(Press-News.org) Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have discovered a new genetic disorder characterized by developmental delays and malformations of the brain, heart and facial features. Named linkage-specific-deubiquitylation-deficiency-induced embryonic defects syndrome (LINKED), it is caused by a mutated version of the OTUD5 gene, which interferes with key molecular steps in embryo development. The findings indicate that the newly identified pathway may be essential for human development and may also underlie other disorders that are present at birth. The information will help scientists better understand such diseases--both common and rare--and improve patient care. The results were reported Jan. 20, 2021 in Science Advances.
"Our discovery of the dysregulated neurodevelopmental pathway that underlies LINKED syndrome was only possible through the teamwork of geneticists, developmental biologists and biochemists from NIH," said Achim Werner, Ph.D., an investigator at the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) and lead author. "This collaboration provided the opportunity to pinpoint the likely genetic cause of disease, and then take it a step further to precisely define the sequence of cellular events that are disrupted to cause the disease."
The project began when David B. Beck, M.D., Ph.D., a clinical fellow in the laboratory of Dan Kastner M.D., Ph.D., at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) and co-first author, was asked to consult on a male infant who had been born with severe birth defects that included abnormalities of the brain, craniofacial skeleton, heart and urinary tract. An in-depth examination of siblings' and family members' genomes, combined with genetic bioinformatics analyses, revealed a mutation in the OTUD5 gene as the likely cause of the condition. Through outreach to other researchers working on similar problems, Beck found seven additional males ranging from 1 to 14 years of age who shared symptoms with the first patient and had varying mutations in the OTUD5 gene.
The gene contains instructions for making the OTUD5 enzyme, which is involved in ubiquitylation, a process that molecularly alters a protein to change its function. Ubiquitylation plays a role in governing cell fate, where stem cells are instructed to become specific cell types in the early stages of embryo development.
"Based on the genetic evidence, I was pretty sure OTUD5 mutations caused the disease, but I didn't understand how this enzyme, when mutated, led to the symptoms seen in our patients," said Beck. "For this reason we sought to work with Dr. Werner's group, which specializes in using biochemistry to understand the functions of enzymes like OTUD5."
To start, the NIH team examined cells taken from patient samples, which were processed at the NIH Clinical Center. Normally, OTUD5 edits or removes molecular tags on certain proteins (substrates) to regulate their function. But in cells from patients with OTUD5 mutations, this activity was impaired.
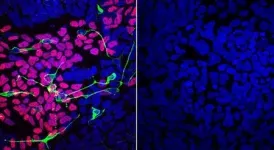
Using a method to return mature human cells to the stem cell-like state of embryo cells, the scientists found that OTUD5 mutations were linked to abnormalities in the development of neural crest cells, which give rise to tissues of the craniofacial skeleton, and of neural precursors, cells that eventually give rise to the brain and spinal cord.
In further experiments, the team discovered that the OTUD5 enzyme acts on a handful of protein substrates called chromatin remodelers. This class of proteins physically alters the tightly packed strands of DNA in a cell's nucleus to make certain genes more accessible for being turned on, or expressed.
With help from collaborators led by Pedro Rocha Ph.D., an investigator at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the team found that chromatin remodelers targeted by OTUD5 help enhance expression of genes that control the cell fate of neural precursors during embryo development.
Taken together, the researchers concluded, OTUD5 normally keeps these chromatin remodelers from being tagged for destruction. But when OTUD5 is mutated, its protective function is lost and the chromatin remodelers are destroyed, leading to abnormal development of neural precursors and neural crest cells. Ultimately, these changes can lead to some of the birth defects seen in LINKED patients.
"Several of the chromatin remodelers OTUD5 interacts with are mutated in Coffin Siris and Cornelia de Lange syndromes, which have clinically overlapping features with LINKED syndrome," said Werner. "This suggests that the mechanism we discovered is part of a common developmental pathway that, when mutated at various points, will lead to a spectrum of disease."
"We were surprised to find that OTUD5 elicits its effects through multiple, functionally related substrates, which reveals a new principle of cellular signaling during early embryonic development," said Mohammed A. Basar, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in Werner's lab and co-first author of the study. "These findings lead us to believe that OTUD5 may have far-reaching effects beyond those identified in LINKED patients."
In future work, Werner's team plans to more fully investigate the role that OTUD5 and similar enzymes play in development. The researchers hope the study can serve as a guiding framework for unraveling the causes of other undiagnosed diseases, ultimately helping clinicians better assess and care for patients.
"We're finally able to provide families with a diagnosis, bringing an end to what is often a long and exhausting search for answers," said Beck.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by NIH intramural research programs at NIDCR, NICHD, NHGRI and the NIH Undiagnosed Diseases Program. Support also came from the Estonian Research Council, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development.
