A critical review of graphene quantum dots and their application in biosensors
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) In a paper published in NANO, researchers from Hubei, China discuss the top-down and bottom-up strategies for the synthesis of Graphene quantum dots (GQDs). The respective advantages and disadvantages of these methods are summarized. With regard to some important or novel ones, the mechanisms are proposed for reference. In addition, the application of GQDs in biosensors is highlighted in detail.
At present, various top-down methods, such as oxidative cutting, hydrothermal or solvothermal reactions, electrochemical oxidation, ultrasonic-assisted or microwave-assisted process, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) have been reported to produce GQDs. Meanwhile, the bottom-up methods have been developed rapidly, which mainly include carbonization methods and stepwise organic synthesis. Owing to excellent photoelectric properties, good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, GQDs are of great value in various domains. In particular, as a novel luminescent nanomaterial, GQDs have played a leading role in the development of biosensors.
The authors review the latest progresses on the synthesis of GQDs. Different methods are presented in order to study their characteristics and the influence on the final properties of the GQDs. The mechanisms of some novel methods are proposed for offering enlightenment in the synthesis. Furthermore, the potential application of GQDs in biosensors and their design solution are introduced. Finally, a brief outlook and further development for GQDs are discussed. This review not only provides a useful guide on the synthesis of GQDs, but also facilitates designing novel biosensor devices for researchers.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge the support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 21805166), the 111 Project of Hubei Province (grant numbers: D20015), and Foundation of Science and Technology Bureau of Yichang City (grant number: A18-302-a07).
Corresponding author of the paper is Weifeng Chen (chenweifeng_2016@ctgu.edu.cn).
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
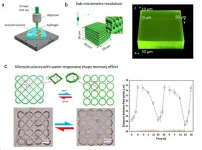
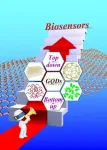
IMAGE
Caption:
A schematic illustration of the synthesis of GQDs with different stratagies and their applications in the domain of biosensors.
NANO is an international peer-reviewed monthly journal for nanoscience and nanotechnology that presents forefront fundamental research and new emerging topics. It features timely scientific reports of new results and technical breakthroughs and publishes interesting review articles about recent hot issues.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 140 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organizations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com.
For more information, contact Tay Yu Shan at ystay@wspc.com.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
Changes in climate that occur over short periods of time influence biodiversity. For a realistic assessment of these effects, it is necessary to also consider previous temperature trends going far back into Earth's history. Researchers from the University of Bayreuth and the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg show this in a paper for Nature Ecology and Evolution. According to the paper, future climate-related species extinction could be less severe than predictions based only on the current trend of global warming. However, the researchers do not give the all-clear. At present, the effects of climate change are being exacerbated ...
2021-01-21
In nature, many things have evolved that differ in size, color and, above all, in shape. While the color or size of an object can be easily described, the description of a shape is more complicated. In a study now published in Nature Communications, Jacqueline Nowak of the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology and her colleagues have outlined a new and improved way to describe shapes based on a network representation that can also be used to reassemble and compare shapes.
Jacqueline Nowak designed a novel approach that relies on a network-based shape representation, named visibility graph, along with a tool for analyzing shapes, ...
2021-01-21
The study explains the benefits of both the wing shape and the flexibility of their wings.
The Lund researchers studied the wingbeats of freely flying butterflies during take-off in a wind tunnel. During the upward stroke, the wings cup, creating an air-filled pocket between them. When the wings then collide, the air is forced out, resulting in a backward jet that propels the butterflies forward. The downward wingbeat has another function: the butterflies stay in the air and do not fall to the ground.
The wings colliding was described by researchers almost 50 years ago, but it is only in this study that the theory has been tested on real butterflies in free ...
