Scientists to global policymakers: Treat fish as food to help solve world hunger
Sustainable seafood central to strengthening food security if viewed as more than just a natural resource
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Scientists are urging global policymakers and funders to think of fish as a solution to food insecurity and malnutrition, and not just as a natural resource that provides income and livelihoods, in a newly-published paper in the peer-reviewed journal Ambio. Titled "Recognize fish as food in policy discourse and development funding," the paper argues for viewing fish from a food systems perspective to broaden the conversation on food and nutrition security and equity, especially as global food systems will face increasing threats from climate change.
The "Fish as Food" paper, authored by scientists and policy experts from Michigan State University, Duke University, Harvard University, World Bank and Environmental Defense Fund, among others, notes the global development community is not on track to meet goals for alleviating malnutrition. According to the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization, the number of malnourished people in the world will increase from 678 million in 2018 to 841 million in 2030 if current trends continue -- an estimate not accounting for effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Fish provide 17% of the animal protein consumed globally and are rich in micronutrients, essential fatty acids and protein essential for cognitive development and maternal and childhood health, especially for communities in developing countries where fish may be the only source of key nutrients. Yet fish is largely missing from key global food policy discussions and decision-making.
"Fish has always been food. But in this paper, we lay out an agenda for enhancing the role of fish in addressing hunger and malnutrition," says Abigail Bennett, assistant professor in the Center for Systems Integration and Sustainability in the Department of Fisheries and Wildlife at Michigan State University. "We are urging the international development community not only to see fish as food but to recognize fish as a nutrient-rich food that can make a difference for the well-being of the world's poor and vulnerable. What kinds of new knowledge, policies and interventions will be required to support that role for fish?" she adds.
The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2, Zero Hunger, does not mention fisheries or aquaculture by name, nor does it offer specific guidance on fish production systems. Fish also appear underrepresented in international development funding priorities, such as by the World Bank, the paper finds.
"Fish -- and aquatic foods in general -- are largely ignored in the food policy dialogue," says Kristin Kleisner, lead senior scientist for Environmental Defense Fund Oceans program and a co-author of the paper. "This is a huge oversight, as fish offer a critical source of nutrition unparalleled by any other type of food, and it is often the only source of key nutrients for vulnerable populations around the world.
"By refocusing on nutrition, in addition to the many other benefits fisheries provide, we're amplifying a call to action for governments, international development organizations and society more broadly to invest in the sustainability of capture fisheries and aquaculture," adds Kleisner.
"Fisheries will be ever more important as the world faces mounting challenges to feed itself," says Kelly Brownell, director of the World Food Policy Center at Duke University.
Global policymakers and funders framing fish as food, the authors state, can encourage innovative policies and actions to support the role of fish in global food and nutrition security.
The paper identifies four pillars of suggested action to begin framing fish as food, not just a natural resource. These pillars are:
1. Improve metrics. There is currently a paucity of metrics to assess and communicate the contributions of fish to food and nutrition security. Governments and researchers can collaborate to develop better tools to raise the profile of fish in broader food and nutrition security policies and investment priorities.
2. Promote nutrition-sensitive fish food systems. Current management regimes emphasize the "maximum sustainable yield" for a given fishery. Managing for "optimal nutritional yield" would focus on not just rebuilding and conserving fish populations -- an important goal in and of itself -- but also on sustainably managing nutrient-rich fisheries.
3. Govern distribution. Availability, access and stability are key features of food and nutrition security. Even though fish is one of the most traded food commodities in the world, there is limited information about its distribution and links to nutrition security. There is also a need to promote equitable distribution of capital and property rights to access fisheries, particularly that recognize the importance of small-scale fisheries and roles women play in fishing and aquaculture sectors.
4. Situate fish in a food systems framework. Policymakers need the tools to conceptualize fishing and aquaculture as components of the food systems framework. A "fish as food" framing requires a better understanding of the connections among fish production and distribution, terrestrial agriculture and planetary health.
Sustainable fisheries and aquaculture are key to feeding the world and alleviating malnutrition and already provide valuable nutrition and livelihood contributions. Including a nutrition lens when illustrating the multiple benefits of sustainable fisheries production can help to elevate the importance and impact of fish as a key component of the global food system and to ensure that we do not fall behind in global food security targets.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
HOUSTON - (Jan. 19, 2021) - Microscopic bubbles can tell stories about Earth's biggest volcanic eruptions and geoscientists from Rice University and the University of Texas at Austin have discovered some of those stories are written in nanoparticles.
In an open-access study published online in Nature Communications, Rice's Sahand Hajimirza and Helge Gonnermann and UT Austin's James Gardner answered a longstanding question about explosive volcanic eruptions like the ones at Mount St. Helens in 1980, the Philippines' Mount Pinatubo in 1991 or Chile's Mount Chaitén in 2008.
Geoscientists have long sought to use tiny bubbles in erupted lava and ash to reconstruct some of the conditions, ...
