike teeth that were packed edge to edge to make a serrated blade and resemble those of certain sharks. The cutting teeth let the small, agile mosasaur, about the size of a small porpoise, punch above its weight, cutting fish in half and taking large bites from bigger animals.
Dr Nick Longrich, Senior Lecturer at the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University of Bath and lead author on ...
Clumsy kids can be as aerobically fit as their peers with better motor skills, a new Finnish study shows. The results are based on research conducted at the Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences of the University of Jyväskylä and the Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Eastern Finland, and they were published in Translational Sports Medicine.
Aerobic fitness doesn't go hand in hand with motor skills
According to the general perception, fit kids also have good motor skills, while low aerobic fitness has been thought to be a link ...