DNA origami enables fabricating superconducting nanowires
Fabricating nanoelectronic circuits of the future just got a lot more interesting, thanks to DNA origami
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- The quest for ever-smaller electronic components led an international group of researchers to explore using molecular building blocks to create them. DNA is able to self-assemble into arbitrary structures, but the challenge with using these structures for nanoelectronic circuits is the DNA strands must be converted into highly conductive wires.
Inspired by previous works using the DNA molecule as a template for superconducting nanowires, the group took advantage of a recent bioengineering advance known as DNA origami to fold DNA into arbitrary shapes.
In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, researchers from Bar-Ilan University, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Columbia University, and Brookhaven National Laboratory describe how to exploit DNA origami as a platform to build superconducting nanoarchitectures. The structures they built are addressable with nanometric precision that can be used as a template for 3D architectures that are not possible today via conventional fabrication techniques.
The group's fabrication process involves a multidisciplinary approach, namely the conversion of the DNA origami nanostructures into superconducting components. And the preparation process of DNA origami nanostructures involves two major components: a circular single-strand DNA as the scaffold, and a mix of complementary short strands acting as staples that determine the shape of the structure.
"In our case, the structure is an approximately 220-nanometer-long and 15-nanometer-wide DNA origami wire," said Lior Shani, of Bar-Ilan University in Israel. "We dropcast the DNA nanowires onto a substrate with a channel and coat them with superconducting niobium nitride. Then we suspend the nanowires over the channel to isolate them from the substrate during the electrical measurements."
The group's work shows how to exploit the DNA origami technique to fabricate superconducting components that can be incorporated into a wide range of architectures.
"Superconductors are known for running an electric current flow without dissipations," said Shani. "But superconducting wires with nanometric dimensions give rise to quantum fluctuations that destroy the superconducting state, which results in the appearance of resistance at low temperatures."
By using a high magnetic field, the group suppressed these fluctuations and reduced about 90% of the resistance.
"This means that our work can be used in applications like interconnects for nanoelectronics and novel devices based on exploitation of the flexibility of DNA origami in fabrication of 3D superconducting architectures, such as 3D magnetometers," said Shani.
INFORMATION:
The article "DNA origami-based superconducting nanowires" is authored by Lior Shani, Philip Tinnefeld, Yafit Fleger, Amos Sharoni, Boris Shapiro, Avner Shaulov, Oleg Gang, and Yosef Yeshurun. The article will appear in AIP Advances on Jan. 19, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0029781). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0029781.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences--applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/adv.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
Youths with mood disorders who use and abuse cannabis (marijuana) have a higher risk for self-harm, death by all causes and death by unintentional overdose and homicide, according to research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
Study findings are published in the JAMA Pediatrics.
"Marijuana use and addiction is common among youth and young adults with mood disorders, but the association of this behavior with self-harm, suicide and overall mortality risk is poorly understood in this already vulnerable population. These findings ...
2021-01-19
If you ever saw a honeybee hopping elegantly from flower to flower or avoiding you as you passed by, you may have wondered how such a tiny insect has such perfect navigation skills. These flying insects' skills are partially explained by the concept of optical flow: they perceive the speed with which objects move through their field of view. Robotics researchers have tried to mimic these strategies on flying robots, but with limited success. A team of TU Delft and the Westphalian University of Applied Sciences researchers therefore present an optical flow-based learning process that allows robots to estimate distances through the visual appearance (shape, color, texture) of the objects ...
2021-01-19
The older we grow, the weaker our muscles get, riddling old age with frailty and physical disability. But this doesn't only affect the individual, it also creates a significant burden on public healthcare. And yet, research efforts into the biological processes and biomarkers that define muscle aging have not yet defined the underlying causes.
Now, a team of scientists from lab of Johan Auwerx at EPFL's School of Life Sciences looked at the issue through a different angle: the similarities between muscle aging and degenerative muscle diseases. They have discovered protein aggregates that deposit in skeletal muscles during natural aging, and that blocking this can prevent the detrimental features of muscle ...
