The interconnection of global pandemics -- Obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19
2021-01-21
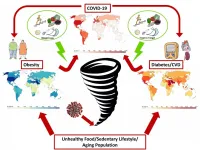
(Press-News.org) In a Nature Reviews Endocrinology article authors from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) highlight the interconnection of obesity and impaired metabolic health with the severity of COVID-19. First, they provide information about the independent relationships of obesity, disproportionate fat distribution and impaired metabolic health with the severity of COVID-19. Then they discuss mechanisms for a complicated course of COVID-19 and how this disease may impact on the global obesity and cardiometabolic pandemics. Finally, they provide recommendations for prevention and treatment in clinical practice and in the public health sector to combat these global pandemics.
Norbert Stefan, Andreas Birkenfeld and Matthias Schulze summarize and discuss data from large and well-performed studies that investigated independent relationships of obesity with the severity of COVID-19. Thereby, they can disentangle the contribution of obesity, visceral fatness and impaired metabolic health for the course of COVID-19. In this respect they found convincing evidence that obesity and overt diabetes, but also visceral obesity and even mild hyperglycemia, represent important risk factors for the disease course. Thus, these risk factors most probably may have an additive effect on the severity of COVID-19.
Then they discuss the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 infection on organ function, focusing on the cardiometabolically relevant tissues and organs as the vessel wall, heart, kidneys, liver, gut and pancreas. Thereby, they address both, the immediate damage of COVID-19 to the organs and the long-term effects of the disease, most probably boosting the development of obesity and cardiometabolic diseases. Thus, obesity and cardiometabolic diseases do not only trigger a more severe course of COVID-19, the SARS-CoV-2 infection does promote the development of these conditions.
The authors further highlight how treatment of obesity and impaired cardiometabolic health helps to avert a severe COVID-19 in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. In this respect health professionals and politicians should now, more than ever, promote the health benefits of physical activity and support efforts to implement programmes and policies to facilitate increased physical activity and to promote a healthy diet. This might not only be relevant to directly reduce the burden of COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality among those infected, but may also be important in the context of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, where response should be carefully evaluated in patients with obesity and/or diabetes mellitus, because of a potentially reduced or shortened response.
INFORMATION:
Publication:
Stefan N, Birkenfeld AL, Schulze MB. Global pandemics interconnected - obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021, doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-00462-1
Contact:
Prof. Norbert Stefan
German Center for Diabetes Research
Department of Internal Medicine IV
Tübingen University Hospital
Otfried-Müller-Str. 10, 72076 Tübingen, Germany
Phone: +49 (0)7071 29-80390
Email: norbert.stefan@med.uni-tuebingen.de
The German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) is one of six German Centers for Health Research. It brings together experts in the field of diabetes research and integrates basic research, epidemiology, and clinical applications. By adopting an innovative, integrative approach to research, the DZD aims to make a substantial contribution to the successful personalized prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. The members of the DZD are Helmholtz Zentrum München - German Research Center for Environmental Health, the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) in Düsseldorf, the German Institute of Human Nutrition (DIfE) in Potsdam-Rehbrücke, the Institute of Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, the Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the Carl Gustav Carus University Hospital of TU Dresden, associated partners at the universities in Heidelberg, Cologne, Leipzig, Lübeck and Munich, and other project partners. http://www.dzd-ev.de/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-21
Letters, syllables, words and sentences--spatially arranged sets of symbols that acquire meaning when we read them. But is there an area and cognitive mechanism in our brain that is specifically devoted to reading? Probably not; written language is too much of a recent invention for the brain to have developed structures specifically dedicated to it.
According to this novel paper published in Current Biology, underlying reading there is evolutionarily ancient function that is more generally used to process many other visual stimuli. To prove it, SISSA ...
2021-01-21
Research led by the universities of Kent and Oxford has found that fans of the least successful Premier League football teams have a stronger bond with fellow fans and are more 'fused' with their club than supporters of the most successful teams.
The study, which was carried out in 2014, found that fans of Crystal Palace, Hull, Norwich, Sunderland, and West Bromwich Albion were found to have higher loyalty towards one another and even expressed greater willingness to sacrifice their own lives to save the lives of other fans of their club. This willingness was much higher than that of Manchester United, Arsenal, Chelsea, Liverpool or Manchester City fans. A decade of club statistics from 2003-2013 was used to identify the ...
