INFORMATION:
Article Title: Sex differences in the development and expression of a preference for familiar vocal signals in songbirds
Funding: This work was supported by MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI Grant, Numbers 17H06380 to KO & 17J07023 to TGF. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. (https://www.jsps.go.jp/index.html)
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0243811
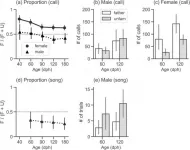
Female Bengalese finches have lifelong preference for their father's song to other birds'
2021-01-20
(Press-News.org) Daddies' girls? Female Bengalese finches prefer their father's song to that of other birds throughout their lives - while sons lose this preference as they grow up.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers uncover potentially promising therapeutic combination for renal cell carcinoma
2021-01-20
Boston, Mass. -- Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of cancer of the kidney. In 2018, there were an estimated 403,000 new cases of RCC and 175,000 deaths due to kidney cancer worldwide. Currently, the 5-year survival rate for patients with metastatic RCC is only about 12 percent. Current treatments include inhibitors of the VEGF and PD-1 pathways. However, resistance to therapy occurs in most patients and new combination treatments are still needed to enhance the efficacy of these current approaches.
Now, investigators have demonstrated that ACE2 expression is a good prognostic factor in RCC, that loss ...
Cats love silver vine and catnip for a more practical reason than developing euphoria
2021-01-20
Catnip and silver vine have been known as cat attractant plants. Cat lovers use dry leaves of these plants and toys stuffed with the leaves to give joy to their pet cats. But how does this work? What is the biological significance of the responsive behavior? A research group at Iwate University, Nagoya University, Kyoto University, and University of Liverpool found that the behavior had more practical reasons than getting euphoria.
"The first appearance of silver vine ("Matatabi" in Japanese) as a cat attractant in literature in Japan dates back to more than 300 years ago. A folklore Ukiyo-e drawn in 1859 shows a group of mice trying to tempt some ...
Squid-inspired robot swims with nature's most efficient marine animals
2021-01-20
Scientists at the University of Southampton and University of Edinburgh have developed a flexible underwater robot that can propel itself through water in the same style as nature's most efficient swimmer - the Aurelia aurita jellyfish.
The findings, published in Science Robotics, demonstrate that the new underwater robot can swim as quickly and efficiently as the squid and jellyfish which inspired its design, potentially unlocking new possibilities for underwater exploration with its lightweight design and soft exterior.
Co-author Dr Francesco Giorgio-Serchi, ...
NIH researchers identify new genetic disorder that affects brain, craniofacial skeleton
2021-01-20
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have discovered a new genetic disorder characterized by developmental delays and malformations of the brain, heart and facial features. Named linkage-specific-deubiquitylation-deficiency-induced embryonic defects syndrome (LINKED), it is caused by a mutated version of the OTUD5 gene, which interferes with key molecular steps in embryo development. The findings indicate that the newly identified pathway may be essential for human development and may also underlie other disorders that are present at birth. The information will help scientists better understand such diseases--both common ...
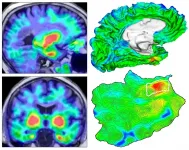
Automated imaging reveals where TAU protein originates in the brain in Alzheimer's disease
2021-01-20
Researchers have developed an automated method that can track the development of harmful clumps of TAU protein related to Alzheimer's disease in the brain, according to work involving 443 individuals. The method revealed that TAU primarily emerged in an area of the brain called the rhinal cortex before spreading elsewhere, suggesting that targeting TAU here could potentially slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease. The buildup of toxic amyloid-beta and TAU proteins is responsible for many of the symptoms and damage to neurons seen in Alzheimer's disease. However, current therapies have shown reduced efficacy, at least in part because the therapies were administered long ...
Deep sleep takes out the trash
2021-01-20
A new Northwestern University study reaffirms the importance of getting a good night's sleep.
By examining fruit flies' brain activity and behavior, the researchers found that deep sleep has an ancient, restorative power to clear waste from the brain. This waste potentially includes toxic proteins that may lead to neurodegenerative disease.
"Waste clearance could be important, in general, for maintaining brain health or for preventing neurogenerative disease," said Dr. Ravi Allada, senior author of the study. "Waste clearance may occur during wake and sleep but is substantially enhanced during deep sleep."
The ...
Intoxicating chemicals in catnip and silver vine protect felines from mosquito bites
2021-01-20
Rubbing against catnip and silver vine transfers plant chemicals that researchers have now shown protect cats from mosquitoes. The results also demonstrate that engaging with nepetalactol, which the study identified as the most potent of many intoxicating iridoid compounds found in silver vine, activates the opioid reward system in both domesticated felines and big jungle cats. While nepetalactol had been previously identified, these studies directly illuminate its extremely potent effect on cats. And by revealing the biological significance of well-known feline behaviors, ...
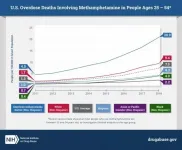
Methamphetamine overdose deaths rise sharply nationwide
2021-01-20
Methamphetamine overdose deaths surged in an eight-year period in the United States, according to a study published today in JAMA Psychiatry. The analysis revealed rapid rises across all racial and ethnic groups, but American Indians and Alaska Natives had the highest death rates overall. The research was conducted at the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Deaths involving methamphetamines more than quadrupled among non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives from 2011-2018 (from 4.5 to 20.9 per 100,000 people) overall, with ...
Diabetes powerfully associated with premature coronary heart disease in women
2021-01-20
BOSTON -- While deaths related to heart disease have declined among older people, studies suggest that death rates among younger patients have remained stagnant or increased slightly. To understand what factors put younger individuals at higher risk of premature coronary heart disease (CHD), researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Mayo Clinic analyzed more than 50 risk factors in 28,024 women who participated in the decades-long Women's Health Study. Notably, women under 55 with type-2 diabetes had a tenfold greater risk of having CHD over the next two decades, with lipoprotein insulin resistance ...
New metamaterial offers reprogrammable properties
2021-01-20
Over the past 20 years, scientists have been developing metamaterials, or materials that don't occur naturally and whose mechanical properties result from their designed structure rather than their chemical composition. They allow researchers to create materials with specific properties and shapes. Metamaterials are still not widely used in everyday objects, but that could soon change. Tian Chen, a post-doc at two EPFL labs - the Flexible Structures Laboratory, headed by Pedro Reis, and the Geometric Computing Laboratory, headed by Mark Pauly - has taken metamaterials one step further, ...