About the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research:
NIDCR is the nation's leading funder of research on oral, dental and craniofacial health.
About the National Institutes of Health:
NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments and cures for both common and rare diseases.
Reference:
Beck D.B., Basar M.A., et al. Linkage-specific deubiquitylation by OTUD5 defines an embryonic pathway intolerant to genomic variation. Science Advances. Jan 20, 2021. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe2116
Visit Dr. Achim Werner's lab website.
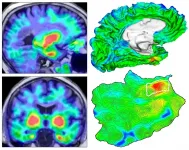
Researchers have developed an automated method that can track the development of harmful clumps of TAU protein related to Alzheimer's disease in the brain, according to work involving 443 individuals. The method revealed that TAU primarily emerged in an area of the brain called the rhinal cortex before spreading elsewhere, suggesting that targeting TAU here could potentially slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease. The buildup of toxic amyloid-beta and TAU proteins is responsible for many of the symptoms and damage to neurons seen in Alzheimer's disease. However, current therapies have shown reduced efficacy, at least in part because the therapies were administered long ...
A new Northwestern University study reaffirms the importance of getting a good night's sleep.
By examining fruit flies' brain activity and behavior, the researchers found that deep sleep has an ancient, restorative power to clear waste from the brain. This waste potentially includes toxic proteins that may lead to neurodegenerative disease.
"Waste clearance could be important, in general, for maintaining brain health or for preventing neurogenerative disease," said Dr. Ravi Allada, senior author of the study. "Waste clearance may occur during wake and sleep but is substantially enhanced during deep sleep."
The ...
Rubbing against catnip and silver vine transfers plant chemicals that researchers have now shown protect cats from mosquitoes. The results also demonstrate that engaging with nepetalactol, which the study identified as the most potent of many intoxicating iridoid compounds found in silver vine, activates the opioid reward system in both domesticated felines and big jungle cats. While nepetalactol had been previously identified, these studies directly illuminate its extremely potent effect on cats. And by revealing the biological significance of well-known feline behaviors, ...
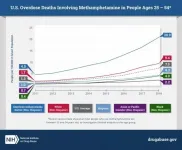
Methamphetamine overdose deaths surged in an eight-year period in the United States, according to a study published today in JAMA Psychiatry. The analysis revealed rapid rises across all racial and ethnic groups, but American Indians and Alaska Natives had the highest death rates overall. The research was conducted at the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health.
Deaths involving methamphetamines more than quadrupled among non-Hispanic American Indians and Alaska Natives from 2011-2018 (from 4.5 to 20.9 per 100,000 people) overall, with ...
BOSTON -- While deaths related to heart disease have declined among older people, studies suggest that death rates among younger patients have remained stagnant or increased slightly. To understand what factors put younger individuals at higher risk of premature coronary heart disease (CHD), researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Mayo Clinic analyzed more than 50 risk factors in 28,024 women who participated in the decades-long Women's Health Study. Notably, women under 55 with type-2 diabetes had a tenfold greater risk of having CHD over the next two decades, with lipoprotein insulin resistance ...
Over the past 20 years, scientists have been developing metamaterials, or materials that don't occur naturally and whose mechanical properties result from their designed structure rather than their chemical composition. They allow researchers to create materials with specific properties and shapes. Metamaterials are still not widely used in everyday objects, but that could soon change. Tian Chen, a post-doc at two EPFL labs - the Flexible Structures Laboratory, headed by Pedro Reis, and the Geometric Computing Laboratory, headed by Mark Pauly - has taken metamaterials one step further, ...
What The Study Did: This observational study examined how COVID-19-related government-mandated closures and restrictions were associated with changes in mobility and the spread of COVID-19 in Nigeria.
Author: Daniel O. Erim, M.D., Ph.D., M.Sc., of Parexel International in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32101)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# ...
Suppose Smokey the Bear were to go on a tear and start setting forest fires instead of putting them out. That roughly describes the behavior of certain cells of our immune system that become increasingly irascible as we grow older. Instead of stamping out embers, they stoke the flames of chronic inflammation.
Biologists have long theorized that reducing this inflammation could slow the aging process and delay the onset of age-associated conditions, such as heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, cancer and frailty, and perhaps even forestall the gradual loss of mental acuity that happens to nearly everyone.
Yet the question of ...
What The Study Did: Researchers examined individuals' motivation to self-test and to distribute self-test kits given the urgent need to increase COVID-19 testing coverage and contact tracing.
Author: Cedric Bien-Gund, M.D., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34001)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # ...
What The Study Did: This investigation analyzed U.S. county-level associations of income inequality, racial/ethnic composition and political attributes with COVID-19 cases and mortality.
Author: Tim F. Liao, Ph.D., of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.34578)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: ...