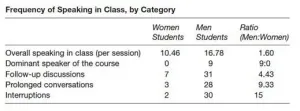
Rethinking spin chemistry from a quantum perspective
Osaka City University breaks from convention with a true quantum algorithm that can calculate energy differences between the electronic ground and excited spin states of molecular systems
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Understanding how the natural world works enables us to mimic it for the benefit of humankind. Think of how much we rely on batteries. At the core is understanding molecular structures and the behavior of electrons within them. Calculating the energy differences between a molecule's electronic ground and excited spin states helps us understand how to better use that molecule in a variety of chemical, biomedical and industrial applications. We have made much progress in molecules with closed-shell systems, in which electrons are paired up and stable. Open-shell systems, on the other hand, are less stable and their underlying electronic behavior is complex, and thus more difficult to understand. They have unpaired electrons in their ground state, which cause their energy to vary due to the intrinsic nature of electron spins, and makes measurements difficult, especially as the molecules increase in size and complexity. Although such molecules are abundant in nature, there is a lack of algorithms that can handle this complexity. One hurdle has been dealing with what is called the exponential explosion of computational time. Using a conventional computer to calculate how the unpaired spins influence the energy of an open-shell molecule would take hundreds of millions of years, time humans do not have.
Quantum computers are in development to help reduce this to what is called "polynomial time". However, the process scientists have been using to calculate the energy differences of open-shell molecules has essentially been the same for both conventional and quantum computers. This hampers the practical use of quantum computing in chemical and industrial applications.
"Approaches that invoke true quantum algorithms help us treat open-shell systems much more efficiently than by utilizing classical computers", state Kenji Sugisaki and Takeji Takui from Osaka City University. With their colleagues, they developed a quantum algorithm executable on quantum computers, which can, for the first time, accurately calculate energy differences between the electronic ground and excited spin states of open-shell molecular systems. Their findings were published in the journal Chemical Science on 24 Dec 2020.
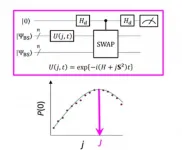
The energy difference between molecular spin states is characterized by the value of the exchange interaction parameter J. Conventional quantum algorithms have been able to accurately calculate energies for closed-shell molecules "but they have not been able to handle systems with a strong multi-configurational character", states the group. Until now, scientists have assumed that to obtain the parameter J one must first calculate the total energy of each spin state. In open-shell molecules this is difficult because the total energy of each spin state varies greatly as the molecule changes in activity and size. However, "the energy difference itself is not greatly dependent on the system size", notes the research team. This led them to create an algorithm with calculations that focused on the spin difference, not the individual spin states. Creating such an algorithm required that they let go of assumptions developed from years of using conventional computers and focus on the unique characteristics of quantum computing - namely "quantum superposition states".
"Superposition" lets algorithms represent two variables at once, which then allows scientists to focus on the relationship between these variables without any need to determine their individual states first. The research team used something called a broken-symmetry wave function as a superposition of wave functions with different spin states and rewrote it into the Hamiltonian equation for the parameter J. By running this new quantum circuit, the team was able to focus on deviations from their target and by applying Bayesian inference, a machine learning technique, they brought these deviations in to determine the exchange interaction parameter J. "Numerical simulations based on this method were performed for the covalent dissociation of molecular hydrogen (H2), the triple bond dissociation of molecular nitrogen (N2), and the ground states of C, O, Si atoms and NH, OH+, CH2, NF and O2 molecules with an error of less than 1 kcal/mol", adds the research team.
"We plan on installing our Bayesian eXchange coupling parameter calculator with Broken-symmetry wave functions (BxB) software on near-term quantum computers equipped with noisy (no quantum error correction) intermediate-scale (several hundreds of qubits) quantum devices (NISQ devices), testing the usefulness for quantum chemical calculations of actual sizable molecular systems."
INFORMATION:
We are Osaka City University - the oldest research university in Osaka. With 9 undergraduate faculties and 11 graduate schools all dedicated to making urban life better, energy cleaner, and people healthier and happier, we have won numerous awards and have produced 2 Nobel laureates. For more information, please visit our website at https://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
Men speak 1.6 times more often than women in college classrooms, revealing how gender inequities regarding classroom participation still exist, according to a Dartmouth study. By comparison, women are more hesitant to speak and are more apt to use apologetic language. The findings are published in Gender & Society.
When students didn't have to raise their hands to participate in class, men spoke three times more often than women. "You would think that it would be more equitable for students to not have to raise their hands to speak in class because then anyone could talk ...