2021-01-21
Three-dimensional (3D) direct laser writing (DLW) based on two-photon polymerisation (TPP) is an advanced technology for fabricating precise 3D hydrogel micro- and nanostructures for applications in biomedical engineering. Particularly, the use of visible lasers for the 3D DLW of hydrogels is advantageous because it enables high fabrication resolution and promotes wound healing. Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGda) has been widely used in TPP fabrication owing to its high biocompatibility. However, the high laser power required in the 3D DLW of PEGda microstructures using a visible laser in a high-water-content environment limits its applications to only those below the biological laser power safety level.
In a new paper ...
2021-01-21
Rather like David versus Goliath, it appears that Saturn's tilt may in fact be caused by its moons. This is the conclusion of recent work carried out by scientists from the CNRS, Sorbonne University and the University of Pisa, which shows that the current tilt of Saturn's rotation axis is caused by the migration of its satellites, and especially by that of its largest moon, Titan.
Recent observations have shown that Titan and the other moons are gradually moving away from Saturn much faster than astronomers had previously estimated. By incorporating this increased migration rate into their calculations, the researchers concluded that ...
2021-01-21
To process information in our brains, nerve cells produce brief electrical impulses, called action potentials, triggered from one highly specialized region. Research from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, together with researchers from Heidelberg University and the University of Göttingen in Germany, now show that the electrical trigger sites surprisingly change with experience; they are either becoming smaller with increasing number of experiences and, vice versa, they grow larger when less input arrives in the brain. The results were published in Nature Communications.
Exploring the environment
Rodents learn about their environment by moving their highly sensitive whiskers, with which they touch ...
2021-01-21
Researchers from the Sonia and Marco Nadler Institute of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University unraveled the function of flint tools known as 'chopping tools', found at the prehistoric site of Revadim, east of Ashdod. Applying advanced research methods, they examined use-wear traces on 53 chopping tools, as well as organic residues found on some of the tools. They also made and used replicas of the tools, with methods of experimental archaeology. The researchers concluded that tools of this type, found at numerous sites in Africa, Europe and Asia, were used by prehistoric humans at Revadim to neatly break open bones of medium-size animals such as fallow deer, gazelles and ...
2021-01-21
UV-radiation can affect hormone levels of postmenopausal women negatively and this may contribute to several health issues.
The concentration of oestrogens in the blood affects a woman's health in many ways. For example, oestrogens contribute to a strong bone structure and help wounds heal more quickly:
"When a woman reaches menopause, we see the levels of oestrogens decline and an increase of other hormones, called gonadotropins", says Kai Triebner at the University of Bergen.
For several years, he has studied the hormonal balance of women in relation to menopause: What effects changing hormone levels ...
2021-01-21
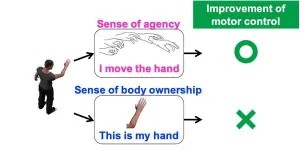
With Japan's society rapidly aging, there has been a sharp increase in patients who experience motor dysfunctions. Rehabilitation is key to overcoming such ailments.
A researcher from Tohoku University has developed a new virtual reality (VR) based method that can benefit rehabilitation and sports training by increasing bodily awareness and?improving motor control.
His research was published in the Journal Scientific Report.
Not only can we see and touch our body, but we can sense it too. Our body is constantly firing off information to our brains that tell us where our limbs are in real-time. This process makes us aware of our body and gives us ownership over it. Meanwhile, our ability to control ...
2021-01-21
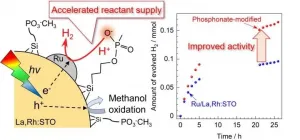
Water splitting research for solar hydrogen production has focused on physical processes inside the semiconductor, such as light absorption, charge separation, and chemical processes on the surface that are highly complex and rely on the development of new materials. However, processes inside the solution had yet to be thoroughly explored.
One recent approach to improve photocatalytic hydrogen production was proposed by loading phosphonate groups on the surface of the visible-light-responsive photocatalyst lanthanum and rhodium-doped strontium titanate (La,Rh:STO) with a silane coupling agent. The phosphonate functional group functions as a mediator of proton supply (i.e., promotes the supply of reactants) and improves hydrogen production activity.
There have been ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A critical review of graphene quantum dots and their application in biosensors