2021-01-21
Schools are closing again in response to surging levels of COVID-19 infection, but staging randomised trials when students eventually return could help to clarify uncertainties around when we should send children back to the classroom, according to a new study.
Experts say that school reopening policies currently lack a rigorous evidence base - leading to wide variation in policies around the world, but staging cluster randomized trials (CRT) would create a body of evidence to help policy makers take the right decisions.
The pandemic's rapid ...
2021-01-21
Despite being the subject of increasing interest for a whole century, how preeclampsia develops has been unclear - until now.
Researchers believe that they have now found a primary cause of preeclampsia.
"We've found a missing piece to the puzzle. Cholesterol crystals are the key and we're the first to bring this to light," says researcher Gabriela Silva.
Silva works at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Centre of Molecular Inflammation Research (CEMIR), a Centre of Excellence, where she is part of a research group for inflammation in pregnancy led by Professor Ann-Charlotte Iversen.
The findings are good news for the approximately three per cent of pregnant ...
2021-01-21
Amsterdam, NL, January 21, 2021 - The bacterial gut microbiome is strongly associated with Parkinson's disease (PD), but no studies had previously investigated he role of fungi in the gut. In this novel study published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease, a team of investigators at the University of British Columbia examined whether the fungal constituents of the gut microbiome are associated with PD. Their research indicated that gut fungi are not a contributing factor, thereby refuting the need for any potential anti-fungal treatments of the gut in PD patients.
"Several studies conducted since 2014 have characterized changes in the gut microbiome," explained lead investigator Silke Appel-Cresswell, MD, Pacific Parkinson's Research Centre and Djavad ...
2021-01-21
The cause of the inflammatory lung disease sarcoidosis is unknown. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have investigated whether a type of immune cell called a monocyte could be a key player in sarcoidosis pathogenesis and explain why some patients develop more severe and chronic disease than others. The study, which is published in The European Respiratory Journal, opens new possibilities for future diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that in 90 percent of cases affects the lungs, but can also attack the heart, skin and lymph system. The cause of the disease is not yet established, and there is currently ...
2021-01-21
Scientists have developed a pioneering new technique that could revolutionise the accuracy, precision and clarity of super-resolution imaging systems.
A team of scientists, led by Dr Christian Soeller from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, which champions interdisciplinary research and is a hub for new high-resolution measurement techniques, has developed a new way to improve the very fine, molecular imaging of biological samples.
The new method builds upon the success of an existing super-resolution imaging technique called DNA-PAINT ...
2021-01-21
Scientists have been pondering if the microbiome of plants is due to nature or nurture. Research at Stockholm University, published in Environmental Microbiology, showed that oak acorns contain a large diversity of microbes, and that oak seedlings inherit their microbiome from these acorns.
"The idea that seeds can be the link between the microbes in the mother tree and its offspring has frequently been discussed, but this is the first time someone proves the transmission route from the seed to the leaves and roots of emerging plants", says Ahmed Abdelfattah, researcher at the Department of Ecology Environment and Plant ...
2021-01-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- In 2018, passengers onboard a flight to Australia experienced a terrifying 10-second nosedive when a vortex trailing their plane crossed into the wake of another flight. The collision of these vortices, the airline suspected, created violent turbulence that led to a free fall.
To help design aircraft that can better maneuver in extreme situations, Purdue University researchers have developed a modeling approach that simulates the entire process of a vortex collision at a reduced computational time. This physics knowledge could then be incorporated into engineering design codes so that the aircraft ...
2021-01-21
(Boston)--While aging is an unavoidable biological process with many influencing factors that results in visible changes to the hair, there is limited literature examining the characteristics of hair aging across the races. Now a new study describes the unique characteristics of hair aging among different ethnicities that the authors hope will aid in a culturally sensitive approach when making recommendations to prevent hair damage during one's life-time.
Among the findings: hair-graying onset varies with race, with the average age for Caucasians being mid-30s, that for Asians being late 30s, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The interconnection of global pandemics -- Obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19