2021-01-19
RICHLAND, Wash.--E-cigarettes stress and inflame the lungs of rats, compromising important regulatory proteins through exposure, according to research recently published in the journal Redox Biology. The findings, made possible by a biomolecular technique developed by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, reveal that vaping induces subtle structural changes in proteins, marking the first time researchers have measured such damage. The results suggest that common compounds in the electronic alternative to conventional cigarettes are not without their own harms.
After exposing rats to e-cigarette vapor for three one-hour sessions ...
2021-01-19
Some say future wars will be fought over water, and a billion people around the world are already struggling to find enough water to live.
Now, researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) are coming to the rescue. They have created a substance that extracts water from air without any external power source.
In the earth's atmosphere, there is water that can fill almost half a trillion Olympic swimming pools. But it has long been overlooked as a source for potable water.
To extract water from this under utilised source, a team led by Professor Ho Ghim Wei from the NUS Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering created a type of aerogel, a solid material that weighs almost nothing. Under the microscope, it looks like a sponge, but it ...
2021-01-19
University of South Australia scientists have developed the world's first test to accurately predict mood disorders in people, based on the levels of a specific protein found in the brain.
Links between low levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (mBDNF) and depression are well known but, until now, it hasn't been possible to distinguish between the three forms of the BDNF protein in blood samples.
The mature form promotes the growth of neurons and protects the brain, but the other two BDNF forms - its precursor and the prodomain of BDNF - bind to different receptors, causing nerve degeneration ...
2021-01-19
SINGAPORE, 19 January 2021 - Duke-NUS Medical School researchers, together with collaborators in Singapore, have designed armoured immune cells that can attack recurring cancer in liver transplant patients, while temporarily evading immunosuppressant drugs patients take to avoid organ rejection. The findings were published in the journal Hepatology.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer and the sixth most common cancer worldwide. It often develops in people with chronic liver disease following hepatitis B infection.
A common treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma is to completely ...
2021-01-19
Topologically tailored photonic crystals (PhC) have opened up the possibility for attaining robust unidirectional transport of classical and quantum systems. The demand for unprecedented guiding capabilities that support unhindered transport around imperfections and sharp corners at telecom wavelengths, without the need for any optimization, is fundamental for efficient distribution of information through dense on-chip photonic networks. However, transport properties of experimental realizations of such topologically non-trivial states have been inferred by transmission measurements and even though robustness ...
2021-01-19
Overview:
A team of researchers led by Assistant Professor Yuki Arakawa (Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan) has successfully developed sulfur-containing liquid crystal (LC) dimer molecules1) with oppositely directed ester bonds, which exhibit a helical liquid crystal phase, viz. twist-bend nematic (NTB) phase, 2) over a wide temperature range, including room temperature. Collaboration with a team at the Advanced Light Source research facility (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, USA) revealed that the ester bond direction in the molecular structures largely impacts the pitch lengths of helical nanostructures in the NTB phase. It is expected that this molecular design ...
2021-01-19
Overview:
A research group from the Active Intelligent System Laboratory (AISL) at Toyohashi University of Technology (TUT) has proposed a new framework for training mobile robots to quickly navigate while maintaining low collision rates. The framework combines deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and curriculum learning in the training process for robots to learn a fast but safe navigation policy.
Details:
One of the basic requirements of autonomous mobile robots is their navigation capability. The robot must be able to navigate from its current position to the specified target position ...
2021-01-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- The fossilized insect is tiny and its genital capsule, called a pygophore, is roughly the length of a grain of rice. It is remarkable, scientists say, because the bug's physical characteristics - from the bold banding pattern on its legs to the internal features of its genitalia - are clearly visible and well-preserved. Recovered from the Green River Formation in present-day Colorado, the fossil represents a new genus and species of predatory insects known as assassin bugs.
The find is reported in the journal Papers in Palaeontology.
Discovered in 2006 by breaking open ...
2021-01-19
Simple vision tests can predict which people with Parkinson's disease will develop cognitive impairment and possible dementia 18 months later, according to a new study by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Movement Disorders, adds to evidence that vision changes precede the cognitive decline that occurs in many, but not all, people with Parkinson's.
In another new study published today in Communications Biology, the same research team found that structural and functional connections of brain regions become decoupled throughout the entire brain in people with Parkinson's disease, particularly among people with vision problems.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Rethinking spin chemistry from a quantum perspective
Osaka City University breaks from convention with a true quantum algorithm that can calculate energy differences between the electronic ground and excited spin states of molecular systems