2021-01-19
FLAGSTAFF, Ariz. -- Jan. 19, 2021 -- The results of a study led by Northern Arizona University and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest the immune systems of people infected with COVID-19 may rely on antibodies created during infections from earlier coronaviruses to help fight the disease.
COVID-19 isn't humanity's first encounter with a coronavirus, so named because of the corona, or crown-like, protein spikes on their surface. Before SARS-CoV-2 -- the virus that causes COVID-19 -- humans have navigated at least 6 other types of coronaviruses.
The study sought to understand how coronaviruses (CoVs) ignite the human immune system and conduct a deeper dive on the inner workings of the antibody response. The ...
2021-01-19
Researchers looked at neurons within the basal ganglia, a part of the brain that, when damaged, can severely impact a person's motor ability, making seemingly simple reaching-and-grasping tasks near impossible
They focused on a large group of neurons, which has two distinct types - D1 direct striatal output neurons and D2 indirect output neurons
These neurons are implicated in the development of Parkinson's and Huntington's - neurodegenerative diseases that result in the progressive degeneration or death of nerve cells
In this research, mice were trained to reach for and grasp a chocolate pellet, and optical methods were used to either excite or inhibit their D1 or D2 neurons
The researchers ...
2021-01-19
Biology - Volcanic microbes
Oak Ridge National Laboratory contributed to an international study that found almost 300 novel types of microbes living near a deep sea volcano. These microbes, which could be used in biotechnology, reveal new insights about their extreme underwater environment.
Two distinct communities of heat-loving and many acid-loving microbes live near Brother's Volcano, located about 200 miles northeast of New Zealand and 6,000 feet underwater. Known as extremophiles, these microbes thrive in water heated by magma and hydrothermal vents.
Though they live close to one another, the microbial communities reflect differences in water chemistry and temperature from geological ...
2021-01-19
Half of all young people treated for severe obesity have neuropsychiatric problems, according to a new study by researchers from Lund University and Gothenburg, Sweden, among others. Two thirds of the teens suffered from some type of mental health problem, as reported by themselves or their parents.
Both obesity and mental illness have increased among young people during the 2000s. Researchers have long observed a connection between obesity and ADHD/depression/eating disorders, but it has seldom been studied.
The present study involved 48 teenagers (73% girls), ...
2021-01-19
People on a low-fat, plant-based diet ate fewer daily calories but had higher insulin and blood glucose levels, compared to when they ate a low-carbohydrate, animal-based diet, according to a small but highly controlled study at the National Institutes of Health. Led by researchers at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), the study compared the effects of the two diets on calorie intake, hormone levels, body weight, and more. The findings, published in Nature Medicine, broaden understanding of how restricting dietary carbohydrates or fats may impact health.
"High-fat foods have been thought to result in excess calorie intake because they have many calories per bite. Alternatively, high-carb ...
2021-01-19
Scientists from the Joint Institute for High Temperatures Russian Academy of Sciences (JIHT RAS) and Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) have experimentally confirmed the presence of an intermediate phase between the crystalline and liquid states in a monolayer dusty plasma system. The theoretical prediction of the intermediate - hexatic - phase was honoured with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2016: the prize was awarded to Michael Kosterlitz, David Thouless and Duncan Haldane with the formulation "for theoretical discoveries of topological phase transitions and topological phases of matter."
In a scientific article in the journal Scientific Reports, the JIHT RAS scientists published their observations ...
2021-01-19
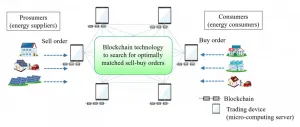
A Tokyo Tech research team led by Specially Appointed Professor Takuya Oda of the Institute of Innovative Research and Professor Keisuke Tanaka of the School of Computing, in collaboration with Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, has developed a new technology an original blockchain[1] technology that can optimize peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading[2]. The technology is expected to contribute to more effective use of surplus electricity from renewable energy by creating trading environments that flexibly respond to shared trading needs, particularly to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] DNA origami enables fabricating superconducting nanowires
Fabricating nanoelectronic circuits of the future just got a lot more interesting, thanks to DNA origami