2021-01-19
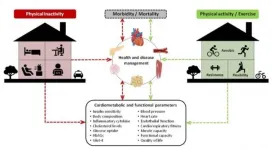
Social distancing and working from home help prevent transmission of the novel coronavirus but can be conducive to unhealthy behavior such as bingeing on fast food or spending more time in a chair or on a couch staring at a screen, and generally moving about less during the day. Scientists believe the reduction in physical activity experienced during the first few months of the pandemic could lead to an annual increase of more than 11.1 million in new cases of type 2 diabetes and result in more than 1.7 million deaths.
The estimates are presented by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP), Brazil, in a review article published in Frontiers in Endocrinology. The authors stress that there is an "urgent need" to recommend physical activity during ...
2021-01-19
Just how close are the world's countries to achieving the Paris Agreement target of keeping climate change limited to a 1.5°C increase above pre-industrial levels?
It's a tricky question with a complex answer. One approach is to use the remaining carbon budget to gauge how many more tonnes of carbon dioxide we can still emit and have a chance of staying under the target laid out by the 2015 international accord. However, estimates of the remaining carbon budget have varied considerably in previous studies because of inconsistent approaches and assumptions used by researchers.
Nature Communications Earth and Environment just published a paper by a group of researchers led by Damon Matthews, professor in the Department of Geography, Planning and Environment. In it, ...
2021-01-19
TAMPA, Fla. - Cells need energy to survive and thrive. Generally, if oxygen is available, cells will oxidize glucose to carbon dioxide, which is very efficient, much like burning gasoline in your car. However, even in the presence of adequate oxygen, many malignant cells choose instead to ferment glucose to lactic acid, which is a much less efficient process. This metabolic adaptation is referred to as the Warburg Effect, as it was first described by Otto Warburg almost a century ago. Ever since, the conditions that would evolutionarily select for cells to exhibit a Warburg Effect have been in debate, as it is much less efficient and produces toxic waste ...
2021-01-19
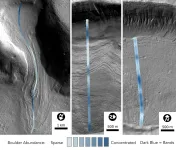
In a new paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academies of ScienceS (PNAS), planetary geologist Joe Levy, assistant professor of geology at Colgate University, reveals a groundbreaking new analysis of the mysterious glaciers of Mars.
On Earth, glaciers covered wide swaths of the planet during the last Ice Age, which reached its peak about 20,000 years ago, before receding to the poles and leaving behind the rocks they pushed behind. On Mars, however, the glaciers never left, remaining frozen on the Red Planet's cold surface for more than 300 million years, covered in debris. "All the rocks and sand carried on that ice have remained ...
2021-01-19
ATLANTA--Early in the U.S. COVID-19 pandemic, unemployment claims were largely driven by state shutdown orders and the nature of a state's economy and not by the virus, according a new article by Georgia State University economists.
David Sjoquist and Laura Wheeler found no evidence the Payroll Protection Program (PPP) affected the number of initial claims during the first six weeks of the pandemic.
Their research explores state differences in the magnitude of weekly unemployment insurance claims for the weeks ending March 14 through April 25 by focusing on three factors: the impact of COVID-19, the effects of state economic structures and state orders closing non-essential ...
2021-01-19
The offspring of older animals often have a lower chance of survival because the parents are unable to take care of their young as well as they should. The Seychelles warbler is a cooperatively breeding bird species, meaning that parents often receive help from other birds when raising their offspring. A study led by biologists from the University of Groningen shows that the offspring of older females have better prospects when they are surrounded by helpers. This impact of social behaviour on reproductive success is described in a paper that was published ...
2021-01-19
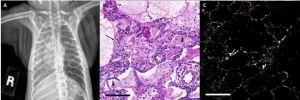
Philadelphia, January 19, 2021 - Aged, wild-caught African green monkeys exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with clinical symptoms similar to those observed in the most serious human cases of COVID-19, report researchers in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier. This is the first study to show that African green monkeys can develop severe clinical disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that they may be useful models for the study of COVID-19 in humans.
"Animal models greatly enhance our understanding of diseases. The lack of an animal model for severe manifestations of COVID-19 has hampered our understanding of this form of the disease," explained lead investigator Robert V. Blair, DVM, PhD, ...
2021-01-19
ATLANTA--Georgia State University biology researchers have found that infecting the nasal passages of mice with the virus that causes COVID-19 led to a rapid, escalating attack on the brain that triggered severe illness, even after the lungs were successfully clearing themselves of the virus.
Assistant professor Mukesh Kumar, the study's lead researcher, said the findings have implications for understanding the wide range in symptoms and severity of illness among humans who are infected by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
"Our thinking that it's more of a respiratory disease is not necessarily ...
2021-01-19
HOUSTON - (Jan. 19, 2021) - Carbon nanotube fibers are not nearly as strong as the nanotubes they contain, but Rice University researchers are working to close the gap.
A computational model by materials theorist Boris Yakobson and his team at Rice's Brown School of Engineering establishes a universal scaling relationship between nanotube length and friction between them in a bundle, parameters that can be used to fine-tune fiber properties for strength.
The model is a tool for scientists and engineers who develop conductive fibers for aerospace, automotive, medical and textile applications like smart clothing. Carbon nanotube fibers have been considered as a possible basis for a space elevator, a project Yakobson has studied.
The research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists to global policymakers: Treat fish as food to help solve world hunger
Sustainable seafood central to strengthening food security if viewed as more than just a natural resource